Commitment to SDG-Centered Education through Curriculum Development at BSRU
In 2023, BSRU demonstrates its commitment to providing meaningful education centered around the SDGs through its curriculum development process. Every curriculum at the university adheres to the Thai Qualification Framework 2 (TQF2), which ensures that all educational programs consider key aspects of societal needs and align with global and national development goals. All curricula address these critical questions and can be accessed and downloaded from the Academic Affairs and Registration (AAR) website.
Under the TQF2 framework, curriculum planning is influenced by several external factors. First, the economic situation (as outlined in point 11.1) drives the need to incorporate skills and knowledge that promote sustainable economic growth, ensuring that students are prepared for a dynamic and evolving workforce. Second, social and cultural developments (point 11.2) are taken into account, ensuring that the curriculum fosters social cohesion, cultural awareness, and respect for diversity, while encouraging students to actively contribute to societal well-being. Finally, professional standards (point 11.3) are a crucial consideration, ensuring that students meet the necessary qualifications to thrive in their respective fields, with a focus on ethics, responsibility, and sustainability.
The impact of these considerations on curriculum development is evident in the continuous effort to integrate sustainability into all programs (point 12.1). This ensures that graduates not only gain technical knowledge but also understand their role in promoting sustainable development. Moreover, the alignment of the curriculum with the university’s mission (point 12.2) underscores BSRU’s dedication to producing responsible citizens and professionals who contribute to the global effort to achieve the SDGs. The university thus ensures that all students, regardless of their field of study, are exposed to the principles of sustainability and are equipped with the skills to make a positive impact.
Empowering Future Leaders: BSRU’s Commitment to Sustainability Education and the SDGs
BSRU Sustainability Education offers specialized courses designed to align with the university’s mission as a leader in area-based and community engagement. With five faculties and two colleges, including the Faculty of Science and Technology and the Faculty of Humanities and Social Sciences, Bansomdejchaopraya Rajabhat University (BSRU) integrates sustainability into its academic offerings to address global challenges like climate change and social inequality. These courses aim to equip BSRU’s 9,925 students with the skills and knowledge needed to drive sustainable development both locally and globally. By focusing on hands-on learning and community involvement, the courses prepare students to become advocates and leaders in the realization of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Through a commitment to fostering local development and educational quality, BSRU empowers its students to make meaningful contributions to sustainability initiatives.
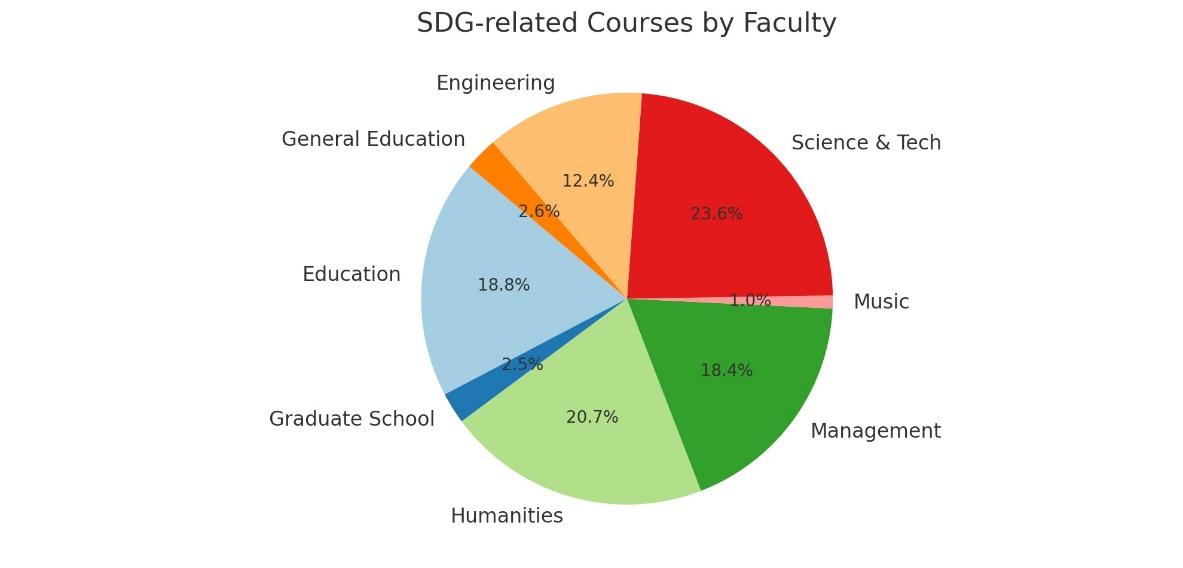
In the academic year 2566-2567, BSRU offers a total of 2,803 courses, with 691 courses aligning with the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), accounting for approximately 24.65% of all courses. These SDG-related courses cover a wide range of goals, with the majority focusing on SDG 4 (Quality Education), followed by SDG 8 (Decent Work and Economic Growth) and SDG 3 (Good Health and Well-being). The largest contributors are the Faculty of Science and Technology, Faculty of Humanities, and Faculty of Education, showcasing BSRU’s strong commitment to sustainability across various academic fields.
College of Music
The College of Music at Bansomdejchaopraya Rajabhat University (BSRU) integrates sustainability into its curriculum by offering courses that align with the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Through a diverse range of music-related programs, the college equips students with technical, creative, and business skills while fostering ethical entrepreneurship and social responsibility. These courses not only enhance students’ musical expertise but also prepare them to contribute to sustainable economic growth, quality education, and mental well-being, directly supporting global sustainability efforts outlined in the SDGs.
College of Music: 7 courses which are embedded with sustainability, are offered by Bansomdejchaopraya Rajabhat University as follows.
|
N |
Course Name |
Course Description |
SDGs Embedded |
|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Principles of Thai Music Marketing and Business Administration |
Principles of marketing strategies, production and distribution management of quality Thai music instruments, principles of public relations, elementary accounting for Thai music business, raising business virtues and morals; being steadfast to ethics for music entrepreneurship |
The course supports SDGs 8 by Make per capita economic growth sustainable in the context of the country. |
|
2 |
Fundamental of Keyboard Skills |
Beginning level of keyboard performance skills, fingering, sitting, piano score reading, relationship of left & right hand and beginning music level |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Technical and vocational skills for employment. |
|
3 |
Computer Aided Music |
After Effect program for making letters and pictures, Sibelius program for music composition, Premiere program for picture and sound sequencing which is applied in various media channels |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Professional training and an information and communication technology program. |
|
4 |
Introduction to Psychology |
Introduction to psychology concepts of human behavior: maturity, habit,perception, learning, feelings, emotions, motivation, personality, differences between individuals, mental health and adaptation |
The course supports SDGs 3 by Support mental health and wellbeing. |
|
5 |
Fundamental of Music Business Law |
Trade business law, civil and commercial law, copyright laws in the music industry, music label contract, laws and regulations in work related to music and entertainment industry |
The course supports SDGs 10 and 8 by Strengthen regulatory implementation, Promote development-oriented policies that support productive activities and create decent works. |
|
6 |
Music Prodution for Media |
Music production techniques for movies, television, advertising and documentaries, computer programming for music, applied computer programs in media production, personnel and personnel development in music for media |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Technical and vocational skills for employment. |
|
7 |
Sound Design for Film |
Producing process of audio for motion picture; animation, multimedia, production and design producing systems in the production of other media together with other works, recording, editing and image synchronization. And the sound to comply the industry standards |
The course supports SDGs 8 by Technology and innovation upgrades. |
Faculty of Education

The Faculty of Education at Bansomdejchaopraya Rajabhat University (BSRU) is committed to fostering future educators who align with the principles of sustainability and the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Through a wide array of specialized courses, the faculty equips students with technical and vocational skills, emphasizing ethical teaching, educational innovation, and community engagement. Courses cover topics such as psychology, curriculum development, classroom management, and educational technology, all designed to ensure quality education and promote a culture of peace and inclusivity. By integrating SDGs into the curriculum, the Faculty of Education prepares students to become transformational teachers who contribute to sustainable development both locally and globally.
Faculty of Education: 130 courses, which are concerned about sustainability, are offered by Bansomdejchaopraya Rajabhat University as follows.
|
N |
Course Name |
Course Description |
SDGs Embedded |
|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Virtue and Ethics for Teachers |
Virtue; ethics; teachers’ spirit; teachers’ self-governance respected by learners and community members; analysis, synthesis, and integration of knowledge; teacher’s value; teaching professional ethics; laws for teachers and conditions of teaching professional development; practice of reflection as to apply to teaching self-development; behaviors in conformity to professional ethics, positive attitude towards nation, good citizens, and wellrounded modern, and adaptive transformational teachers. |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Technical and vocational skills for employment |
|
2 |
Psychology for Teachers |
Principles, concepts, theories of psychology; developmental psychology, educational psychology, guidance psychology, psychology for special need learners; developing learners to full potential with regard to individual differences; psychological study and using psychological tools to help and encourage learners; case study and report the results of learners’ quality development; counseling and giving feedback to students, parents and related parties. |
The course supports SDGs 4 by All learners gain the knowledge and skills necessary to promote sustainable development. |
|
3 |
Communication Strategies for Teachers |
Principles, concepts, theories, teaching strategies using rhetorics for teachers; techniques for communication; practice of listening, speaking, reading, and writing; body language for communication in learning management; classroom communication and student development; application of language to appropriate learning management in accordance with contexts and differences of individual learners; self-awareness for modernity and transformation literacy; use of different languages and diverse cultures for peaceful coexistence in society for the teaching profession. |
The course supports SDGs 4 byPromoting a culture of peace and non-violence. |
|
4 |
Educational Philosophy and Curriculum Development |
Analyzing educational philosophy; concepts, theories, and foundation of multicultural transformation; types of curricula; components of educational institute curriculum; development process, planning, designing, and developing curriculum; applying educational philosophy and fundamental concept to developing basic education, early childhood education, and course curriculum according to major programs, institutes’ context, and communities either as national or global citizens |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Providing quality preprimary education for early childhood children. |
|
5 |
Internship 2 |
Teaching practice in educational institutions continues from teaching practice in educational institutions 1, integrating all knowledge in the major field of study for use in teaching practice in educational institutions and performing other assigned teaching duties, preparing learning plans and organizing learning processes, measuring and evaluating and applying the results to managing learning and developing students, exchanging knowledge or sharing knowledge in educational seminars, conducting research to develop students by synthesizing knowledge gained from studying according to the curriculum, and practicing professional experience to create a graduate thesis. |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Technical and vocational skills for employment |
|
6 |
Practicum 1 |
Development of characteristics reflecting love and faith in teaching profession; professional ethics; duties of teachers; coordinating with parents to provide learners’ care, assistance, and development; providing well-organized report of learner development; applying the knowledge of psychology and digital technology; curriculum and activity development; developing teacher profession; observing and analysing teacher performance; concluding the lesson learned from learning experience in educational institution; synthesizing the body of knowledge and using the learning results in after action review (AAR), as well as sharing and learning under the context of profession learning community (PLC). |
The course supports SDGs 4 byTechnical and vocational skills for employment |
|
7 |
Practicum 2 |
Pre-requisite : 1190205 Practicum 1 Behaving oneself as a good example according to professional ethics; working as a teacher assistant with a mentor; integrating knowledge in educational administration, innovation design, educational quality assurance, learning management and learning atmosphere; cooperating with parents to develop, help and assist students; self-development to be a professional teacher of both professional teaching and core major study; participating in projects to promote cultural conservation and local wisdom; bringing learning results from educational institutions to evaluate after action review (AAR) and exchange knowledge in the form of professional learning community (PLC). |
The course supports SDGs 4 byTechnical and vocational skills for employment |
|
8 |
Internship 1 |
Required Course: 1190303 Practicum 2 Practice of teaching in educational institutions; behaving oneself as a good example according to professional ethnics; designing and managing a classroom atmosphere; organizing learning activities to encourage students to create advanced thinking processes; applying digital technology or educational innovations; collaborating with parents to solve learners’ problems with research; reflecting learners’ participation in activities to promote professional progress; conducting projects to promote cultural conservation and local wisdom; bringing learning results from educational institutions to evaluate after action review (AAR) and exchange knowledge in the form of professional learning community (PLC). |
The course supports SDGs 4 byCreate and upgrade educational equipment and tools. |
|
9 |
Internship 2 |
Required Course: 1190401 Internship 1 Working in teacher duties; behaving oneself as a good example according to professional ethics; designing educational innovations and managing learning activities happily to develop advanced thinking processes to be an innovator; integrating community contexts with learning activity management; creating networks with parents and communities to develop and solve learners’ problems with research; reflecting the results from participating in activities promoting the professional advancement; conducting cultural conservation and local wisdom projects; bringing learning results from educational institutions to evaluate after action review (AAR) and exchange knowledge in the form of professional learning community (PLC) to develop oneself knowledge, modernity and literacy of changes. |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Technical and vocational skills for employment. |
|
10 |
School Internship 2 |
Pre-requisite : 1231112 School Internship 1 Integration of all knowledge to be applied in school teaching of major subject; devising student centered instructional plan, designing learning process, selecting and producing media and innovation in compliance with learning management, utilizing of techniques and strategies of learning management, measuring and evaluating learning, conducting classroom research, applying evaluation results to enhance learning management and to develop learner quality, recording and reporting learning results, and organizing educational seminar. |
The course supports SDGs 4 byTechnical and vocational skills for employment. |
|
11 |
Language and Culture for Teacher |
Meanings and importance of language and culture as a national identity for teachers; enhancement of the learners’ awareness in recognizing the value of Thai language and Thai culture; development of skills in Thai and foreign language regarding listening, speaking, reading and writing for meaning communication in teaching profession; use of language and culture for peaceful co-existence in cultural diversity. |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Technical and vocational skills for employment |
|
12 |
Quality Assurance of Education |
Principles, concepts, practical guidelines for educational quality assurance; knowledge management of quality assurance in teaching profession; devise of activities relating to quality assurance of education, and continuous development of learning quality; roles of quality assurance personnel; educational standards and indicators; devise of activities; evaluation of learning activities; report writing of the educational quality assurance. |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Technical and vocational skills for employment |
|
13 |
Trend of Elementary Education |
Philosophy, approaches and evolution of elementary education; national education act; education development plan; elementary education management in Thailand and foreign countries; skills and attributes teachers’ elementary in century 21st; trend and direction of Thai’s elementary education in future. |
The course supports SDGs 4 byEnsure that all boys and girls complete quality primary and secondary education. |
|
14 |
Media Digital Technology and Innovation for Elementary School Teachers |
Analyze information about the principles of media; media design; media selection principles; principles of media production; practice in producing offline media; elementary level digital media technology; evaluate the effectiveness of the media creatively. |
The course supports SDGs 4 byCreate and upgrade educational equipment and tools to provide a safe learning environment. |
|
15 |
Learning Management for Thinking Skill Development |
Brain function related to learning The relationship between the brain and the learning process, theories and principles related to thinking and intellectual development The importance needed to practice basic thinking analytical thinking, problem solving, creative thinking critical thinking And Buddhist thinking skills assessment of basic thinking skills and integrating strategies in using basic thinking skills and teaching. |
The course supports SDGs 4 byTechnical and vocational skills for employment. |
|
16 |
Mathematics for Elementary Education Teachers |
Number sense; concept of rational number; real number system; properties of numbers; operation of numbers; pattern; estimation for measurement; geometry; geometric properties; visualization; related geometric; geometric theories; statistical operations and statistical problem-solving; mathematical processes skills, logical thinking and applied to real life situations |
The course supports SDGs 4 byTechnical and vocational skills for employment |
|
17 |
Thai Language Curriculum and Learning Management in Elementary Education |
Analyzing standards and indicators of Thai language for elementary education level; instructional; learning methods and techniques related Thai subject; designing unit of instruction and lesson plan; writing in longhand; writing board; selection and production of materials teaching; measurement and evaluation; practicing learning management of Thai language |
The course supports SDGs 4 byTechnical and vocational skills for employment |
|
18 |
Mathematics Curriculum and Learning Management in Elementary Education |
Analyzing learning standards and indicators of mathematics curriculum for elementary education level; teaching model, teaching method, teaching technique related nature mathematics; design of learning unit, writing a learning management plan and practice of extra-curricular activities related mathematics curriculum from learning resources and research; selection and production of materials teaching mathematics; measurement and evaluation; practice in mathematics learning management. |
The course supports SDGs 4 byEnsure that all boys and girls complete quality primary and secondary education. |
|
19 |
Science and Technology for Elementary Education Teachers |
Concept of living things, living processes Physical diversity, ecosystems, material properties and force and motion Energy and energy deformation Solar system and space technology advancement Structure and elements of the world Physical properties of soil, water and air, factors that cause natural changes And the effects of natural changes. |
The course supports SDGs 2 and 4 byStrengthening resilience to climate change and technical and vocational skills for employment. |
|
20 |
Social Studies for Elementary Education Teachers |
Basic concepts of social studies religious concepts principles of buddhism at the elementary level democracy democracy in school citizens’ duty being a good member in a democratic society social skills and working with others cultural diversity basic principles of economics economic systems and institutions sufficient economy meaning, importance of time and historical era historical methods development of humanity from the past to the present history of the thai nation thai culture and wisdom physical characteristics of the world, the use of maps and geographic tools Interaction between human and physical environment environmental conservation for sustainable development. |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Promoting a culture of peace, non-violence, and global citizenship |
|
21 |
Science and Technology Curriculum and Learning Management in Elementary Education |
Analysis of learning standards and indicators of science and technology learning subject groups at the elementary level And writing a learning management plan organizing scientific experiment activities Science Project From learning resources and research selection and use of science teaching media Measurement and evaluation in science courses Practice in managing science learning at the elementary leve. |
The course supports SDGs 4 byCreate and upgrade educational equipment and tools. |
|
22 |
Learning and moral management for Elementary School Students |
Meaning and importance of moral, values and changing values; values in society, both past and present; the creation and development of virtues and values for elementary students; creating cultural values Thailand; manners and performance in society; roles and responsibilities citizens and citizens of the world; instilling moral values by incorporating in the process of teaching and learning activities and experience inside and outside the classroom. |
The course supports SDGs 4 byPromoting a culture of peace and non-violence. |
|
23 |
Classroom management and Relationship building with parents |
Preparation and design of physical and psychological classes; contact and meeting arrangements for parents; administrative classes; the role of teachers in primary education; classroom communication; behavior modification; writing a positive student identification book. |
The course supports SDGs 4 byTechnical and vocational skills for employment. |
|
24 |
Social Studies Curriculum and Learning Management in Elementary Education |
Analysis of learning standards and indicators of social studies learning at the elementary level, patterns, methods and teaching techniques that are consistent with the nature of the unit design, learning and writing of learning management plans geographic process geographic skills selection, use and production of social studies teaching materials measurement and evaluation in social studies courses The practice of learning management in social studies at the elementary level. |
The course supports SDGs 4 byCreate and upgrade educational equipment and tools. |
|
25 |
Occupation Health Physical and Art Curriculum and Learning Management in Elementary Education |
Analysis of learning standards and indicators, learning strands, occupation, health education, physical education and art at the elementary level Learning unit design and writing of learning management plans Practice in learning management, occupation, health education, physical education and art at the elementary level. |
The course supports SDGs 4 byTechnical and vocational skills for employment. |
|
26 |
English Language Curriculum and Learning Management in Elementary Education |
Analyzing standards and indicators of occupation for elementary education level; instructional; learning methods and techniques related occupation subject; designing unit of instruction and lesson plan; selection and production of materials teaching; measurement and evaluation; practicing learning management of occupation. |
The course supports SDGs 4 byCreate and upgrade educational equipment and tools. |
|
27 |
Extra Curricular Activity in Elementary Educatio |
Principles, concepts, theories of organizing student development activities, guidelines for the scope of student development activities at the elementary level, design and writing plans for student development activities organizing extra-curricular activities for student development activities organizing rallies selection, use and production of instructional media for student development activities measurement and evaluation in the course of student development activities practice in learning management of primary school learners development activities. |
The course supports SDGs 4 byTechnical and vocational skills for employment. |
|
28 |
Guidance in Elementary Education |
Meaning, principles and importance Of guidance activities Guidance services at the elementary level. Guidance activities for primary education Techniques and tools for guidance Student support system Guidance problems in primary schools. |
The course supports SDGs 4 byTechnical and vocational skills for employment. |
|
29 |
Research and Seminar in Elementary Classroom |
Issues trend and theory of elementary education; studying and analyzing students’ problem; classroom action research; designing classroom action research project in elementary education; creating and testing research tools psychometric property; writing research report; practicing seminar. |
The course supports SDGs 4 byCreate and upgrade educational equipment and tools. |
|
30 |
English for Communication and Study of Elementary School Teachers |
Reading strategies of English for searching the main idea; the sequence of ideas; the use exposure from media, articles and research; speaking to the timely and proper person; strategies for writing a letter variations; making notes presented in various forms; writing bibliographies and reference resources; synthesis bugs to solve communication problems. |
The course supports SDGs 4 byTechnical and vocational skills for employment. |
|
31 |
Elementary Education |
Basic concept, aims, philosophy of elementary education; evolution in elementary education; National Education Act and related laws elementary education; management of elementary education in Thailand and foreign countries; attributes of elementary teacher; trends and directions of Thai’s elementary education management in future; a transition between kindergarten elementary and secondary education grade classrooms with the form of an inquiry method for seeking knowledge using educational information technology. |
The course supports SDGs 4 byEnsure that all boys and girls complete quality primary and secondary education. |
|
32 |
Organization Counseling |
Concepts, theories, techniques, process and procedures about family, school, workplace and community counseling theories, application of counseling theories, counseling practices and related researches. |
The course supports SDGs 3 byFamily planning. |
|
33 |
Crisis Counseling |
Concepts crisis counseling theories, intervention with persons in crisis, violent behaviors in school, domestic violent, conflicts in the workplace, sexual abuse, disaster, human disaster, prevention, problem-solving and improving the quality of life and continuous monitoring. |
The course supports SDGs 4, 5 and 16 byPromoting a culture of peace, non-violence, and eliminating all forms of violence against women and girls. |
|
34 |
Research Methodology and Statistics in Counseling Psychology |
Defining research, research questions, research designs, research processes, research objectives, research hypothesis, literature reviews, selecting populations and samples, research definition, statistical analyzing, counseling psychological research proposal, presentation and research ethics. |
The course supports SDGs 17 bySupporting statistical capacity building in developing countries. |
|
35 |
Theories of Educational Administration in the 21st Century |
Analysis of administration and educational administration principles and theories including system and process of educational management in the 21st century, management of internal control system, environment and facilities. Paradigms in organization theories the application of organization theories with educational administration in the 21st century, including a study and analysis of various changes affecting administration. Using moral and ethical principles including good governance for management. |
The course supports SDGs 4 byTechnical and vocational skills for employment. |
|
36 |
Leadership for Educational Change Management |
Meaning and importance of leadership for educational change management, leadership theories and characteristics of efficient leadership for educational change management, strategies for leadership development in the areas of good governance, change management, plans for changes, development of leadership skills including vision formulation, creative thinking, motivation and cooperation building, team building, conflict solution, communication, presentation and decision making. An analysis of current problems of Thai educational leadership and application of research results for educational leadership development in Thailand. |
The course supports SDGs 4 byTechnical and vocational skills for employment. |
|
37 |
Advanced Research Methodology for Educational Administration |
Advanced research design, sampling techniques, variables measurement, data analysis, selection of statistics appropriate for research design, data types, use of computer program for data analysis, statistical result interpretations, principles and techniques of educational measurement and evaluation and writing high quality research proposals and reports and Analysis of moral and ethical principles for educational administration. |
The course supports SDGs 17 bySupporting statistical capacity building in developing countries. |
|
38 |
Seminar in Educational Administration Digital Technology in the 21st Century |
Seminar in educational administration digital technology in the 21st century. leadership for educational change management in the range of administration of policies and strategies, academic affairs, human resource, budget and finance, buildings and facilities, general affairs, leadership promotional activities, building collaboration between schools, educational offices and faculty members, a local or overseas study trip to explore and gain experience in educational management and to be able to organize a seminar related to the topics concerning in educational management. |
The course supports SDGs 4 byTechnical and vocational skills for employment. |
|
39 |
Administration and Management in Educational Digital Technology Organization |
Principles and theories on the administration and management in educational technology organizations, vital competencies of administrators in educational technology organizations. An application of educational technology as knowledge management to create an excellent learning organization to technology digital organization and a practice of those principles both body and mind as a model for colleagues students. |
The course supports SDGs 4 byCreate and upgrade educational equipment and tools. |
|
40 |
Learning Measurement and Evaluation |
Principles, concepts of learning measurement and evaluation; qualifications of evaluators; learning measurement and evaluation models; educational behavior; learning measurement instruments; authentic assessment; performance assessment and construction of instruments of learning measurement; test validation; statistics for data analysis of learning measurement and evaluation; learning assessment and giving feedback on learners’ development and learning management. |
The course supports SDGs 17 bySupporting statistical capacity building in developing countries. |
|
41 |
Learning Innovation Research and Development |
Principles, concepts of research; researchers’ code of ethics; analysis of problems and needs for learners’ development; action research methodology and design; action research proposal writing; application of digital technology to learning development; innovation development for learning improvement and problem solving; construction of research instruments and test validation; statistics and data analysis; research report writing; application of research results to solve learners’ problems and improve learners’ learning. |
The course supports SDGs 17 bySupporting statistical capacity building in developing countries. |
|
42 |
Educational Research Data Analysis |
Educational research data, variables and scales of measurement; principles of educational research analysis using application package; data file creation; data screening and editing; data computation and data transform; descriptive statistics analysis; mean comparison analysis; analysis of variance; correlation analysis; regression analysis; educational research data analysis report writing. |
The course supports SDGs 17 bySupporting statistical capacity building in developing countries. |
|
43 |
Computer for Educational Measurement and Evaluation |
Computer foundation for educational measurement and evaluation; computer manipulating for basic statistics analysis about scoring, score position, standard score; assessment of quality of items and test ; interpretation and reporting of learning results. |
The course supports SDGs 4 byCreate and upgrade educational equipment and tools. |
|
44 |
Digital Tools for Educational Measurement Evaluation and Research |
Definitions, importance, types of digital tools; analysis of learner characteristics , determine the purpose of using digital tools; application and feedback from digital tools for educational measurement evaluation and research. |
The course supports SDGs 4 byCreate and upgrade educational equipment and tools. |
|
45 |
Classroom Action Research |
Basic principles, types, process of classroom action research; research designs; analysis and state the problem of classroom action research; research instrument and data collection, statistics, data analysis and interpretation; writing research reports and applying the results to improve teaching and learning |
The course supports SDGs 4 and 17 byTechnical and vocational skills for employment, supporting statistical capacity building in developing countries. |
|
46 |
Statistics Teaching Methodology |
Principles, concept and learning theories; model and technique for statistical learning; lesson plan and learning unit design in statistics; using and creating learning media in statistics; application of digital technology to enhance learning; classroom management and design of statistical reasoning learning environment; giving feedback to correct statistical misconceptions; learning outcomes measurement and evaluation in statistics |
The course supports SDGs 17 bySupporting statistical capacity building in developing countries. |
|
47 |
Administration of Educational Measurement and Evaluation |
Trends and policies on educational measurement and evaluation; characteristic of measurement and evaluation in the educational organization; roles and responsibilities of personnel in measurement and evaluation promoting department; planning to manage measurement and evaluation in education organization; problems and guidelines for problems solving in the educational measurement and evaluation in educational organization |
The course supports SDGs 4 byTechnical and vocational skills for employment. |
|
48 |
Project Teaching Methodology |
Principles, concepts of project based learning; instructional design of project teaching; learner needs assessment; lesson plan design; integrated learning and teaching; project topic identification; learning resources and environments design; data and information retrieval and quality assessment; data collection; knowledge synthesis and summarization; project monitoring and consulting; project learning outcomes evaluation. |
The course supports SDGs 4 byTechnical and vocational skills for employment. |
|
49 |
Application of Word Processor for Academic Report |
Techniques of using word processor for research; touch typing; page layout setting; text formatting, document formatting, tables formatting; merged mail; writing a list of references and bibliographies; application of digital technology and word processor to increase efficiency in academic report and research. |
The course supports SDGs 4 byProfessional training and an information and communication technology program. |
|
50 |
College Algebra |
Functions and their graphs; polynomial and rational inequalities; polynomial functions; analytic geometry and conic section; exponential and logarithm functions; trigonometry functions; applying technology for knowledge integration in various situations. |
The course supports SDGs 4 byTechnical and vocational skills for employment. |
|
51 |
Behavioral Study in Young Children |
Principles, concepts and theories related to study and develop child behavior; behavior of young children age 3 to 6 years old; causes and problems of child behavior; data collection and instruments used in child behavior study; observation of child behavior; reflective and interpretation of child behavior; writing observation report; protection child behavior’s problems and behavior modification; roles of teachers in child behavior observation. |
The course supports SDGs 4 byProviding quality preprimary education for early childhood children. |
|
52 |
Brain and Learning of Young Children |
Principles, concepts and theories related to brain; brain structures and functions of brain; brain development of young children; relationship of brain and Neuroscience (NS); Executive Functions(EF); fine motors and gross motors development according to cerebellum and Neuroscience (NS) of young children development; brain and learning; design and providing learning for enhancing brain and thinking skills of young children; reflect thinking on providing learning for enhancing brain and thinking skills of young children. |
The course supports SDGs 4 byProviding quality preprimary education for early childhood children. |
|
53 |
Education for Young Children with Special Needs |
Principles, concepts and theories related to special education management for early childhood relate to Neurolinguistics Science Process (NLSP); types and characteristics of children with special needs; practice in using tools for observation early childhood with special needs; practice designing to use the lessons to help early childhood children with special needs; practice designing activities to help early childhood with special needs that are consistent with economic, social and cultural status; developing specific target groups to receive learning opportunities that are appropriate for the specific characteristics of children with special needs. |
The course supports SDGs 4 byEnsure that vulnerable groups, including people with disabilities, indigenous peoples, and children, have access to education. |
|
54 |
Health and Safety for Young Children |
Principles, concepts and theories related to health and safety for young children; factors affecting the health and safety of young children; common diseases in the children; accidents in house, outdoor and in school; study of research related to health and safety for young children; practice in the measurement instrument to measure development, health and hygiene for young children; practice in first aid; approach to health and safety with the participation of parents, community and local according to development and individual. |
The course supports SDGs 4 byEnsure that all boys and girls have access to development and care. |
|
55 |
Creative Arts Activities for Young Children |
Principles, concepts and theories related to art development of young children; selecting, supplying art materials for young children; types of art activities for young children learning; principles of providing art for young children; techniques and methods in art integration activities for young children; promoting creativity for young children; analysis and evaluate of art development of young children; working with parents to helping, promoting and developing creative art for young children. |
The course supports SDGs 4 byProviding quality preprimary education for early childhood children. |
|
56 |
Technology and Materials for Young Children |
Principles, concepts and theories related to technology and creative materials to develop for young children; types of technology and materials to develop for young children; learning sources; selecting and supplying materials to develop for young children; using technology of media management learning for young children; design using the technology of media management learning for young children; assessing media efficiency; reflective thinking about develop and improve design media for young children; work with parents and families, community, the local context for solve problems, help and promoting using the technology of media to develop for young children. |
The course supports SDGs 4 byCreate and upgrade educational equipment and tools to provide a safe learning environment. |
|
57 |
Provision of Experiences in Psychomotor for Young Children |
Principles, concepts and theories related to provision of experiences in psychomotor for young children; structure and function of various organs in the body with the relationship of the brain; study research related to provision of experiences in psychomotor for young children; ecosystem management of learning experiences that promote psychomotor for young children; practice in provision of experiences, instruction media and assessment in provision of experiences in psychomotor for young children; role of the teachers, parents in provision of experiences in psychomotor for young children. |
The course supports SDGs 4 byProviding quality preprimary education for early childhood children. |
|
58 |
Tales and Dramatic play for Young Children |
Principles and concepts related to tales and dramatic play for young children; types of tales; principles using tales for develop of young children; study of research related to use tales for develop of young children; choosing tales for young children according to brain function; patterns and techniques of storytelling; composing tales for young children; making props and puppets for storytelling and dramatic play for young children; practicing emotional communication skills; design and manage dramatic show. |
The course supports SDGs 4 byProviding quality preprimary education for early childhood children. |
|
59 |
Music for Early Childhood Teachers |
Concepts and theories related to music; music with language development and emotion development; foundation of the development of songs and music; types of music instrument, music notes; choosing music for young children’s activities; composing music for young children; singing and practice to play music instrument for children development; roles of the teachers with music for young children activities. |
The course supports SDGs 4 byProviding quality preprimary education for early childhood children. |
|
60 |
Mathematics for Young Children |
Principles, concepts and theories related to mathematics development of young children; brain and mathematics learning of young children; scope of learning area and mathematic process skills for young children; media on promoting learning mathematics for young children; provision learning experiences to enhance the learning of mathematics for young children; environment management conducive to learning mathematics in early childhood education; assessment of provision mathematics learning experiences for young children; roles of the teachers, parents and persons involving in promoting mathematics learning for young children. |
The course supports SDGs 4 byProviding quality preprimary education for early childhood children. |
|
61 |
Literature for Young Children |
Principles and concepts related to literature for young children; types of appropriate literature for young children; literature standards for young children; basic knowledge relate to brain and Neuroscience (NS) and Neurolinguistics Science Process (NLSP); selection and using literature to enhancing development for young children; study of research relate to literature to enhancing development for young children; design literature for young children according to brain function; reflective thinking about improve literature for develop of young children; work with parents and families, community, local context for solve problems, help and promoting for young children habit of reading. |
The course supports SDGs 4 byProviding preparation for primary education. |
|
62 |
Curriculum Development for Early Childhood Education |
Principles, concepts and goals of curriculum for early childhood education; types of curriculum; components of curriculum; curriculum development processes; factors affecting the curriculum; organizing early childhood education programs according to the concept of early childhood educators; analysis of curriculum for early childhood education in Thailand; comparative studies of Thai and international curriculum for early childhood education; training for development of early childhood educational curriculum to preparation of the school curriculum and curriculum evaluation. |
The course supports SDGs 4 byProviding quality preprimary education for early childhood children. |
|
63 |
Provision of Learning Experiences for Children under 3 Years Old |
Principles, concepts and theories involved in early childhood development under 3 years old; linking the relationship of science in neurology linguistics; growth and development of early childhood under 3 years old; bringing-up method, media and plan to organize educational environment that is conducive to learning for early childhood under 3 years old; practice designing early childhood development assessment ; practice designing activities to integrated learning experience plan; practicum of providing learning experience according to learning experience plan. |
The course supports SDGs 4 byCreate and upgrade educational equipment and tools to provide a safe learning environment. |
|
64 |
Language Development of Young Children |
Principles, concepts and theories related to language; relationship of Neurolinguistics Science Process (NLSP) and language development of young children; emergent literacy and early literacy of young children; activity guidelines for language learning provision; media to enhance language acquisition; management of environmental conducive to language learning of young children; assessing language development of young children; design and provision of language learning experiences for young children; collaboration with family, community in promoting development and language learning of young children. |
The course supports SDGs 4 byProviding quality preprimary education for early childhood children. |
|
65 |
Sciences for Young Children |
Principles, concepts and theories related to science for young children; scope of learning content; science process skills for young children; learning media on promoting science process skills for young children; design science activities that consistent with brain functions; application of STEM education and little scientists house project; environment management conducive to learning science in early childhood education; assessment of provision of science learning experiences for young children; enhance positive attitudes towards science; working with parents, helping, promoting learning and developing positive attitudes towards science for young children. |
The course supports SDGs 4 byCreate and upgrade educational equipment and tools to provide a safe learning environment. |
|
66 |
Provision of Experiences in Emotion-Mind and Social for Young Children |
Principles, concepts and theories related to provision of experiences in emotion-mind and social for young children; influence of family, school, community and local on provision of experiences in emotion-mind and social for young children; enhance of emotional quotient, Executive Functions(EF), social behavior development and cultivating sufficiency economy, morality, ethics for young children; study research related to provision of experiences in emotion-mind and social for young children; provision of experiences in emotion-mind and social for young children; assessment of young children’s provision of experiences in emotion-mind and social for young children; role of the teachers, parents in provision of experiences in emotion-mind and social for young children. |
The course supports SDGs 4 byProviding quality preprimary education for early childhood children. |
|
67 |
Assessment of Young Children Development |
Principles and concepts in development and learning assessment of young children; relationship of Neuroscience (NS), Neurolinguistics Science Process (NLSP) and neurological system of cerebellum; types of assessment of young children development; technique and method to assess development; authentic assessment; portfolio; documentation; study research related to assessment of young children development; technology that using assessment of young children development; create and use assessment tools for measurement and evaluation development; composing report evaluation; using assessment report to provide activities for promoting young children development; working with parents, family, community and local to solving problems, helping, promoting learning and developing young children. |
The course supports SDGs 4 byProviding quality preprimary education for early childhood children. |
|
68 |
Provision of Integrated Learning Experience for Children 3 to 6 Years Old |
Concepts and theories related to providing learning experiences for young children ; learning styles of children age between 3 to 6 years old; principles and concepts of sufficiency economy philosophy; principles of providing experiences for children age between 3 to 6 years old; providing daily activities in accordance with learning styles of children age between 3 to 6 years old; management of environmental conducive to learning for young children; assessment of development and learning; curriculum implementation to providing learning experiences; design integrated learning experience plan for children between 3 to 6 years old; practicum of providing learning experience according to learning experience plan with micro activities; collaboration with families and communities in provision of learning experiences; reflective thinking about practicum of providing a learning experience of children between 3 to 6 years old. |
The course supports SDGs 4 byProviding quality preprimary education for early childhood children. |
|
69 |
Creative Arts for Early Childhood Teachers |
Foundation of the arts for early childhood teachers; art aesthetics; techniques and methods of artwork creation; creating art with paper, scraps and local materials; decorating bulletin board; interior and exterior decoration of classroom with artworks; using art to promote learning of young children and parents; work exhibition of young children learning. |
The course supports SDGs 4 byTechnical and vocational skills for employment. |
|
70 |
Community Relations for Development of Young Children |
Principles, concepts and theories related to the characteristic of families and communities; roles of families communities and social that effect to take caring and developing of young children; promoting and empowering families and communities; building positive relationship and interaction among educational institutions, families and communities to develop young children; involvement among families, communities and mass media in encouraging development and learning of young children; content, model and method of parental education; analyze, plan and design activities for families, communities and local; organizing educational project and parental involvement between school, parent and community to develop young children. |
The course supports SDGs 4 byProviding quality preprimary education for early childhood children. |
|
71 |
Research for Development of Young Children |
Principles and concepts related to research for the development of young children; ethics and integrity in research; classroom research for early childhood education; research methodology and research techniques for development of young children; studying issues and selecting research topics for the development of young children; research design and planning; writing a research proposal; design and create innovations in research; research instruments; data collection; data analysis and presentation of data analysis by using instant software; operations research at the early childhood education classroom; writing a report of research; applying research results for young children development. |
The course supports SDGs 4 byProfessional training and an information and communication technology program. |
|
72 |
Management in Kindergarten and Child Development Center |
Principles, concepts and theories related to early childhood education management; educational quality assurance for early childhood level; administrative tasks and organization in early childhood education institutions and child development centers; systems and processes for educational quality assurance; quality assessment in early childhood classroom and applying the results of educational quality assessment to develop learning; preparation of action plans in early childhood education; personality, roles, duties and skills of early childhood school administrators, reflective thinking and application of knowledge on policy, problems, social opportunities in order to have leadership skills and cooperation with personnel; study and creating acceptance in the community. |
The course supports SDGs 4 byTechnical and vocational skills for employment. |
|
73 |
Psychology of Sex Education |
Meaning, importance and necessity of sex education psychology, sexual behavior and expression; growth and sexual development; relationship between sex beliefs and misconceptions about sex ; sexually transmitted diseases, sexual learning promotion process, family life planning, thinking, analyzing, solving problems and rejecting when in a sexual risk situation, the design and arrangement of activities related to sex education can be appropriate to the age range and the application of gender psychology in everyday life. |
The course supports SDGs 5 byAccess to sexual and reproductive health. |
|
74 |
Guidance Activities for Life Skills Development |
Organizing guidance activities according to structures of guidance work; principles, patterns, and processes of organizing guidance activities to promote and develop learners’ life skills in 21st century – flexibility and adaptability, creativity and self-directed skills, social and cross-culture learning skills, leadership and responsibility ; designing activities and training programs for promoting and developing learners’ life skills in 21st century; encouraging learners to live their life happily with other people in the rapidly-changing societies. |
The course supports SDGs 8 byReduce the proportion of youth who are unemployed, uneducated, and untrained. |
|
75 |
Life and Career Planning |
Approaches and theories of career development; using occupational measuring forms; developing persons for life and career advancement; using technology for life planning; career counseling and career activities managing in school. |
The course supports SDGs 4 byEssential skills include technical and vocational skills for employment. |
|
76 |
Psychology for Persons with Special Needs |
Definitions, types, causes, psychological characteristics and cares for persons with special needs; screening, behavioral adjustment, psychological environmental management affecting learning of persons with special needs; assistance of persons with special needs regarding the differences of behaviors; case studies for persons with special needs in schools. |
The course supports SDGs 4 byEnsure that vulnerable groups, including people with disabilities, have access to education. |
|
77 |
Independent Study in Psychology and Guidance |
Definition, importance, objectives and principles of independent study in psychology and guidance ; independent study on interesting topic as related to psychology and guidance and report writing under the instructor supervision; application of independent study in psychology and guidance. |
The course supports SDGs 4 byEssential skills include technical and vocational skills for employment. |
|
78 |
Statistics for Research in Psychology |
Introduction to statistical concepts; measures of central tendency; measuresof dispersion; statistical hypothesis testing; analysis of differences and relationships; conducting statistics in psychological research. |
The course supports SDGs 17 bySupporting statistical capacity building in developing countries. |
|
79 |
Using and Maintenance of Computer Equipment and Digital Technology for Education |
Fundamental of electric, electronic, and computer devices and digital technology tools; Analysis, problem solving, installation, security, maintenance of computer and digital technology tools; Environmental planning for computer and digital technology with accurately and safely application. |
The course supports SDGs 4 byEssential skills include technical and vocational skills for employment. |
|
80 |
Science and Mathematics for Digital Technology Teachers |
Search for information on biological science content, physical sciences, science, understanding scientific process skills scientific method scientific advances, study of electronic digital circuits, various numbering systems, base number, addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, base code numbers, various logic gates, and circuit designs for the application of digital technology for education. |
The course supports SDGs 4 byCreate and upgrade educational equipment and tools. |
|
81 |
Digital Technology for Students with Special Needs |
Principles, concepts and theories of digital technology for designing and producing instructional media for learners with special needs; Digital media, hardware media, technique and method media; Instructional media assessment for learners with special needs. |
The course supports SDGs 4 byCreate and upgrade educational equipment and tools that are sensitive to children and people with disabilities. |
|
82 |
Website Design Technology for Education |
Principles, theory of graphic design technology for use on internet; hardware and software, writing source code for website creation; accessing to database; design and develop interactive website; procedure of educational website development; practical in design and development of educational website. |
The course supports SDGs 4 byProfessional training and an information and communication technology program. |
|
83 |
Digital Print Media Technology |
Principles of design, fundamental knowledge, steps, and process of technology digital printing media production; usage of characters, photograph, motion picture and sound for digital printing media. |
The course supports SDGs 4 byProfessional training and an information and communication technology program |
|
84 |
Design and Development Digital Technology for Education |
Principles, concepts and theories of design, system, communication, learning and instructional model; Principle of digital technology for education; Analysis, design, development, implementation and evaluation of instructional media and related instructional design; Trend of future instructional media design; Practice of analysis, conclusion, selection, design, produce, apply and evaluate the instructional media appropriately for all learners. |
The course supports SDGs 4 byCreate and upgrade educational equipment and tools. |
|
85 |
Graphic Animation and Digital Media Design for Education |
Principles, concepts, and related theories of graphic design, animation and digital media for education; Process of graphic media production, animation and digital media; Practice of graphic design, animation and digital media for education. |
The course supports SDGs 4 byCreate and upgrade educational equipment and tools. |
|
86 |
Database Systems for Education |
Principles, concepts, and theories of data base system, database architecture; Application of database and application; Structured Query Language: SQL; Database security system; Practice of database analysis, design, development for applying in schools and workplaces. |
The course supports SDGs 4 byCreate and upgrade educational equipment and tools. |
|
87 |
Information System and Digital for Education |
Concepts and theories of design and management of information technology and digital for education; Analyze, design, and develop information technology system and digital for education; Design the characteristics of equipment and direction of information technology system for future education; Sharing appropriate idea of designing information technology for education to the institutions; Use and maintain networking system according to the components and standard of computer network, network connection medium, protocol; Types of computer network connection, equipment of information technology, access and use of computer data for communication and portable electronic devices; Design, develop, use, install and maintain internet system; Practice of designing online learning system for digital learning for education. |
The course supports SDGs 4 byProfessional training and an information and communication technology program. |
|
88 |
Network System and Cloud Computing Systems Management for Education |
Concepts, theories, and composition of network system and cloud technology management for education; Design, development and application of network system in education; Database of school, parents, teachers, students and class management; Applying database in analysis, synthetization to gain information for networking development or decision making; Practice of network system management and cloud technology in schools. |
The course supports SDGs 4 byCreate and upgrade educational equipment and tools. |
|
89 |
Portrait Photography |
Definition, characteristics of portrait photography, influence of contemporary photography; selection of materials and equipment in portrait photography, make-ups, costumes, posture, settings and other environment, lighting, photo retouching; practical in portrait photography both inside and outside studio and photo retouching. |
The course supports SDGs 4 byTechnical and vocational skills for employment, decent work, and entrepreneurship. |
|
90 |
Computational Science for Digital Technology Teachers |
Analysis of techniques and method of problem solving, computational thinking, and abstraction thinking; Practice of problem-solving step by step, decomposition of problem, show troubleshooting by writing, explain, draw or symbolizing; Design and programming with software or basic technological devices to apply in daily life with effective decision making and realize on safely use of information technology; Develop digital technological project for education and creatively integrated with another field and real life situation. |
The course supports SDGs 4 byAll learners gain the knowledge and skills necessary to promote sustainable development. |
|
91 |
Advanced Digital Technology and Computer for Education |
Trends of digital technology and computer for education; Design and development of digital technology and computer innovation for education; Practice of innovative creation for learning management. |
The course supports SDGs 4 byCreate and upgrade educational equipment and tools. |
|
92 |
Computer Programing and Developing Applications for Education |
Concepts, and related theories of computer programming and application development; Computer program development, properties of any type of program languages; Basic principles of composition, commands, steps, analysis, design of educational application and software evaluation; Practice of computer programming and developing applications for education. |
The course supports SDGs 4 byCreate and upgrade educational equipment and tools. |
|
93 |
Technical Learning Management of Digital technology for Education |
Principles, concepts, and theories of digital technology for education, learning psychological theory, instructional technique; Need assessment of learners, content sequencing, classroom management, provision of learning experience and ecosystem management of digital learning; Practice of designing lesson plan and evaluation. |
The course supports SDGs 4 byTechnical and vocational skills for employment, decent work, and entrepreneurship. |
|
94 |
Research in Digital Technology for Education |
Principles, concepts of research methodology of digital technology for education; Trends of research in digital technology for education; Research proposal writing,research report for solving and developing learning innovation creatively with digital technological research. |
The course supports SDGs 4 byAll learners gain the knowledge and skills necessary to promote sustainable development. |
|
95 |
Management of Training and Seminar in Digital Technology for Education |
Principles, concepts, theories and benefits of training and seminar; Techniques and strategies, roles, characteristics, personality, ethics, teamworking of training and seminar organizers; Planning, designing and developing the training course and seminar; Operate the training program and seminar, evaluation and report the training and seminar program in digital technology for education. |
The course supports SDGs 4 byAll learners gain the knowledge and skills necessary to promote sustainable development. |
|
96 |
Creativity Digital Television Program for Education |
Production of educational television program in studio; tools and equipment in studio, program directing technique, management of setting and lighting, visual effect design and graphics; practical in television program production in studio, setting, lighting, and visual special effect and graphics. |
The course supports SDGs 4 byTechnical and vocational skills for employment, decent work, and entrepreneurship. |
|
97 |
Design of 3 Dimensions Media |
Definition, importance and basic principles of 3 dimensions media design, types of 3 dimensions media design, bas-relief, high-relief, sunk-relief, media, models, figurines and toys; 3 dimensions learning media, application of computer program in 3 dimensions media production; practical in design and evaluate 3 dimensions work. |
The course supports SDGs 4 byProfessional training and an information and communication technology program. |
|
98 |
Digital Technology for Education |
Principles, competencies, limitation, evolution, roles, and digital technology ; characteristics of digital technology teachers for education; learning management with digital technology in the 21st century; acts concerned digital technology for education; trends of digital technology for education. |
The course supports SDGs 16 byProvide legal identity for everyone. |
|
99 |
Using and Maintenance of Computer Equipment and Digital Technology for Education |
Fundamental of electric, electronic, and computer devices and digital technology tools; analysis, problem solving, installation, security, maintenance of computer and digital technology tools; planning and practicing the environment of computer equipment and digital technology with accurately and safely application. |
The course supports SDGs 4 byEnsure that all learners acquire the knowledge and skills necessary to promote development. |
|
100 |
Teaching for Folk Dance |
Significance of folk song, amusement, Thai dramatic arts in various; roles of local society and culture; inheritage local cultural capital knowledge for Soft Power; transmittal to New Generation and teaching methods; practice of learning management for local dramatic. |
The course supports SDGs 4 byPromote appreciation of cultural diversity and the contribution of culture to sustainable development. |
|
101 |
Recreation Leader and Camping |
The importance of recreation leaders, different types of leaders, comparing characteristics of leaders and administrators, differences and relationships between leaders and followers, roles and duties of recreation leaders, operations, common problems in the work of recreation leaders, practical training in leadership in various recreational activities, history, purposes and characteristics of camps, the relationship of camping to field study, types of camps, writing projects and plans for organizing camps, program equipment, measurement and evaluation of camps, organizing practical camps. |
The course supports SDGs 5 by Ensure that women are fully involved and have equal opportunities for leadership at all levels of decision-making. |
|
102 |
Classroom Research in Physical Education |
Principles and approach in Physical Education, research in classroom, specifying problems, posting forms of research, setting objectives and assumptions, collecting information, making questionnaire, analyzing and interpreting information, using statistics for research, writing report and presenting the findings. |
The course supports SDGs 17 bySupporting statistical capacity building in developing countries. |
|
103 |
Games and Recreation Activities |
Definition; knowledge, understanding and significance of games and recreation activities; scopes and type of games and recreation activities; managing activities of games and recreation activities and different kinds of learner’s development activities; importance and roles duties of games and recreation activities leader; techniques of games and recreation activities leaders; practicing on being a leader in different games and recreation activities. |
The course supports SDGs 5 byEnsure that women are fully involved and have equal opportunities for leadership at all levels of decision-making. |
|
104 |
Prevention and First Aid for Injuries |
Meaning; importance of care-taking; prevention and first aid for various plays and sports injury; causes and mechanism of the sports injury; drug using; dangers of doping; prevention and first aid by various; methods such as physical therapy; using cold and hot, massaging; cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR). |
The course supports SDGs 3 byStrengthen the prevention and treatment of substance misuse. |
|
105 |
Physical Education for the Disabled |
Definition and types of disabled; importance of physical education management for disabled; disabled assessment; selection physical activity, physical education activities, recreation activity; learning management techniques according to the type of disabled; evaluation of physical education learning of disabled. |
The course supports SDGs 4 byEnsure that vulnerable groups, including people with disabilities, have access to education. |
|
106 |
Basic Movement Activities and Physical Activity for Kids |
Concepts; principles and methods of organizing activities in accordance with kids of various ages; classification and principles of choosing basic movement activities and physical activities for kids. |
The course supports SDGs 4 byEnsure that all boys and girls complete quality primary and secondary education. |
|
107 |
Instruction Management in Health Education |
Analysis; philosophy; teaching Health Education; learning management of Health Education; methods and techniques of Health Education, primary level, secondary level, university level and also non-formal education; problem solving; development and evaluation of Health Education for its efficiency. |
The course supports SDGs 4 byEnsure that all boys and girls have access to development and care. |
|
108 |
Physical Education Curriculum Development |
Importance of physical education curriculum; curriculum factor; relationship between educational philosophy and physical education philosophy on curriculum development; principles of physical education curriculum design in schools; procedures for conducting physical education curriculum in schools; learning unit preparation and course structure. |
The course supports SDGs 4by Ensure that all learners acquire the knowledge and skills necessary to promote development. |
|
109 |
Learning Management in Physical Education |
Definition and importance of physical education learning management; standards, learning outcomes, indicators and learning objectives; applying the learning psychology principles in teaching; principles of physical education teaching; physical education method; organizing and managing physical education classes; selection of evaluation methods for learning management; qualification of being a physical education teacher; teacher professional standards; preparation of physical education management plans. |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Essential skills include technical and vocational skills for employment. |
|
110 |
Classroom Action Research in Physical Education |
Basic knowledge of research; importance of research on the development of learners, teachers and physical education curriculum according to learning standards; Importance of classroom action research in physical education; principles of classroom action research in physical education, research planning, problem determination, research form selection, classroom action research in physical education process, report writing and dissemination of research. |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Essential skills include technical and vocational skills for employment. |
|
111 |
Science Learning Management in Primary Education |
Analysis of learning area of science and science matters in primary education, Development of learning units, Application of learning psychology knowledge Learning management techniques and methods, Learning medias Measurement and evaluation for planning and designing learning activities based on students in line with active learning and being consonant to nature of science learning, Development of lesson plan, Development of medias and micro teaching practice, Teaching practicum, Employment of classroom educational process to improve professional science learning management competency. |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Ensure that all boys and girls complete quality primary and secondary education. |
|
112 |
Science Learning Management in Secondary Education |
Analysis of learning area of science and science matters in secondary education, Development of learning units, Application of learning psychology knowledge Learning management techniques and methods, Learning medias Measurement and evaluation for planning and designing learning activities based on students in line with active learning and being consonant to nature of science learning, Development of lesson plan, Development of medias and micro teaching practice, Teaching practicum, Employment of classroom educational process to improve professional science learning management competency. |
The course supports SDGs 4by Ensure that all boys and girls complete quality primary and secondary education. |
|
113 |
School and Community Waste Management |
Meaning, sources, types of school and municipal waste and its impact on the environment and humans; management principles to eliminate the exploitation and management; zero waste; the law and the relevant authorities and the involvement of the public on waste management, practical techniques in the field of waste management; guidelines for learning management about waste in schools and communities into classrooms. |
The course supports SDGs 8, 11 and 12 by Continuously improve the efficiency of the use of the world’s resources in consumption and production, waste management, and reduce waste generation through prevention. |
|
114 |
Organizing Sciences Integrated Field Trips |
Elements of tourism, routing, integrating with learning management in sciences; interpretation technique; sciences communication. |
The course supports SDGs 8byDesign and implement policies that promote sustainable tourism, which will create jobs. |
|
115 |
Earth System Science |
Practice to be proficient in elements and relationships of earth system, process of changing within earth and its surface, geological disaster, mineral resources, geological map and its utilization, earth’s energy balance, circulation of air in the earth, formation of clouds, circulation of water in the ocean, process of global climate changes that affect living things and environment, weather forecast; Explain natural phenomena with science; Apply knowledge to science learning management. |
The course supports SDGs 11 and 13byPaying special attention to air quality and raising awareness on climate change mitigation. |
|
116 |
Environmental Science |
Take action to study and learn about the context and local wisdom, natural resources and local environment, education for real life, social, and environment, way of life of local people, conservation of local environmental; Create science courses in schools using knowledge gained from local studies; Manage science learning by using local wisdom and local learning resources that are consistent with the community context and suitable for learners. |
The course supports SDGs 15byEmpowering local communities. |
|
117 |
Electricity and Energy |
Practice to be proficient in electricity and energy, source of electricity, electrical power production, solar energy, geothermal energy, wind energy, biomass energy, energy from fuel, water energy, nuclear energy, ocean energy, applications for the use as renewable and alternative energy, production and saving of energy, energy and environment; Apply science knowledge related to electricity, energy, and alternative energy for environmental management and science learning management. |
The course supports SDGs 7byIncrease the share of renewable energy in the global energy mix. |
|
118 |
Biology for Science Teachers 1 |
The study of biology; cell structure and function; cell transport; cell division; nutrients and energy in living organism; digestion; excretion; gas exchange; animal circulation; blood and immune system; homeostasis; animal coordinate system; animal reproduction; animal growth and development; related laboratory; biology learning management in secondary education. |
The course supports SDGs 4byEnsure that all boys and girls complete quality primary and secondary education. |
|
119 |
Science and Community Products |
Fundamental scientific knowledge regarding daily life product; study and extraction of important substances from plants and natural materials; exploration of local plants and natural materials; method for product development utilizing local plants and natural materials |
The course supports SDGs 12byPromote local culture and products. |
|
120 |
Practice in Visual Art 1 |
Specific techniques of visual art process ; art working skill learning management process development, think process, visual art creative by concept and techniques ; specific techniques skills practice. |
The course supports SDGs 4byEssential skills include technical and vocational skills for employment. |
|
121 |
Learning Management of Art Education for Secondary Education |
International level secondary art education Curriculum development, the basic art education core curriculum, school curriculum, secondary visual art, secondary learning psychology and art development psychology ; teaching styles, teaching methods and teaching techniques; guide line of secondary visual art learning ; media and learning center development, technology learning, evaluate learning, learning management plan and practice in managing visual arts learning in real situations or simulations. |
The course supports SDGs 4byEnsure that all boys and girls complete quality primary and secondary education. |
|
122 |
Printmaking |
Meaning history type and value of printing ; basic printing theory, printing evaluate ; using special printing equipment properly ; basic skill printing, relief printing, intaglio printing, planographic printing and Stencil printing for art education teaching. |
The course supports SDGs 4byEssential skills include technical and vocational skills for employment. |
|
123 |
Learning Management of Art Education for Primary Education |
International level primary art education Curriculum development, the basic art education core curriculum, school curriculum, primary visual art, primary learning psychology and art development psychology ; teaching styles, teaching methods and teaching techniques; guide line of primary visual art learning ; media and learning center development, technology learning, evaluate learning, learning management plan and practice in managing visual arts learning in real situations or simulations. |
The course supports SDGs 4byEnsure that all boys and girls complete quality primary and secondary education. |
|
124 |
Morals, Ethics, Code of Ethics, and Teachers’ Spirituality |
Behavior; practice according to code of ethics; learner development with teachers’ spirituality; analyzing, synthesizing and integrating body of knowledge about teachers’ values; ethics of teaching profession; morals and ethics of teachers; teachers’ spirituality; professional laws; professional development situations; experience – based learning management, case study and contemplative practice; self – development for being good teachers; modernity and transformation literacy. |
The course supports SDGs 4byEssential skills include technical and vocational skills for employment. |
|
125 |
Curriculum Development |
Principles, concepts, theories of curriculum development; foundation of educational philosophy, psychology, society, culture and technology for curriculum development; curriculum evolution in Thailand; curriculum patterns; curriculum development processes; curriculum implementation; curriculum assessment and revision; core curriculum; school curriculum; basic education curriculum; problems and trends in curriculum development; school curriculum design and development. |
The course supports SDGs 4byEnsure that all learners gain the knowledge and skills necessary to promote sustainable development. |
|
126 |
Innovation and Information Technology for Educational Communication Learning |
Principles, concepts, and theories of innovation and information technology for educational communication learning; digital technology laws and codes of ethics; using digital technology for design of learning management according to the nature of major areas of study to develop intellectual and innovative learners; learners with special needs; analysis, selection, design, development, evaluation, integration and application of using innovation and information technology for educational communication and learning efficiently, infringement of an intellectual property, applying reflections to self-development to be a good teacher with knowledge, modernity and transformation literacy. |
The course supports SDGs 4byCreate and upgrade educational equipment and tools that are sensitive to children and people with disabilities. |
|
127 |
Communication Skills and Culture for Teachers |
Importance of Thai language, English language and Thai culture for teachers; practice of listening, speaking, reading and writing skills; communication skill; techniques for giving presentation; practising oneself concerning Thai culture in school, community and Thai society. |
The course supports SDGs 4byEssential skills include technical and vocational skills for employment. |
|
128 |
Individual Studies |
Examining research topics based on individual interest pertaining to early childhood education; data collection based on systematic data investigation; data analysis; data systems; writing reports based on the methodology and writing the report under a supervision and assessment of instructors. |
The course supports SDGs 4byProviding quality preprimary education for early childhood children. |
|
129 |
Research in Educational Administration |
Definition of research; types of research in educational administration; research techniques; research design; writing proposal of research in educational administration; creating a research tools; statistics for research; writing a research report; evaluation; synthesis; research Implementation for educational administration, research for educational professional development, research ethic. |
The course supports SDGs 4byEnsure that all learners gain the knowledge and skills necessary to promote sustainable development. |
|
130 |
Academic Affairs Administration and Quality Assurance in Education |
Signification and limit of academic affairs administration, curriculum development, instruction, supervision, academic administration for quality and excellence, principles and method of quality assurance, quality assurance in academic affairs administration, curriculum, teachers and students according to educational standard in all level; internal and external quality assurance systems, factors analysis, indicators, monitoring and evaluation system; total quality management system, analyzing and application of total quality management for developing educational organizations, educational quality assurance system according to educational laws, professional administrators roles for standard educational quality assurance. |
The course supports SDGs 4byEnsure that all learners gain the knowledge and skills necessary to promote sustainable development. |
Faculty of Engineering and Industrial Technology

The Faculty of Industrial Technology at Bansomdejchaopraya Rajabhat University (BSRU) plays a pivotal role in promoting sustainable development through its specialized courses aligned with the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Covering areas such as industrial automation, quality management, renewable energy, and sustainable production, the faculty equips students with the technical skills and knowledge needed to drive innovation in industry. By focusing on sustainable practices, industrial development, and environmental management, these courses prepare students to become leaders in creating inclusive, sustainable, and forward-thinking industrial solutions that contribute to both local and global sustainability efforts.
Faculty of Engineering and Industrial Technology : 86 courses, which are embedded with sustainability, are offered by Bansomdejchaopraya Rajabhat University as follows.
|
N |
Course Name |
Course Description |
SDGs Embedded |
|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
English for Engineering and Industrial Technology |
Study and integrate technical English in listening; speaking, reading and writing skills for engineering and industrial technology; English usage and technical vocabulary for industrial, number, unit of measure; shape, manual for the production process of various machines; material properties; using of tools and equipment; classification of types of materials; description of production process; signs, important symbols; report writing and presentation in bar graph; charts and tables |
The course supports SDGs 4 and 9 by Ensure that all young men and women are able to read and write. Increasing access to information and communication technologies. |
|
2 |
Industrial Automation System |
Introduction to industrial control, analog signal conditioning, digital signal conditioning, sensors and transducers, analog controllers, digital controllers, sequence control, Programmable Logic Controllers (PLC), PLC programming, PLC interfaces, PLC application in automation systems. |
The course supports SDGs 9 by Promote inclusive and sustainable industrial development |
|
3 |
Operations Research Laboratory |
Co-requisites : 4131312 Operations Research Laboratory on problem solving; mathematical models, linear programming, optimization, job assignment, transportation model, using computer programs to solve problems in decision making process |
The course supports SDGs 12 by Awareness of sustainable development and a way of life in harmony with nature. |
|
4 |
Industrial Quality Assurance Management Workshop |
Co-requisites : 4131316 Industrial Quality Assurance Management Workshop in industrial quality assurance management; usage of quality assurance tools and process of quality assurance management |
The course supports SDGs 9 by Promote inclusive and sustainable industrial development |
|
5 |
Continuous Improvement Process and Quality Management |
Quality and productivity; philosophy and system to continuously improve the quality of products and processes; identify activities that do not add value; control at the source; just-in-time production, and methods of Kaizen, modern techniques in the planning and management |
The course supports SDGs 8 by Promote development-oriented policies that support productive activities and create decent works. |
|
6 |
Industrial Computer Programming |
The concept of programming language for industrial applications, debug, operator, control statement, loop statement, array; function |
The course supports SDGs 9 by Promote inclusive and sustainable industrial development |
|
7 |
Industrial Computer Programming Laboratory |
Co-requisites : 4131324 Industrial Computer Programming Operation of programming language for industrial applications, debug, operator, control statement, loop statement, array; function |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Professional training and an information and communication technology program |
|
8 |
Computer for Production Planning and Control |
Using computer-assisted planning and production control; demand forecasting and assigning factors of production; planning and capacity utilization; project planning to identify production schedule; production sequencing and scheduling; material requirements planning; planning and production control to suit production system |
The course supports SDGs 12 by Developing to strengthen scientific and technological capabilities that will drive towards more sustainable production and consumption patterns. |
|
9 |
Computer for Production Planning and Control Laboratory |
Co-requisites : 4131328 Computer for Production Planning and Control Laboratory on using computer-assisted planning and production control; demand forecasting; capacity and aggregate planning; inventory control; material requirement planning; job sequencing and scheduling; production line balancing |
The course supports SDGs 12 by Awareness of sustainable development and a way of life in harmony with nature. |
|
10 |
Technology and Innovation Management |
Basic knowledge of technology management; technology life cycles; innovation process; technology strategy; technology planning; the acquisition and exploitation of technology; technology transfer; industrial production technology |
The course supports SDGs 8 by Promote development-oriented policies that support productive activities, entrepreneurship, creativity, and innovation. |
|
11 |
Small Industrial Management |
Types of small industries; form of ownership; the role of small industries in the development of the country; business planning; business activities in production, marketing, finance, accounting, human resource management; factors for small industries success and the cause of small businesses failure; guidelines for operation development of efficient small industries |
The course supports SDGs 8 by Make per capita economic growth sustainable in the context of the country. |
|
12 |
Information for Industrial Management |
Structure of the fundamental data; concept and design of management information system in business and industry, the fundamental computer system; data processing techniques to meet the needs of the organization in order to improve information systems; determining and evaluating system operating costs, process management information systems |
The course supports SDGs 9 by Promote inclusive and sustainable industrial development |
|
13 |
Enterprise Resource Planning |
Principle of the ERP system and the traditional ERP; evolution and the framework of the ERP, industrial processes management, importance of the infrastructure system in support of industrial processes and systems and infrastructure system associated, how ERP system implement to application in the enterprise; how ERP system implementation to application in the enterprise, evaluation of ERP system |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Professional training and an information and communication technology program |
|
14 |
Industrial Computer Programming |
Concepts of programming language for industrial applications; search and debug; operator; control statement; loop statement; array function |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Professional training and an information and communication technology program |
|
15 |
Fundamental Industrial Electricity Laboratory |
Corequisites course : ET 31106 Fundamental Industrial Electricity Laboratory on principle circuit and electrical measurement tool; control and prevention of electrical machinery in the industry |
The course supports SDGs 9 and 4 by Promote inclusive and sustainable industrial development, All learners gain the knowledge and skills necessary to promote sustainable development. |
|
16 |
Software for Industry |
Programs package for word processing; statistical and numerical calculation; data presentation; current graphics software and its applications; application software in industry |
The course supports SDGs 9 by Promote inclusive and sustainable industrial development |
|
17 |
Engineering Quality Control |
Principles of quality control in industry; application of statistical techniques in quality control; control charts in quality assurance; process capability analysis; acceptance sampling, sampling plan and standard sampling tables for inspection; reliability; product testing |
The course supports SDGs 9 by Promote inclusive and sustainable industrial development |
|
18 |
Industrial Inventory Management |
Importance of Industrial inventory management; management and inventory control; types of inventory; costs related to inventory management; economic order quantity; appropriate demand forecasting; Industrial inventory management planning |
The course supports SDGs 9 by Promote inclusive and sustainable industrial development |
|
19 |
Industrial Transportation Management |
Principles of Industrial transportation management; decision model for transportation; analysis of various types of transportation system; scheduling and routing in Industrial transportation |
The course supports SDGs 11 by Participatory management of human settlements |
|
20 |
Operations Research |
Principles of industrial problem solving; mathematical models; linear programming; optimization; job assignment; transportation model; queuing theory and simulation in decision making process |
The course supports SDGs 11 by Efficiency of resource use |
|
21 |
Industrial Materials |
Fundamental of industrial material ; material types; properties and structure of material; advantages of material; principle of material producing and processing ; application of material; new material in industrial; material and environmental effects |
The course supports SDGs 9 by Promote inclusive and sustainable industrial development |
|
22 |
Industrial Productivity |
Definition; principles and methods of productivity in industrial; technique of productivity; productivity improvement tools; measurement of productivity; development of innovation for productivity improvement; strategy of higher working efficiency; waste eliminate techniques; quality function deployment; failure mode and effect analysis |
The course supports SDGs 8 by Develop and implement a global strategy for youth employment and implement the International Labor Organization’s Global Work Compact. |
|
23 |
Computer Application for Industry |
Analyzing of industrial data by Minitab, SPSS and Basic Artificial Intelligence principal; Applying principle calculation for quality control; production planning, forecasting, data management, statistics analysis; others programs involved in industrial management |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Professional training and an information and communication technology program |
|
24 |
Special Topics in Industrial Management Technology |
Preliminary research writing and research presentation on topics related to the interesting field or any issue in industrial management such as techniques to increase labour productivity, energy management, renewable energy, which is used as guideline in the research project providing knowledge and research skills based on research methodology to students |
The course supports SDGs 7 and 8 by Increase the share of renewable energy in the global energy mix. Achieve higher levels of economic productivity through diversification. |
|
25 |
Science for Industrial Work |
Measurement and units; scalar; vector; motion; force; law of motion; work; energy; momentum; momentum conservation; vibrations and waves; thermodynamics; fluid; electric fields; magnetic field; light; sound; application in industrial work |
The course supports SDGs 7 and 9 by Increase the share of renewable energy in the global energy mix. Promote inclusive and sustainable industrial development |
|
26 |
Industrial Organization and Management |
Industrial organization; industrial management for production planning and control; section arrangement; personal and relationship in industrial; motivating and cooperation; wage and salary management; industrial financial statement; marketing; decision making from case study |
The course supports SDGs 8 and 10 by Insurance and financial services for everyone. Empower and promote social, economic, and political inclusivity for all. |
|
27 |
Plant Layout and Design |
Systematic layout design in the industrial sector; location determination; plant layout for organization; detailed layout design; plant layout evaluation; installation and project management; using programs to design layouts |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Professional training and an information and communication technology program |
|
28 |
Safety and Occupational Health in Enterprises |
occupational health and safety management; regulation and law of occupational health and safety; International standard related to occupational health and safety; principle and technic related to occupational health and safety |
The course supports SDGs 3 by Protecting public health and, in particular, universal access to medicines. |
|
29 |
Production and Operation Management Technology |
Manufacturing and operation management in organization; planning; operating; organization constructing; location selection; product design; research and development; decision making; cost controlling; purchasing; shipping; storage; quantitative techniques for the industrial problems |
The course supports SDGs 8 and 9 by Design and implement policies that promote sustainable tourism, which will create jobs, Increasing access to information and communication technologies. |
|
30 |
Multimodal Transportation |
Technology for decision making for multimodal transport; land transport; water transportation; air transport; rail transport; Pipeline transportation; transportation network; linking and modifying transportation patterns; factors affecting the decision to choose the transportation model; calculating the cost of choosing a transportation model; choosing the right conveyor; sorting goods in each transport format |
The course supports SDGs 7 by Expand infrastructure and develop technologies for delivering modern energy services. |
|
31 |
English for Logistics 1 |
English structures in various forms of English writing in daily life; practice using English structures for communication in listening, speaking, reading, and writing skills in everyday for the benefit of a career in a specific field of study for students |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Ensure that all youth are able to read and write. |
|
32 |
Industrial Economics |
Feasibility study of the project; cash flow diagram; project comparison by present worth analysis, annual worth analysis, internal rate of return, break-even point; depreciation; sensitivity analysis; software for industrial economics analysis |
The course supports SDGs 8 and 10 by Insurance and financial services for everyone. Empower and promote social, economic, and political inclusivity for all. |
|
33 |
Laws and Regulations for Warehouse and Transportation |
Laws, regulations and regulations concerning various types of warehouses; law on the use of equipment and vehicles in cargo transportation by land, water, air and pipeline |
The course supports SDGs 11 by Efficiency of resource use |
|
34 |
Transportation System Design Technology |
Prerequisite : 4151243 Multimodal Transportation Technology for the study of physical transport patterns; transportation by land, water, air, pipeline; shipping transportation system design and transportation routes; using technology to assist in transportation planning which can track transportation, evaluate; calculate the transportation costs and transportation time |
The course supports SDGs 11 by Efficiency of resource use |
|
35 |
Logistics and Supply Chain Management |
Process that involves planning, operating and effective controlling in moving and storing of finished goods, services, and information from a place of origin to its intended destination to meet customer’s needs within Supply chain. Apply advanced knowledge, tools, and techniques for planning, implementing, and controlling various logistics activities in an organization |
The course supports SDGs 9 by Promote inclusive and sustainable industrial development |
|
36 |
English for Logistics |
English gramma structure in writing; practice using English structures for communication in listening, speaking, reading, and writing skills in daily life for career benefit in a specific field of study for students |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Ensure that all youth are able to read and write. |
|
37 |
Manufacturing and Supply Chain Management for Industrial Engineering |
Principles for operation and Industrial Engineering management; production planning and operating; production decision ; productivity concepts ; leader ship and organization constructing; energy and environmental management for industry; supply chain and logistic management concepts; relationships between supply chain for industrial management; The role and process features of supply chain and logistics ; purchasing shipping and storage management for inventory and raw material; industry management case study |
The course supports SDGs 9 by Promote inclusive and sustainable industrial development |
|
38 |
Quality Control in Industry |
Principles of industrial quality control; role of quality control in industrial; 7 QC. Tools; statistical quality control; control chart; process capability analysis; acceptance sampling technique; related computer program |
The course supports SDGs 9 by Promote inclusive and sustainable industrial development |
|
39 |
Energy and Environmental Management in Industry |
The principle of energy management for efficiency; cost of energy usage analysis; energy usage investigating; evaluating of energy information; reduction technique of energy consumption in building and factory plants; technical for energy usage in lighting , heating and air conditioning systems ; industrial motor; feasibility analysis in energy saving project; renewable energy; laws and environmental management for industrial |
The course supports SDGs 11, 13, and 7 by Paying special attention to air quality and raising awareness on climate change mitigation, Increase the share of renewable energy in the global energy mix. |
|
40 |
Industrial Engineering and Supply Chain Economics |
Cost structure; cost analysis for manufacturing and supply chain processes; break even analysis ;economic decision making process; analysis of the value of money that changes over time; net present worth; annual worth; internal rate of return; payback period; depreciation calculation; analysis under risks and uncertainties; industrial operation decisions cases; project feasibility case study; application of computer program in investment analysis in Industry |
The course supports SDGs 12 by Awareness of sustainable development and a way of life in harmony with nature. |
|
41 |
Design of Experiment |
Statistical principles used in design of experiment and analysis; hypothesis testing; analysis of mean (ANOM); analysis of variance (ANOVA); linear and non-linear regression analysis; sampling statistical; inference statistical; using statistical software packages; case study in Industrial Engineering |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Professional training and an information and communication technology program |
|
42 |
Food Product Development |
Importance of food product development; factors affecting to food product development; procedures of food product development; consumer need; consumer test; practice |
The course supports SDGs 2 by Strengthening resilience to climate change |
|
43 |
English for Food Entrepreneurs |
Principle and stratergies in reading and writing food ingredients, menu, recording, ordering food; practice |
The course supports SDGs 4 and 8 by Ensure that all young men and women are able to read and write. Entrepreneurship, creativity, and innovation |
|
44 |
Nutrition |
Importance of nutritive for health; five types of food; nutrient and sources of nutrients; digestive system; adsorption and excretion; calculation of food quality; domestic malnutrition problems; nutrition flag and food-based dietary guidelines; nutrition labeling |
The course supports SDGs 2 by Strengthening resilience to climate change |
|
45 |
Food Microbiology |
Importance of food microbiology; microorganisms in food product; microbial contamination; food spoilage microorganisms; food poisoning microorganisms; prevention of food spoilage causing microorganism; benefits of food microorganisms; microbiological analysis of foods; microbiological standard of foods |
The course supports SDGs 3 by Reduce the number of deaths and illnesses from hazardous chemicals and from pollution and contamination. |
|
46 |
English for Cookery and Food service |
English skills in reading, writing, listening and speaking for Cookery and Food service; writing and reading recipes, reimbursement-dispensing list of food ingredients, advertising documents about food and food items; listening and speaking in food service, taking orders, delivering orders, providing information and public relations about food. |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Ensure that all youth are able to read and write. |
|
47 |
Food and Service Business Operation |
Meaning and importance of food and service business; characteristics of a good food service business entrepreneurs; the beginning of building a food and service business; analysis of food and service business opportunities; planning of food and service business; organizational structure for food and service business; food and service business resource management; food business service model; accounting and investment budget management; cost calculation and profit; purchasing and managing raw materials; food quality and safety management; risk management in food service business; ethics for food and service business entrepreneurs |
The course supports SDGs 8 by Develop and implement a global strategy for youth employment and implement the International Labor Organization’s Global Work Compact. |
|
48 |
Marketing and sales for Food Business |
Meaning and importance of marketing; marketing theory; types of food service marketing; nature of marketing competition in food business; food consumption behavior and factors affecting the purchasing decision of consumers; marketing planning for food and service businesses; marketing mix of food and service businesses; food businesses marketing strategies to generate sales; creating content to promote food business; selling strategies for food and service businesses; food sales techniques by staff; food service staff training; using electronic systems to help sell food; marketing and selling online; Good Ethics in Marketing Food and Service Businesses |
The course supports SDGs 8 by Develop and implement a global strategy for youth employment and implement the International Labor Organization’s Global Work Compact. |
|
49 |
Food Preservation |
Food spoilage and prevention; Principles of food preservation; the cause of Food spoilage and protect method; using tools to preserve the food; preserving foods by drying, heating, chilling, using sugar, pickling, using chemical and etc. for consuming purposes and for cottage industry; practicing food preservation |
The course supports SDGs 2 and 12 by Adopt measures that ensure the proper functioning of food commodities and derivative markets and facilitate timely access to market information and food reserves to limit extreme food price volatility, Access to high-quality essential health services and access to medicines. |
|
50 |
Sanitation and Food Laws |
Personal hygiene; buildings equipment and facilities design; principles of cleaning; pest control; waste management; food laws and regulations; food label; good manufacturing practices (GMPs); hazard analysis and critical control points (HACCPs) |
The course supports SDGs 2 by Strengthening resilience to climate change |
|
51 |
Local Food |
Meaning and importance; local food from 4 regions; the uniqueness of popular raw materials; preserve local food; local food from 4 popular regions; practice the popular dishes of each locality |
The course supports SDGs 2 by Strengthening resilience to climate change |
|
52 |
Fast food and A la carte |
Cooking fast food, a la carte, snacks, and popular desserts using rice, starch, vegetable, fruit, meat, and meat products; food decoration, presentation for selling; practice fast food and a la carte |
The course supports SDGs 2 by Strengthening resilience to climate change |
|
53 |
Preparing for Professional Career |
Techniques for application and interview; selected establishments; application letter; resume and job interviews. Basic knowledge about labor law; quality management system; social adjustment; personality development; English language; information technology and communications; human relations; teamwork and ethics in practice |
The course supports SDGs 8 by Promote development-oriented policies that support productive activities and create decent works. |
|
54 |
Biomass Energy Technology |
Biomass; composition, biomass sources; biomass producing; type and problem of biomass using; potential of biomass which use as energy; thermal and/or catalytic conversion of biomass; biochemical conversion, biofuels; bioethanol; biodiesel; biogas; bio oil; gasification process; thermal process; direct combustion; biomass diverting to fuel gas; pyrolysis process; biomass using for gas turbine engine; property of biofuels and upgrading |
The course supports SDGs 7 by Increase the share of renewable energy in the global energy mix. |
|
55 |
Solar Energy and Its Applications |
Nature of solar radiation; measurement and interpretation of local solar radiation data; transmission through and radiation absorption by transparent media; selective surfaces; theories of flat plate collectors and focusing collectors, production of solar thermal energy; production of electricity from solar energy; principle of solar collectors and solar cells; dimensioning and economic calculation, examples of applications |
The course supports SDGs 7 by Increase the share of renewable energy in the global energy mix. |
|
56 |
Community Energy Technology |
Charcoal production technology, green fuel production technology; biodiesel production technology; ethanol production technology; biogas technology production; biomass gasification technology; thermal renewable energy technology for community cooking and drying; building construction from mud and agricultural waste; community small power producer |
The course supports SDGs 7 by Increase the share of renewable energy in the global energy mix. |
|
57 |
Smart Grid |
Information technology and communication for grid management; smart power generation control; smart transmission system; smart distribution system; renewableenergy grid connection system; small scale distributed renewable energy generation; energy storage system control; smart meter; smart home and building |
The course supports SDGs 7 by Increase the share of renewable energy in the global energy mix. |
|
58 |
English for Work 2 |
Reading job classified sections; completing job application forms; resume writing and a cover letter; reading easy manuals and descriptions of statistics; graphs and pictures |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Ensure that all youth are able to read and write. |
|
59 |
Safety Engineering |
Principles of security management to prevent accidents at work; planning and measures for safety at work; environment design and devices to prevent accidents that may occur at work; standard security management system and health various; laws at about security |
The course supports SDGs 3 by Reduce the number of deaths and injuries from accidents. |
|
60 |
Computer Programming for Engineers |
Concepts and elements of computer systems; hardware and software interface for electronic data processing; how to design and develop a program; programming; uses of software application of advanced programming; language and application of engineering program |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Professional training and an information and communication technology program |
|
61 |
Renewable Energy |
Renewable energy in various forms; wind power, geothermal energy, biomass energy, solar energy, water power, waste energy; alternative energy sources in other forms; potential of technology they came to the advantage; energy situation; energy promotion plan and the amount of energy reserves of the world and Thailand at present |
The course supports SDGs 7 by Increase the share of renewable energy in the global energy mix. |
|
62 |
Energy Conservation and Management of Building and Industry |
Introduction to energy conservation and management of building and industry; energy management plan and promote; investigation and evaluation method; measurement technic and analysis; energy equilibrium; efficiency evaluation for energy conservation; building and industry’s device management for transformer; lighting; steam system; condensation, combustion process; burner, dryer system; air conditioning and refrigeration system; air compressor system; water pump; fan and motor; waste heat recovery; co-heating system; relevant laws, rule / order and law of energy case studies |
The course supports SDGs 11 and 7 by Participatory management of human settlements,Increase the share of renewable energy in the global energy mix. |
|
63 |
Energy Economics and Environment |
Introduction to energy economics: energy demand; energy supply; energy market; discounting and capital values; global oil market a fuel of the future: natural gas; global coal market Energy derivatives: futures; options and swaps risk management, electricity and economics; uranium, nuclear energy, and an introduction to intertemporal production theory energy tax price regulation; deregulation; energy efficiency policy; renewable energy policy |
The course supports SDGs 8 by Continuously improve the efficiency of the world’s resource use in consumption and production. |
|
64 |
Energy Planning and Energy Management System |
Basic principles of planning policy; law and the energy conservation promotion act; energy cost of the organization; energy management systems; documentation energy management report; integrated power management system to the standard of energy management system |
The course supports SDGs 7 by Increase the share of renewable energy in the global energy mix. |
|
65 |
Renewable Energy for Agriculture |
Alternative energy such as solar energy; wind energy; hydro power; bio-mass energy and geothermal energy; alternative energy resources; potential and application technology for agriculture |
The course supports SDGs 7 and 6 by Increase the share of renewable energy in the global energy mix. Integrated water resources management |
|
66 |
English For Design |
General vocabularies in design; practicing listening, speaking reading and writing skill; English subject with design by studying from article, book, newspaper, journal and documentary film |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Ensure that all youth are able to read and write. |
|
67 |
Computer for Automatic Machine Control |
Principles and methods of application program in automatic machine controlling by focusing on productivity with automation machine including creation of work from CNC technology and 3D technology by computer-controlled practice to help finished product |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Professional training and an information and communication technology program |
|
68 |
Package Design for Commercial |
Principles and design of concept; designing types of packaging; studying structure of packaging by focus on component and customers; strategy for designing packaging; universal design; using computer program for designing packaging in structure and graphic; tegy limitation and difference of packaging; studying complex structures; making prototypes by cutting with hand; using technology for forming packaging; studying activities in packaging factory |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Ensure that vulnerable groups, including people with disabilities, have access to education. |
|
69 |
English For Product Design |
Specification vocabularies in industry design; vocabularies in graphic design; furniture, printed matter and packaging, interior design, handicraft, practicing in reading and translating English from article, book, newspaper, journal and movies; technique for presentation from real situation with foreigners |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Ensure that all youth are able to read and write. |
|
70 |
Internship in Industrial Design |
Pre-requisites : 4119403 Preparation for Internship in Industrial Design Practice on industrial product design agencies, state enterprises or private businesses; providing both theoretical and practical knowledge for applying with real situation; internship by providing orientation, follow-up, assessment and improvement; post-training for discussion and summary of professional experiences |
The course supports SDGs 8 by Develop and implement a global strategy for youth employment and implement the International Labor Organization’s Global Work Compact. |
|
71 |
Ethics Code and Intellectual Property Law for Product Design |
Principles and importance of club; association of institute of industrial design and institutions related to industry of product design; information on intellectual property; practicing in designing new products; designing drawings for obtaining licenses and patents; studying of ethics and moral of industrial designers |
The course supports SDGs 9 and 10 by Promote inclusive and sustainable industrial development Strengthen regulatory implementation |
|
72 |
Computer for Graphic Design |
Principles and methods of using package software for decorating images by computer; 2D image retouching techniques for presentation; industrial product design; practicing in photo retouching by using package software |
The course supports SDGs 9 and 4 by Promote inclusive and sustainable industrial development Professional training and an information and communication technology program |
|
73 |
Product Design and Development |
Patterns and concepts of industrial product design in various ways of Thailand and abroad; structure of various forms of products in terms of size, proportions, functions and functions of various organs of the human body; ergonomics and usage behavior in relation to various types of products; practicing in product design and development with appropriate forms; concepts and methods of designing industrial products according to the system international standards; practicing of sketch design, practice speed in design work for limited time and enhancing creativity |
The course supports SDGs 8 by Reduce the proportion of youth who are unemployed, uneducated, and untrained. |
|
74 |
Computer for 2D Drawing |
Prerequisite course: ET22103 Basic Product Drawing Principles and methods of using package programs for creating images with computers; techniques of creating 2D images with emphasis on drawings; computer practicing to help in designing by using package program |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Professional training and an information and communication technology program |
|
75 |
English for Product Design and Development |
Practicing English listening, speaking, reading and writing skills for daily use in industrial product design and development |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Ensure that all youth are able to read and write. |
|
76 |
Computer for 3D Drawing |
Prerequisite course: ET22202 Computer for 2D Drawing Principles and methods of using package programs for creating designs with computers by advanced 3D visualization techniques; practicing for making presentations and applied as creative works of design according to high professional fields; practicing in the classroom; creating model in analysis of prototype product |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Professional training and an information and communication technology program |
|
77 |
Computer Graphic for packaging |
Prerequisite course: ET22105 Computer for Graphic Design Principles and methods of using for graphic design software packages; technique for images making; techniques for arranging different types of compositions; practicing designing symbols; font design; trademark design; texture design; practicing printing on paper and materials; principal of photography for graphic packaging |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Professional training and an information and communication technology program |
|
78 |
Community Product Design and Development |
Patterns and concepts in design and development of community products in various ways with appropriate utility and producing in industrial systems; structure of various forms of products in terms of size, proportions, functions and human body; ergonomics and usage behavior in relation to different types of products; practicing on designing and developing community products focusing on usability, convenience and beauty related to consumer behavior; presenting sketches for designing community product design and development |
The course supports SDGs 12 by Awareness of sustainable development and a way of life in harmony with nature. |
|
79 |
Safety Engineering and Management |
Introduction to safety; safety management; accident analysis and prevention; industrialpsychology; hazard in industry; hazard analysis and risk assessment; work diseases; first aid; personalprotection equipment; safety laws; pollution control principle in industry; environmental management;corporate social responsibility |
The course supports SDGs 9 and 3 by Promote inclusive and sustainable industrial development Reduce the number of deaths and injuries from accidents. |
|
80 |
Computer Programming for Engineering |
Organization of computer systems. overview of the components and operations of hardware and software. concepts of operation system. computer languages and theirs concepts; replacing the computer data in program development. program design and development methodology; sequence, alterations, and iterations; scope of variable and subprogram, and basics of data structures |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Professional training and an information and communication technology program |
|
81 |
Electrical System Design |
Basic design concepts, codes and standards, power distribution schemes, electrical wires and cables, raceways, electrical equipment and apparatus, load calculation, power factor improvement and capacitor bank circuit design, lighting and appliances circuit design, motor circuit design, load, feeder, and main schedule, emergency power systems, short circuit calculation, grounding systems for electrical installation, electrical system designs for office buildings, residential buildings and factories, lightning protection systems, fire protection systems |
The course supports SDGs 11 by Participatory management of human settlements |
|
82 |
Power Plant and Substation |
Load curve; diesel power plant, steam power plant; gas turbine power plant, combined cycle power plant; hydro power plant, nuclear power plant, renewable energy sources, type of substation, substation equipment, substation layout, lightning protection and grounding system |
The course supports SDGs 7 by Increase the share of renewable energy in the global energy mix. |
|
83 |
Renewable Energy Technology |
Renewable energy resources and the technologies for harnessing the resources using; the use of solar, hydro, biomass, plant-oil, ethanol, wind, wave, and geothermal energies; energy efficiency and energy storage |
The course supports SDGs 7 by Increase the share of renewable energy in the global energy mix. |
|
84 |
Energy Conservation and Management |
Fundamentals of energy efficiency; principle of energy efficiency in building and industry; load management; laws and regulations of energy conservation; energy management and analysis in building and industy; technical aspects for energy usage efficiently in lighting systems, heating and ventilating and air conditioning (HVAC) systems, industrial motor; co-generation, energy conservations and management measures and economic analysis |
The course supports SDGs 11 and 9 by Efficiency of resource use,Promote inclusive and sustainable industrial development |
|
85 |
English for Engineering and Industrial Technology |
Study and integrate technical English in listening; speaking, reading and writing skills for engineering and industrial technology; English usage and technical vocabulary for industrial, number, unit of measure; shape, manual for the production process of various machines; material properties; using of tools and equipment; classification of types of materials; description of production process; signs, important symbols; report writing and presentation in bar graph; charts and tables |
The course supports SDGs 4 and 9 by Ensure that all youth are able to read and write. Promote inclusive and sustainable industrial development |
|
86 |
Safety Engineering and Risk Management |
Principles of cause and loss analysis from accidents, accident prevention in industrial work, control of hazards in the workplace, electrical machinery, boilers and pressure vessels, material transport and work environment, design of work for safety, fire prevention and suppression, safety performance assessment, risk analysis and assessment, personal protective equipment, standards and laws related to work safety, safety management. |
The course supports SDGs 9 and 3 by Promote inclusive and sustainable industrial development Reduce the number of deaths and injuries from accidents. |
Faculty of Humanities and Social Sciences

The Faculty of Humanities and Social Sciences at Bansomdejchaopraya Rajabhat University (BSRU) offers a diverse range of courses that integrate the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) into the curriculum. Covering fields such as law, public management, language, and the arts, these courses focus on promoting social equity, cultural preservation, and vocational skills development. By embedding SDG principles in areas like education, sustainable tourism, human rights, and non-discriminatory laws, the faculty equips students with the knowledge and skills necessary to contribute to a more inclusive and sustainable society. Through these courses, BSRU prepares students to become informed, responsible global citizens.
Faculty of Humanities and Social Sciences : 143 courses, which are concerned about sustainability, are offered by Bansomdejchaopraya Rajabhat University as follows.
|
N |
Course Name |
Course Description |
SDGs Embedded |
|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
English for Work |
Reading job advertisements; writing a resume; writing a cover letter; filling an application form; job interview; various situational conversations for work. |
The course supports SDGs 4byEssential skills include technical and vocational skills for employment. |
|
2 |
Law in Everyday Use |
Introduction to civil and commercial law, criminal law, and public law involved in everyday use. |
The course supports SDGs 16byPromote and enforce non-discriminatory laws and policies for sustainable development. |
|
3 |
Technology Design for Dance |
Types, forms, development, and using technological instruction medias for dance; analyses of dance contents; designing and disseminating technological instruction medias for dance; retrival of dramatic information; applying computer programs to desiging technological instruction medias for dance. |
The course supports SDGs 4byProfessional training and an information and communication technology program. |
|
4 |
Learning Management of Dance for Primary Education & Secondary Education Curriculum |
School dance curriculum analyses in Primary Education and Secondary Education Level; curriculum, teaching models, teaching methods, teaching techniques, developing and producing instuctional medias through technologies, learning measurements and evaluations, learners’ development through research; practices of learning management in stimulus and real situations. |
The course supports SDGs 4byEnsure that all boys and girls complete quality primary and secondary education. |
|
5 |
Local Dramatic Arts Education |
Significance, history, Thai dramatic arts in various regions; roles of local dramatic performance for communities; the effects of civilization and cultures on local dramtic performances; inheritage and teacging methods; analyses of dramtic arts concepts for education. |
The course supports SDGs 4byEncouraging the popularity of cultural diversity and the contribution of culture to sustainable development. |
|
6 |
Dance Criticism and retrieval of drama information for dance |
Principles and theories in criticism; practices of criticizing dramas and dances; and retrieval of drama information for dance teachers. |
The course supports SDGs 4byEssential skills include technical and vocational skills for employment. |
|
7 |
Seminar in Public Management |
Seminar in public management in compliance with transformation of globalization; cooperation between public and private sectors; role of public sector in enhancing and supporting private sector’s effective; performance focus on human resources, information resources and organizational resources. |
The course supports SDGs 4byEnsure that all learners acquire the necessary knowledge and skills, human rights, and gender equality. |
|
8 |
Reading, Thinking, and Developing Life |
Knowledge of reading and thinking; concepts and theories which encourage the reading and thinking; principles of efficient reading and thinking; practice reading and thinking which include finding the main idea, summarizing, analyzing, interpreting, evaluating in poetry, prose, fictions, non-fictions, printing media, electronic media, social media; apply the benefit of reading to everyday life. |
The course supports SDGs 4byEssential skills include technical and vocational skills for employment. |
|
9 |
Writing for Academic Communication and Occupation |
Genres in academic writing and business writing; Thai language usage in various genres; practice academic writing and business writing in various types. |
The course supports SDGs 4byEssential skills include technical and vocational skills for employment. |
|
10 |
Design and Production of Thai Language |
Selection, usage and maintenance of Thai language medium; designing, producing, trying, assessing and improving of Thai language medium; innovative development according to Thai learning subjects and Thai learning outcomes, creating and developing the textbooks according to education curriculum. |
The course supports SDGs 4byEnsure that all boys and girls complete quality primary and secondary education. |
|
11 |
Instructional of Thai Language |
Principles, concepts, theories into instructional management practice which include listening, speaking, reading, writing, grammar, literatures and literary works. |
The course supports SDGs 4byEssential skills include technical and vocational skills for employment. |
|
12 |
Basic of Feature Writing for Thai Language Teachers |
Definitions; compositions; styles and techniques of feature writing; analyze the features; practice and present the creative styles ; apply to basic education. |
The course supports SDGs 4byEssential skills include technical and vocational skills for employment. |
|
13 |
Learning Management for Thinking Skills Development through Children Literature |
Analysis of children English literature; components, genres, characteristics of children literature; poetry; prose; fairy tales, nursery rhyme; Aesop fables, picture books; application of literary digital media in learning management for developing thinking and English language skills. |
The course supports SDGs 4byProviding quality preprimary education for early childhood children. |
|
14 |
English Curriculum and Learning Management |
Principles, concepts of learning management according to basic education core curriculum; principles, approaches of learning management of English primary and secondary curricula; secondary curriculum design, planning workshop, implementation, and secondary assessment. |
The course supports SDGs 4byEnsure that all boys and girls complete quality primary and secondary education. |
|
15 |
World Cultures for English Language Teaching |
Comparative analysis of meanings and concepts between Thai and world cultures; cultural differences in world societies; intercultural communication; promoting and propagating local cultures through project work; sharing and learning professional experiences; professional networking of teachers of English regarding world transformation and cultural differences. |
The course supports SDGs 11byStrengthen efforts to protect and preserve the world’s cultural and natural heritage. |
|
16 |
English Materials and Learning Innovations Development |
Selection, design, development, implementation and evaluation of materials and learning innovations for English learning management; exploring research into the development or practical application of using materials and innovations in English language teaching; management and integration of created materials and innovations for learning and teaching in English language classrooms. |
The course supports SDGs 4byCreate and upgrade educational equipment and tools. |
|
17 |
Camp for English Language Development |
Principles and theories related to English camp management integrally; English camp activity management for learning management for secondary education. |
The course supports SDGs 4byEnsure that all boys and girls complete quality primary and secondary education. |
|
18 |
Reading and Reading Promotion |
Definition, significance, type of reading and reading promotion; reading techniques; reading behavior; problems on reading behaviors of different groups of users; psychological of reading; digital reading media and change reading context in online social network age; promotion of a reading habit; concept, principle of reading promotion techniques. |
The course supports SDGs 4byEssential skills include technical and vocational skills for employment. |
|
19 |
Information System Design |
Information system analysis theory; development of information system; problems and feasibility study of information system; requirements analysis and process model or data flow diagram; database system design; tool selection for information system development in information work; language and computer program; guideline of information system evaluation. |
The course supports SDGs 4byProfessional training and an information and communication technology program. |
|
20 |
Electronic Commerce in Information Works |
Definition, significance of electronic commerce; concept, theory of electronic commerce; forms of electronic commerce; process of electronic commerce management; ethics and law related to electronic commerce. |
The course supports SDGs 16byPromote and enforce non-discriminatory laws and policies for sustainable development. |
|
21 |
Korean Reading 1 |
Required course: HU 14104 Korean Language Skills and Culture 2 Basic Korean reading; comprehensive reading techniques, summarizing the main point of written article in daily life. |
The course supports SDGs 4byEnsure that all young men and women are able to read and write. |
|
22 |
Stage Make up |
Knowledge of the theory and practice of applying makeup for performances—including how to analyze facial structure, identify skin color and apply the right shade accordingly, designing faces for various performances, how to select tools for different purposes, learning different procedures for applying makeup, and how to apply makeup for different occasions. |
The course supports SDGs 4byEssential skills include technical and vocational skills for employment. |
|
23 |
Technology in Dance |
Understanding principles, and the significance, influence, and evolution of the creative arts in Thailand—including the connection between idea and creativity in technology, theoretically and practically, for the use of computers and technology of other kinds to be applied to dance. |
The course supports SDGs 4byProfessional training and an information and communication technology program. |
|
24 |
English Language for Dance |
Practicing English language skills—such as speaking, listening, reading, and writing while emphasizing the art of communicating—with the purpose of relaying said information for reports, presentations, projects for the dance community, or for performances when appropriate. |
The course supports SDGs 4byEnsure that all young men and women are able to read and write. |
|
25 |
English for Performing Arts |
Practice English skills that related to performing arts focuses on speaking listening reading and writing for performing arts presentations. |
The course supports SDGs 4byEnsure that all young men and women are able to read and write. |
|
26 |
Lakhon Pan Tang Performing Art |
History; principles of Lakhon Pan Tang performing art; traditions; dancing forms; various elements; identity of Lakhon Pan Tang performing art; in terms of practical skills focuses on Lakhon Pan Tang dancing and techniques. |
The course supports SDGs 4byEssential skills include technical and vocational skills for employment. |
|
27 |
Makeup and Hairdressing |
Principles of makeup; cosmetics selection; makeup equipment; theory of colors; facial structure analysis; sanitized makeup; practice various makeup looks; principles of basic hairdressing; hair products and equipment selection; hairdressing procedure; presentation of creative makeup and hairstyle by the end. |
The course supports SDGs 4byEssential skills include technical and vocational skills for employment. |
|
28 |
Jazz Dance and Modern Dance |
Principles and theories of jazz and modern dance; method; dancing forms; in terms of practical skills focuses on jazz and modern dance; proper gestures; movements; presentation and application jazz and modern dance creatively for entertainment industry including of music videos concerts and opening show products. |
The course supports SDGs 8byPromote development-oriented policies that support productive activities and create decent works. |
|
29 |
Introduction to Public Law |
Principle of public law, theories of states, limitation of state powers, separation of power, Rule of law and democracy principle. |
The course supports SDGs 16byEnsure public access to information and protection of basic freedoms. |
|
30 |
Specific Contracts 1 |
Legal principles relating to sell, exchange, gift, hire of property, hire-purchase, hire of services, hire of work and carriage stipulated in the Civil and Commercial Code, Book 3. |
The course supports SDGs 8byProtect labor rights and promote a safe and secure working environment for all workers. |
|
31 |
Criminal Law 2 |
Prerequisite : 21412105 Criminal Law 1 Offences relating to the security of the kingdom, terrorism, public administration, justice, Religion, public peace, causing public dangers, counterfeit and alteration, trade and sexuality stipulated in the Penal Code, Book 2 Specific Offences (Titles 1-9) |
The course supports SDGs 5byPromote gender equality. |
|
32 |
Constitutional Law |
Basic principles and concepts of constitutional law, structures of Political Institution, rights and liberties according to the Constitution and supremacy of the constitution doctrine. |
The course supports SDGs 10byEnsure equal opportunity and reduce inequalities in outcomes. |
|
33 |
Criminal Law 2 |
Prerequisite : 21412105 Criminal Law 1 Offences relating to the security of the kingdom, terrorism, public administration, justice, Religion, public peace, causing public dangers, counterfeit and alteration, trade, sexuality, life and body, liberty and reputation, property and corpse, stipulated in the Penal Code, Book 2 Specific Offences (Titles 1-13); a petty offence stipulated in the Penal Code, Book 3 Petty Offences. |
The course supports SDGs 10byEnsure equal opportunity and reduce inequalities in outcomes. |
|
34 |
English for Lawyers |
Definition, technical terms and idioms of English language for lawyers using as a basic for reading and researching English documents for legal profession. |
The course supports SDGs 4byEssential skills include technical and vocational skills for employment. |
|
35 |
English Legal Reading and Document Drafting |
Prerequisite : 2141253 English for Lawyers Reading documents in the legal profession, textbooks, articles from foreign countries including to provide English legal document |
The course supports SDGs 4byEnsure that all young men and women are able to read and write. |
|
36 |
International Law |
History, theory and origination of international law; relation between international and internal laws; actions effecting in term of international law, personality in international law and principles of state jurisdiction; laws pertaining to results of recognition of state and government, rights inheritance of state, state responsibilities, diplomatic and consular relations, international legal systems for various territories; principles of private international law pertaining to individual or person entering into international legal relation in all aspects; appropriation for nationality and domicile for private, determination of rights, duties, and status of person; legal contradiction and settlement procedure on nationality, conflict, foreigner and related conventions. |
The course supports SDGs 8byDevelop and implement a global strategy for youth employment and implement the International Labor Organization’s Global Work Compact. |
|
37 |
International Trade Law |
Law, principles and practice of international trade pertaining to principle agreement based transactions on international sale and purchase, transportation by sea, finance and payment, and marine insurance. |
The course supports SDGs 14bySustainable use of marine resources |
|
38 |
Intellectual Property Law |
Principles of law on copyright, patents and trademarks. |
The course supports SDGs 1 and 10byEnsure equal rights to economic resources, ensure equal opportunities, and reduce inequalities in outcomes. |
|
39 |
Intellectual Property Law |
Nature of various types of intellectual property with emphasizing on copyright, patents and trademarks, domestic copyright protection, international copyrights protection,protection of patent, trademarks and copyright under Thai law, protection of other types of intellectual property such as rights over trade name, trade secrete as well as developing countries’ policy in drafting patent law. |
The course supports SDGs 1 and 10byEnsure equal rights to economic resources, ensure equal opportunities, and reduce inequalities in outcomes. |
|
40 |
Human Rights |
Development, theory, concept and philosophy pertaining to basic rights/rules as a law and an abstract; promotion and protection of human rights. |
The course supports SDGs 4byEnsure that all learners acquire the knowledge and skills necessary to promote sustainable development, including sustainable livelihoods |
|
41 |
Labor Law |
Principles of labor law, history of Thai Labor Law, employment contract, Labor Protection Law, Labor Relations Law and other relevant laws. |
The course supports SDGs 8byProtect labor rights and promote a safe and secure working environment for all workers. |
|
42 |
Intermediate Chinese 2 |
Prerequisite : 2104201 Intermediate Chinese 1 Vocabulary, phrase, sentence, conversations; Grammatical structures that are more complex; Applying vocabulary and grammar points to make sentence; make correct Chinese conversation; Practicing listening, speaking, reading, writing; Learning more Chinese vocabulary no fewer than 400 words. |
The course supports SDGs 4byEnsure that all young men and women are able to read and write. |
|
43 |
Advanced Chinese 2 |
Prerequisite : 2104301 Advanced Chinese 1 Using vocabulary, phrase, sentence structures from, selected article; Practicing listening, speaking, reading, writing with an emphasis on analysis of application to real situation; Learning more vocabulary no fewer than 500 words. |
The course supports SDGs 4byEnsure that all young men and women are able to read and write. |
|
44 |
Chinese for Tourism |
Vocabulary; Chinese expressions in tourism; travel; Staying in a hotel; Sightseeing; use Chinese language to recommend famous tourist attractions; have a meal; buying souvenirs. |
The course supports SDGs 8byDesign and implement policies that promote sustainable tourism, which will create jobs. |
|
45 |
Intensive Class for HSK |
Techniques of test taking including listening, reading, writing, Chinese grammar; HSKK; Test practice; Sentences that are present in the test. |
The course supports SDGs 4byEnsure that all young men and women are able to read and write. |
|
46 |
Chinese Language and Culture |
Background and characteristics of Chinese language; listening, speaking, reading, and writing skills in everyday use; arts, culture, and traditions of China as one of the ASEAN and East Asian context. |
The course supports SDGs 5byEnsure that all young men and women are able to read and write. |
|
47 |
Fundamental Chinese 1 |
Chinese phonetic symbols; fundamental Chinese characters; vocabulary, phrases, sentences, and basic conversation in everyday use; fundamental Chinese grammar emphasizing listening, speaking, reading and writing skills; learning vocabulary at least 250 words. |
The course supports SDGs 4byEnsure that all young men and women are able to read and write. |
|
48 |
Fundamental Chinese 2 |
Chinese characters; vocabulary; phrases; interrogative sentences; simple sentences; compound sentences; use of conjunctions; practice of listening, speaking, reading and writing skills; learning additional vocabulary from Fundamental Chinese 1 at least 300 words. |
The course supports SDGs 4byEnsure that all young men and women are able to read and write. |
|
49 |
Chinese Reading 1 |
Reading short basic Chinese essays; practice of reading skills; reading for gist; conclusion of reading passages |
The course supports SDGs 4byEnsure that all young men and women are able to read and write. |
|
50 |
Chinese Reading 2 |
Prerequisite subject: HU 11202 Chinese Reading 1 Reading upper-level Chinese essays; practice of reading for gist, conclusion, analysis, and opinion-giving from reading passages. |
The course supports SDGs 4byEnsure that all young men and women are able to read and write. |
|
51 |
Editorial Technique |
Production process of book, magazine and print media; technical and editorial work procedures; proof reading; manuscript selection and editing; visual element composition; typography and illustration. |
The course supports SDGs 4byEssential skills include technical and vocational skills for employment. |
|
52 |
The Art of Tourism Language |
Basic knowledge of tourism; types of media in tourism; special characteristics of language related to tourism; tourism and cultural vocabularies; folk myth; art of tourism language. |
The course supports SDGs 8byDesign and implement policies that promote sustainable tourism, which will create jobs. |
|
53 |
Official Document Writing |
Regulations and correspondence; types; format; principles of official document writing; application of official document; official internal document writing; official external document writing; order writing; announcement writing; official stamped document writing; official document writing; official writing adaptation; writing letter for electronics media. |
The course supports SDGs 4byEssential skills include technical and vocational skills for employment. |
|
54 |
Master of Ceremonies and Newsreader |
Working principles for master of ceremonies; news reading methods; information preparation; script writing; tone of voice; personality; style; problem solving. |
The course supports SDGs 4byEssential skills include technical and vocational skills for employment. |
|
55 |
Analytical and Interpretative Reading |
Definition of analytical and interpretative reading; importance of analytical and interpretative reading; concepts and approaches of analytical and interpretative reading; analysis and interpretation of literary compositions and other contexts; analysis and interpretation of language usage techniques, composing techniques and other contexts. |
The course supports SDGs 4byEnsure that all young men and women are able to read and write. |
|
56 |
Story in Thonburi |
Story in Thonburi: History of Thonburi; literature in Thonburi period; characteristics, contents, languages, art of literature; concepts, values, and effects on society and politics; study approaches of story in Thonburi. |
The course supports SDGs 4byEncouraging the popularity of cultural diversity and the contribution of culture to sustainable development |
|
57 |
Art of Language Usage for Ceremonies and Newsreader |
Principles for master of ceremonies and newsreader; information preparation; information evaluation; content creation; voice usage; personality and style development; tentative problem solving; art of language usage for mass communication field; content presentation for digital communication; presentation as a role of master of ceremony; presentation as a role of newsreader; preparation and professional practice. |
The course supports SDGs 4byEssential skills include technical and vocational skills for employment. |
|
58 |
Business Thai Language |
Importance of communicational business Thai language; characteristics of business Thai language; listening, speaking, reading and writing skills in organization; fundamental knowledge about meeting; minute of meeting writing; advertisement; public relations. |
The course supports SDGs 4byEnsure that all young men and women are able to read and write. |
|
59 |
Research in Thai Language |
Study and research in Thai language, literature and folklore; data selection; data collection; data analysis; language, literature and folklore theory usage; research report writing; research article writing and presentation of research result. |
The course supports SDGs 4byEnsure that all young men and women are able to read and write. |
|
60 |
Language and Personality Development for Profession |
Importance of language and personality development; personality development appropriate for professions; personality psychology; language usage for relationship building in organization; social etiquette practice. |
The course supports SDGs 4byEssential skills include technical and vocational skills for employment. |
|
61 |
International Relations in East Asia |
Evoluation of international relationship; foreign policy, cooperation, and conflict issue in both of inside East Asia and outside the region; especially, international relationship on 21st century. |
The course supports SDGs 16byPromote the rule of law at both national and international levels. |
|
62 |
Japanese Interpretation |
Principles of basic interpretation; simulation and preparing for any problem that the interpreter may find in this career; professional interpreter techniques. |
The course supports SDGs 4byEssential skills include technical and vocational skills for employment. |
|
63 |
Korean Interpretation |
Principles of basic interpretation; simulation and preparing for any problem that the interpreter may find in this career; professional interpreter techniques. |
The course supports SDGs 4byEssential skills include technical and vocational skills for employment. |
|
64 |
Korean for Industry |
Korean for industry; vocabulary, idioms and conversations in various situations; communication and coordination with various divisions; equipment, and security standard in industrial factory. |
The course supports SDGs 9byPromote inclusive and sustainable industrial development |
|
65 |
Japanese Language and Culture |
Background and characteristics of Japanese language; listening, speaking, reading, and writing skills in everyday use; arts, culture, and traditions of Japan as one of the ASEAN and East Asian context. |
The course supports SDGs 4byEnsure that all young men and women are able to read and write. |
|
66 |
Korean Language and Culture |
Background and characteristics of Korean language; listening, speaking, reading, and writing skills in everyday use; arts, culture, and traditions of Korea as one of the ASEAN and East Asian context. |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Ensure that all young men and women are able to read and write. |
|
67 |
Korean Language Skills and Culture 1 |
Korean alphabets; pronunciation, grammar, sentence structures, developing basic skills in Korean, including listening, speaking, reading, and writing basic sentence to cope with daily matters, related culture. |
The course supports SDGs 4byEnsure that all young men and women are able to read and write. |
|
68 |
Korean Language Skills and Culture 2 |
Required course: HU 14103 Korean Language Skills and Culture 1 Korean sentence structures and grammar; developing basic vocabulary and expressions in daily life; basic skills in Korean, including listening, speaking, reading, and writing short passages about self-matters, and related culture. |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Ensure that all young men and women are able to read and write. |
|
69 |
Japanese Language Skills and Culture 1 |
Hiragana, Katakana, pronunciation, grammar, sentence structures, developing basic skills in Japanese, including listening, speaking, reading, and writing basic sentences to cope with daily matters, and related culture. |
The course supports SDGs 4byEnsure that all young men and women are able to read and write. |
|
70 |
Japanese Language Skills and Culture 2 |
Required course: HU 14119 Japanese Language Skills and Culture 1 Japanese sentence structures and grammar; developing basic vocabulary and expressions in daily life; basic skills in Japanese, including listening, speaking, reading, and writing short passages about self-matters; basic 100 Kanji, and related culture. |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Ensure that all young men and women are able to read and write. |
|
71 |
Japanese Conversation 1 |
Required course: HU 14119 Japanese Language Skills and Culture 1 Japanese conversation emphasizing on correct pronunciation, sentences, vocabulary, expressions, and basic conversations in daily life. |
The course supports SDGs 4byEnsure that all young men and women are able to read and write. |
|
72 |
Korean Language Skills and Culture 3 |
Required course: HU 14104 Korean Language Skills and Culture 3 Korean sentence structures and grammar; vocabulary, expressions, developing basic listening and, speaking skills about social and cultural issues; practicing basic reading and writing medium-length passages. |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Ensure that all young men and women are able to read and write. |
|
73 |
Japanese Reading 1 |
Required course: HU 14120 Japanese Language Skills and Culture 2 Basic Japanese reading; comprehensive reading techniques, summarizing the main point of written article in daily life. |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Ensure that all young men and women are able to read and write. |
|
74 |
Interpretative Reading |
Reading strategies with texts of complexity at advanced vocabulary levels; differentiating facts from opinions; detecting implied meaning and understanding the development of ideas in various texts; interpretation of texts, understanding writer’s attitudes and opinions. |
The course supports SDGs 4byEnsure that all young men and women are able to read and write. |
|
75 |
Seminar in English Language Usage in Thai Social Context |
Seminar and analysis on the various problems in related to English skills namely; listening, speaking, reading, writing and translation in the Thai social context; the discussion of English thematic paper or research relied on the theoretical and practical application. |
The course supports SDGs 4byEnsure that all young men and women are able to read and write. |
|
76 |
English for Communication |
English structures in various forms of English writing in everyday use; practice using English structures for communication in listening, speaking, reading, and writing skills in everyday use in the past, present, and future situations. |
The course supports SDGs 4byEnsure that all young men and women are able to read and write. |
|
77 |
English in Everyday Use |
Communication skills in everyday use; everyday vocabularies usage; listening, speaking, reading, and writing in various situations; greeting and routine conversations; hobby; travelling and hotels; shopping; food and beverage ordering; time and date telling; job applications; presentation in working places. |
The course supports SDGs 4byEnsure that all young men and women are able to read and write. |
|
78 |
English Language Use and Communication |
English language use for communication; presentation of interesting issues; expression of one’s opinions; enquiry of other’s opinions; writing experiences, events, thoughts, and ambitions; writing different types of letters. |
The course supports SDGs 4byEnsure that all young men and women are able to read and write. |
|
79 |
English for Job Application |
Reading job announcements; self-introduction; writing a resume; creating an e-portfolio; filling in job application forms; writing job application letters and emails; using job search websites and applications; making appointments and preparations for job interviews; personality development and etiquette for job interviews. |
The course supports SDGs 4byEssential skills include technical and vocational skills for employment. |
|
80 |
Introduction to English Reading and Writing |
Basic strategies for reading for levels of word, sentence, and paragraph; understanding discourse markers; development of themes; rhetorical modes; reading strategies; writing different types of sentence structures; connecting ideas; punctuations; English paragraph components and paragraph patterns; principles and strategies of paragraph writing; basic English grammar in context; using technology to search information and examine the accuracy of writing. |
The course supports SDGs 4byEnsure that all young men and women are able to read and write. |
|
81 |
Prose and Poetry |
Structures, elements, history, and development of prose; prosody, types, and techniques of poetry; reading and interpretation of selected literary works. |
The course supports SDGs 4byEnsure that all young men and women are able to read and write. |
|
82 |
English Composition 1 |
Prerequisite course: HU 12102 Introduction to English Reading and Writing Writing outlines, introductory paragraph, body paragraph, and concluding paragraph for compositions; short composition writing in general topics. |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Ensure that all young men and women are able to read and write. |
|
83 |
English and Digital Literacy in the Workplace |
English speaking and writing skills for working in the Digital Age; vocabulary and expressions used in situations related to using digital tools; digital literacy in the workplace. |
The course supports SDGs 4byEssential skills include technical and vocational skills for employment. |
|
84 |
English Composition 2 |
Prerequisite course: HU 12102 Introduction to English Reading and Writing Formats, structures, and principles of writing an argumentative essay on the selected topic regarding current trends; use of technology for research, collection, referencing, and presentation of data accompanied in the composition; publishing compositions professionally. |
The course supports SDGs 4byEnsure that all young men and women are able to read and write. |
|
85 |
English for Hospitality Industry |
Types and components of hospitality industry; English listening, speaking, reading, and writing skills for hospitality industry; English language communication in different contexts and situations concerning hospitality industry; vocabulary and expressions used in hospitality industry. |
The course supports SDGs 4byEssential skills include technical and vocational skills for employment. |
|
86 |
Labor Relations |
Background; employee relations; influential factors between employer and employee relationship; relevant labor laws and merit system. |
The course supports SDGs 8byProtect labor rights and promote a safe working environment. |
|
87 |
Statistics and Data Analysis for Public Administrators |
Statistics for research; descriptive statistic; inferential statistic; data processing by using Statistical Package for Social Science (SPSS); data interpretation; research report writing. |
The course supports SDGs 17by Supporting statistical capacity building in developing countries. |
|
88 |
Introduction to International Relations |
Background, concepts and theories on international relations; patterns of international relations from past to present ; factors affecting international relations ; policy political ideology affecting state behavior; interstate relations operations tool development of international relations ; international organizations in the 21st century. |
The course supports SDGs 16byPromote the rule of law at both national and international levels. |
|
89 |
General Economics |
Fundamental concepts in macro-economic and micro-economic; demand, supply and market equilibrium; customer behavior theory; production theory; cost, revenue and profit; market; national income; money and monetary institutions; economic problems and possible solutions. |
The course supports SDGs 10byStrengthen regulatory implementation |
|
90 |
Digital Office Management |
Concepts, administration, and office management; characteristic of office operation; planning for performance in the office, documentation, meeting management, office environment, office procurement management, model of office automation, electronic office, digital office, digital public office management and practice in public and private sectors; Digitalization of Public Administration and Service Delivery Act, B.E.2562 (2019). |
The course supports SDGs 4byEssential skills include technical and vocational skills for employment. |
|
91 |
Public Finance Administration |
Concepts, theories, and principles of public finance; government’s roles in economic; financial system and financial institutions; financial policy and state; fiscal discipline; monetary policy; government’s management of revenues and expenditures; taxation; public debt; budget system and budget process; problems and trends of public finance administration. |
The course supports SDGs 8 and 10byStrengthen domestic financial institutions, develop regulations, and monitor global financial markets and institutions. |
|
92 |
Geoinfomatics for Rural Development |
Using geospatial and computer analysis of spatial data; planning and management of natural resources and the environment; computer operation and survey. |
The course supports SDGs 11byEfficiency of resource use. |
|
93 |
English in Social Sciences for Development |
Importance of using English as a tool in searching the social science knowledge; reading skill , integration to theories or concepts, critique the textbooks or researches of social science for development in textbooks journals medias and so on. |
The course supports SDGs 4byEnsure that all young men and women are able to read and write. |
|
94 |
Community Resources Management for Tourism |
Community tourism concepts; types of natural resources and local culture; appropriated elements and community potential for tourism; accessing tourism destination and transportation, problems and effects; planning for development and participation for local sustainable development. |
The course supports SDGs 8 and 12byDesign and implement policies that promote sustainable tourism that creates jobs and promotes local culture and products. |
|
95 |
Social Environmental Impact Assessment |
Studying background of social impact assessment; process in environmental and social impact assessment; the role and the scope of environmental impact assessment; role of community participation in environmental and social impact assessment; improving communication skills to prevent and resolve environmental conflicts according to environmental and social impact assessment; ethics in environmental impact assessment. |
The course supports SDGs 11byReducing the negative environmental impact per capita in urban areas. |
|
96 |
Thai and Global Society in 21st Century |
Thai society in the global society in the dimension of history, Thai civilization, population, Thai culture as well as the movement of religion; self-sufficiency economy for the sustainable development; the royal projects of His Majesty King Bhumibol Adulyadej (King Rama IX); the local scholars; the context of ASEAN community and ASEAN nations; the contributions of Somdej Chaopraya Borommaha Srisuriyawongse(Chaung Bunnag) to Bansomdejchaopraya Rajabhat University and Thailand. |
The course supports SDGs 12byPromote local culture and products |
|
97 |
ASEAN Citizen in 21st Century |
Basic information of ASEAN member countries; cooperation of the ASEAN community; multiculturalism of society and culture; problems and crises occurring in ASEAN; raising awareness, consciousness and role of socially responsible ASEAN citizenship in the 21st century. |
The course supports SDGs 4byPromoting a culture of peace, non-violence, and global citizenship. |
|
98 |
Information Technology for Social Sciences for Development |
Principles, importance, components of information technology systems; functions and effects of IT in present development; using systematic programs and application software for documental management and presentation; including knowledge searching from database and other sources on internet networks; and IT application in various developmental activities. |
The course supports SDGs 4byProfessional training and an information and communication technology program. |
|
99 |
Economic and Social Development |
Meaning and importance of economy; economic evolution after World War II; foreign trade; multinational business; economic impact on Thai society; self-reliance in line with sufficiency economy; direction and development of the country according to government policies and the National Economic and Social Development Plan No. 13; case studies on the application of knowledge for development. |
The course supports SDGs 8byAchieve higher levels of economic productivity through diversification. |
|
100 |
Natural Resources and Environmental Management |
Meaningand typesof natural and environmental resources; new technology usage effecting to natural resources and environmental changes; natural resources and environmental management; sustainable management; emphasizing participation in problem solving; environmental problem protection in Thailand; case studies. |
The course supports SDGs 11byReducing the negative environmental impact per capita in urban areas |
|
101 |
Statistics for Social Sciences Research |
Concepts of fundamental statistics; descriptive statistics; basic analytical statistics; process and techniques applied in social sciences research; practice analyzing statistics programs. |
The course supports SDGs 17by Supporting statistical capacity building in developing countries. |
|
102 |
Human Ecology |
Ecological concepts and theories; interrelationship of humans, societies and environments in dimension of life qualities, economy, society, resources and resources management in ecosystem; strengthening the balance between ecological processes and human activities; raising an awareness and appreciation of the ecosystem. |
The course supports SDGs 8byContinuously improve the efficiency of the world’s resource use in consumption and production. |
|
103 |
Population Dynamics and Environment |
Relationship between population structure and population composition; density and distribution with environment and natural resources; trends of population changes regarding births, deaths, and migrations; effects of population changes on the use of environment and natural resources; environmental problems caused by the population changes; influences of environmental changes toward the quality of people lives. |
The course supports SDGs 11byParticipatory human settlement planning and management. |
|
104 |
Historical Tourism |
Concepts; forms; methods; values of historical tourism; surveying and planning routes; roles of tourists; planning for sustainable historical tourism. |
The course supports SDGs 8byDesign and implement policies that promote sustainable tourism, which will create jobs. |
|
105 |
Environmental Education for Development |
Meaning of the Environment Education; aim; importance of environmental education; factors that affect the environment; self- Awareness; attitudes; skills; solving environmental problems; ability to evaluate the impact of environment; participation in management of environmental problems in the community. |
The course supports SDGs 11 and 13byPaying special attention to air quality and raising awareness on climate change mitigation. |
|
106 |
Human Geography and Environment |
Geography effected to human’s environmental living; settlement; demography; density, immigration, migration; citizen problems, economic problems; economics, social, politic, governmental and cultural circumstances. |
The course supports SDGs 11byParticipatory management of human settlements. |
|
107 |
Geoinformatics for Developer |
Principles of remote sensing; Geographic information System ( GIS) and Global Positioning System ( GPS) ; tools and equipment for data collection; visual and computers-aided interpretation of data; data analysis techniques for assisting decision making and planning in development; practicum. |
The course supports SDGs 4byEssential skills include technical and vocational skills for employment. |
|
108 |
Digital Sociology |
Meaning; conceptsand digital sociology theories; research in new conceptual frameworks of the digital world; academic digitized; critical sociology of big data; diversity of digital technology usage; innovation of technological communication, digital politics; citizen digital public engagement; identity in the digital world; analysis of social institution roles in various fields; economy, politics, education, religion; trends and role modification; approaches for the sociologists in the future. |
The course supports SDGs 9byIncreasing access to information and communication technologies. |
|
109 |
Public Policy for Development in Digital Age |
Concepts and theories of public policies in digital age; policy cycle, policy design, policy analysis; policy formulation; policy implementation; policy evaluation under the blockchain technology; application public policy for management and development; criticize public polices as a national brain library. |
The course supports SDGs 9byIncreasing access to information and communication technologies. |
|
110 |
Health for Thai Society Development |
History of diseases of Thai people; Thai wisdom to treat disease; arrival of western Medicine; establishment of Thai Public Health for development; health problems in Thai society; public health service; practice of the participation in public health activities in the community. |
The course supports SDGs 3byAccess to high-quality essential health services and access to medicines. |
|
111 |
Environmental Impact Assessment |
Concepts and principles of Environment Impact Assessment (EIA); Environment Impact Assessment in Thailand; scopes and environment impact assessment methods; public participation in environmental impact assessment; determination techniques of protection and prevention to the environmental impact assessment; environmental quality monitoring; case study of environment impact assessment projects. |
The course supports SDGs 11byReducing the negative environmental impact per capita in urban areas. |
|
112 |
Introduction to Economy |
Definitions; importance; history of economics; theories of production; consumer’s behavior; market; price theories; national income; finance and banking; public finance; international trade; cooperative system; application of sufficiency economy philosophy; economic changes in Thailand; world economy; integration with the science of social studies teaching. |
The course supports SDGs 8 by Insurance and financial services for everyone. |
|
113 |
Human Geography |
Environment and population; spatial differentiation and organization of human activity; spatial interaction of human with the Earth’s biophysical systems; spatial decision making behavior; cultural features; migration; population growth; economic development; urbanization; transportation; field trip required; integration with the science of social studies teaching. |
The course supports SDGs 11by Participatory human settlement planning and management. |
|
114 |
Thonburi Studies |
Background and development of Thonburi in Thai history from Ayutthaya to Rattanakosin periods; ethnic diversity and local communities in Thonburi region; the integration of the information on Thonburi’s physical characteristics, history, society, cultural heritages, and local wisdoms; fieldworks required; publishing the findings from fieldworks through various channels; integration with the science of social studies teaching. |
The course supports SDGs 11by Strengthen efforts to protect and preserve the world’s cultural and natural heritage. |
|
115 |
English for Social Studies Teachers |
Structures, writing styles and vocabularies used in English newspapers, non – fiction writings, and academic works in the field of humanities and social sciences; reading techniques. |
The course supports SDGs 4by Ensure that all young men and women are able to read and write. |
|
116 |
Innovation and Social Studies Teaching Methodology |
Concepts of Social Studies innovation and digital media; principle of production and development on innovation and digital media in which suitable for social studies content; analysis and evaluation of Studies innovation and digital media; applying of innovation and digital media for learner’s development; social studies teaching model; teaching methods; social studies teaching skills and techniques; analysis of social studies curriculum for instructional design; writing of lesson plan; instructional media and evaluation. |
The course supports SDGs 4by Essential skills include technical and vocational skills for employment. |
|
117 |
Introduction to Political Philosophy |
Methodology, inquiry of political philosophy; political philosophical debates on ancient, modern, contemporary issues; reading and interpretation of political philosophical texts written by key philosophers in this field; concept of justice; foundation of the state and political society; basic principles of philosophical science; meaning and scope of mainstream and alternative political science; providing principles and theories as an instrument for analyzing and understanding political phenomena. |
The course supports SDGs 10by Empower and promote social, economic, and political inclusivity for all. |
|
118 |
Action Research on Social Studies |
Introduction to action research methodology and various types of social science research; the identification of research problem; literature review and related documents; variables; frameworks and hypothesis research; research design; population and sample; data collecting; verification of research tool; data analysis; statistics for research; data interpretation and presentation; report writing. |
The course supports SDGs 17by Supporting statistical capacity building in developing countries. |
|
119 |
Printmaking |
Techinques, methods of types of printings; skill of using tool to create mould and printing; planning in printing procedure; creating work of graphic print; ways for application in design work. |
The course supports SDGs 4by Essential skills include technical and vocational skills for employment. |
|
120 |
Audio-Visual Editing for Multimedia |
Meaning, significance of multimedia communication design work; skill of writing video and making video; method of ordering video; editing film and sound by using ready-made software; film sequence and sound. |
The course supports SDGs 4by Professional training and an information and communication technology program. |
|
121 |
Motion Graphic Design |
Prerequisite : 2122210 Computer for Design Meaning, significance of design of animation in data communication; principle in creating animation; fundamentals of writing script; skill in designing storyboard; making letters; pictures and elements of animated art; skill of using voice in animated graphic and preparing for stereotype work for dissemination. |
The course supports SDGs 4by Essential skills include technical and vocational skills for employment. |
|
122 |
Creative Market |
Type of business organization design; method and steps to graphic design pricing; method and steps to sell design works in online marketing; guidelines of business design from personal talent of graphic and information design. |
The course supports SDGs 4by Essential skills include technical and vocational skills for employment. |
|
123 |
English for International Design |
Prerequisite : 2122207 English for Professional Design Reading, information design translated; written design brief; art of writing short passages in contemporary media; packaging and new media design; speaking skills English with presentation design. |
The course supports SDGs 4by Ensure that all youth are able to read and write. |
|
124 |
Character Design |
Meaning, significance of character; character design process; personality analysis; expressing emotion; factors that create character identity; skill of designing postures in various dimensions that support the animation process and online media. |
The course supports SDGs 4by Essential skills include technical and vocational skills for employment. |
|
125 |
Publication Design |
Prerequisite : 2122210 Computer for Design Meaning, significance of creation process of printing design and digital media and grid system in page layout; knowledge on material for printing media; digital media system (devices) that support data presentation; ready-made software for layout of letter and pictures and art elements and color; designing and preparing for orginal for the media production by using classic printing system and dissemination by digital system. |
The course supports SDGs 4by Professional training and an information and communication technology program. |
|
126 |
Digital Arts |
Software for digital painting; the usage of the tool; the instruction set for drawing; character drawing; light color drawing; realistic color tone; perspective and landscape painting; sketch design technique or conceptual design for presenting the designing idea. |
The course supports SDGs 4by Professional training and an information and communication technology program. |
|
127 |
Advance Software for Creative Graphics |
Prerequisite course: HU 22103 Basic Software for Creative Graphics Visualization software; photo editing or digital photo manipulation; advance photo editing (Abstract Gradient); both 2 dimension and 3 dimension tool and drawing technique; the technique of making the model; User Experience; User Interface; the doing of mock-up; the skill in determining the color for the printing job and the digital work; the preparation of the file for supporting the using of the linking form in the creative graphic. |
The course supports SDGs 4by Professional training and an information and communication technology program. |
|
128 |
Publication Design and Digital Publishing |
Definitions; importance of printing and the digital publishing; the printing system and the design process and the manufacturing of the printing; the paper and printing materials; the using of the software for designing and the preparation of artwork manuscript; the skill of the organizing design; the preparation of the e-book in the contemporary platform and the digital publishing method. |
The course supports SDGs 4by Essential skills include technical and vocational skills for employment. |
|
129 |
Business Photography |
Photography equipment and the principle of the usability; the lighting; the composition; the photographing technique in other aspects and the special technique including about using of the software for decorating the picture; the image file management; the creating of the revenue from the photo. |
The course supports SDGs 4by Essential skills include technical and vocational skills for employment. |
|
130 |
Business Printmaking |
Brief about other category of graphic arts; materials; equipments and the skill in making the mold for the special case including the printing technique; the creation of the prototype for preparing the mold; the printing on other categories of materials for creating the product from the print and the career opportunity in the creative graphics. |
The course supports SDGs 4by Essential skills include technical and vocational skills for employment. |
|
131 |
Typeface and Font Design |
Structural standard; proportion and letter component; principle in determining type character; advanced drawing of letter; applied software for designing font; staging; testing of quality of type; career opportunity and market of working result of font design. |
The course supports SDGs 4by Essential skills include technical and vocational skills for employment. |
|
132 |
Tourism Attractions Management in ASEAN |
Planning, area management, environmental management, local participation, human resource management in tourism; income management; public relations for tourist attraction in ASEAN |
The course supports SDGs 8by Design and implement policies that promote sustainable tourism, which will create jobs. |
|
133 |
Bahasa Melayu for Mass Communication |
Prerequisite: Bahasa Melayu for Conversation and Communication 2 Bahasa Melayu language skills for mass communication usage; writing news for radio and television reports; reading and writing editorials, newsletters, interviews; listening to news from radio and television. |
The course supports SDGs 4by Ensure that all youth are able to read and write. |
|
134 |
Bahasa Melayu for International Relations |
Prerequisite: Bahasa Melayu for Conversation and Communication 2 Bahasa Melayu vocabularies and idioms structure commonly used in international relations aspects; practice using those vocabularies and idioms both in writing and speaking; practice reading and writing texts focusing on international relations content; reading charters, treaties, agreements and international memorandums of understanding. |
The course supports SDGs 4by Ensure that all youth are able to read and write. |
|
135 |
Lao Language for Mass Communication |
Prerequisite: Lao Language for Conversation and Communication 2 Lao language skills for mass communication usage; writing news for radio and television reports; reading and writing editorials, newsletters, interviews; listening to news from radio and television. |
The course supports SDGs 4by Essential skills include technical and vocational skills for employment. |
|
136 |
Vietnamese Language for International Relations |
Prerequisite: Vietnamese Language for Conversation and Communication 2 Vietnamese vocabularies and idioms structure commonly used in international relations aspects; practice using those vocabularies and idioms both in writing and speaking; practice reading and writing texts focusing on international relations content; reading charters, treaties, agreements and international memorandums of understanding. |
The course supports SDGs 4by Essential skills include technical and vocational skills for employment. |
|
137 |
English for International Business and Diplomacy |
Listening, speaking, reading and writing skills in English language for communication in international business negotiations and diplomacy; planning and procedure of international business negotiations and diplomacy; appropriate techniques and strategies in international business and diplomacy in different situations. |
The course supports SDGs 4by Essential skills include technical and vocational skills for employment. |
|
138 |
Operation and Management of Tourism Business in ASEAN |
Types of tourist business; international tourist operation; procedure of tour company establishment; organizational structure management; financial sources; marketing planning process and office management; operation and information technology systems; financial planning, accounting system, and taxation; principles and techniques of tourist itinerary arrangement, knowledge of ticketing, quality and standards of tourism and services; trends of tourist behaviors in global context; regulations, ethics and standardization of entrepreneurs in tourism business in ASEAN. |
The course supports SDGs 12by Sustainable development for tourism |
|
139 |
Cambodian Language and Culture |
Background and characteristics of Cambodian language; listening, speaking, reading, and writing skills in everyday use; arts, culture, and traditions of Cambodia as one of the ASEAN context. |
The course supports SDGs 4by Ensure that all youth are able to read and write. |
|
140 |
Malay Language and Culture |
Background and characteristics of Malay language; listening, speaking, reading, and writing skills in everyday use; arts, culture, and traditions of Malaysia as one of the ASEAN context. |
The course supports SDGs 4by Ensure that all youth are able to read and write. |
|
141 |
English Communication in Digital Age |
Vocabulary, expressions, and English grammar used in different situations; English listening, speaking, reading, and writing skills for communication in Digital Age; creative integration of the four skills regarding cultural diversity and context of World Englishes. |
The course supports SDGs 4by Ensure that all youth are able to read and write. |
|
142 |
New normal lifestyle |
Knowledge of life survival and adaptation to a new normal lifestyle; balancing the new normal lifestyle in Thai society in various dimensions: elderly, sexuality, consumption behavior, coexistence with nature and environmental conservation, and process of ethical development. |
The course supports SDGs 10by Empower and promote social, economic, and political inclusivity for all, regardless of age and gender. |
|
143 |
Digital Content Entrepreneur |
Digital content entrepreneurship; approach of being digital content entrepreneur; types of digital content; product analysis and strategy for presentation; creating the digital content products; proposing business development plan; financial system and distribution in the online creative market. |
The course supports SDGs 8by Make per capita economic growth sustainable in the context of the country. |
Faculty of Management Science

The Faculty of Management Science at Bansomdejchaopraya Rajabhat University is dedicated to fostering knowledge and skills aligned with the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Our diverse curriculum integrates innovative approaches in communication arts, tourism management, and marketing, preparing students to excel in their professional fields. Through courses that emphasize technical and vocational skills, ethical practices, and sustainability, we empower future leaders to contribute positively to society and the economy. Committed to enhancing educational quality, the faculty promotes lifelong learning and aims to make a significant impact on local and global communities.
Faculty of Management Science : 127 courses, which are embedded with sustainability, are offered by Bansomdejchaopraya Rajabhat University as follows.
|
N |
Course Name |
Course Description |
SDGs Embedded |
|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Computer Graphic |
Principles of basic computer graphics; advertising format analysis; basic problem solution by computer graphic tools; graphic composition; advertising design by computer program in various types of media |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Professional training and an information and communication technology program. |
|
2 |
Computer Design for Advertising |
Advertising creative; computer graphic design, illustration, typography, language, color theory, lighting and picture composition; tasks creative according to various types of tasks objectives; communicate and brand recognition; profession ethics recognition; reflecting great moral and ethical society |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Professional training and an information and communication technology program. |
|
3 |
Music for Advertising and Entertainment Business |
Basic theory of Thai music, international music; the idea of using music to advertising and entertainment business; musical performances planning; the use of media for advertising and public relations; practice instrumental music types in advertising and entertainment business |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Essential skills include technical and vocational skills for employment. |
|
4 |
Computer Graphic |
Principles of using computer graphic tools; graphic composition; analysis of design technique; computer graphic design according to purpose; propose design concepts logically |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Professional training and an information and communication technology program. |
|
5 |
Principles of Film and Video |
History, Evolution, nature and principles of film and video; techniques of storytelling and presentation; production process; positions in various film departments; ethics related to the creator and the audience; analysis and critic of the application of film and video nowadays; utilizing film production program and introduction to video |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Professional training and an information and communication technology program. |
|
6 |
English for Marketing Communication and Entertainment Business |
English communication development on listening, speaking, reading and writing skill; vocabulary and idiom in communication arts; understanding of verbal and nonverbal communication; factors affect utilization of language in culture, believes and ways of life various to geographical |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Ensure that all youth are able to read and write. |
|
7 |
Script Writing for Entertainment Business |
Knowledge for writing the basic structure; composition; technical formats for writing of stage play, television drama, film, documentary, television and radio program, advertisement and master of ceremonies script on various types of entertainment business; developing and training on script writing skill; applying of language used for script creation |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Essential skills include technical and vocational skills for employment. |
|
8 |
English for Communication Arts |
Improve skills in listening, speaking, reading, writing, studying grammar, vocabulary, idiom; practice using English in the communication arts of filmworks, television radio, advertising, public relations and new media |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Ensure that all youth are able to read and write. |
|
9 |
Principles of Photography for Communication Arts |
Basic principles in photography in terms of concept and skill; storytelling through photography; how to use camera and equipments; selecting and directing light and color in photography; selecting perspective and angle; composition; criteria in photo selection and criticism; photography etiquette |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Essential skills include technical and vocational skills for employment. |
|
10 |
Writing for Creative Digital Content |
Principle of writing for digital content communication and target audience; news writing; briefing; article writing; practice of writing skills for digital content communication to be presented on digital media with social responsibility |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Essential skills include technical and vocational skills for employment. |
|
11 |
Infographic Design |
Principle of perception and creation of digital media using graphics; summarizing information; presenting information through infographics; practicing skills in creating infographics |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Essential skills include technical and vocational skills for employment. |
|
12 |
Lifestyle Content Design |
Techniques and design processes of digital content communication; practice of skills in communicating lifestyle content design regarding food, tourism, fashion, technology and products to be presented on digital media |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Essential skills include technical and vocational skills for employment. |
|
13 |
Brand Communication |
Fundamentals of brand communication; brand communication in digital era; integrated marketing communication; brand components; branding strategy; creating a brand identity; media and approaches to communicate a brand with target audiences; laws related to brand communication |
The course supports SDGs 8 by Entrepreneurship, creativity, and innovation. |
|
14 |
Laws and Ethics for Communication Arts |
Philosophy of law; right and freedom of communication according to the constitution; communication law; ethics; code of conduct; social responsibility for communication arts |
The course supports SDGs 10 by Ensure equal opportunity and reduce inequalities in outcomes. |
|
15 |
Creative Design Workshop for Digital Content |
Fundamentals of creative design using software package; vector graphics for design; color theories; design techniques and producing works using techniques on digital platforms without copyright infringement |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Professional training and an information and communication technology program. |
|
16 |
Content Creation on Digital Platform |
Principles of content creation; content management; media production; media creation practices; presentation and evaluation of content on digital platforms |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Professional training and an information and communication technology program. |
|
17 |
Photography for Tourism and Service Business |
Principles of photography including still and motion pictures; practicing outdoor photography; creating photographs for content production; selecting and presenting photographs for tourism and hospitality business |
The course supports SDGs 8 by Design and implement policies that promote sustainable tourism, which will create jobs. |
|
18 |
Marketing Research |
Prerequisite: 3101100 Principles of Marketing and 3103200 Business Statistics Concepts, principle and significance of marketing research, determine the research problem, review the literature work, research design, identify the population, and samples, collection of data analysis interpretation of data writing the research report, and take the result from the research for decision marketing |
The course supports SDGs 17 by supporting statistical capacity building in developing countries. |
|
19 |
Internship in Marketing |
Prerequisite: 3101431 Pre-Internship in Marketing Professional experience in marketing in the organization supervised by the internship advisor; application of theory and practical marketing to work assignment in the workplace; professional experience orientation; seminar and final orientation for professional experience discussion on the problems and solution; special project or professional experience and the thematic paper |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Essential skills include technical and vocational skills for employment. |
|
20 |
Idea Generation and Creative Marketing Design |
Idea generation; design inspiration; data collection; data analysis; principles of design; typography; graphic design; photoediting; creation and design for marketing; application of computer programs to marketing design |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Professional training and an information and communication technology program. |
|
21 |
Business Statistics and Marketing Decision Analysis |
Foundations of statistics; descriptive statistics; inferential statistics; decisionmaking techniques under certainty, uncertainty, and risk; linear programming; game theory; transportation model; Markov model; queuing model; forecasting model; application of package programs to marketing decision-making |
The course supports SDGs 17 by supporting statistical capacity building in developing countries. |
|
22 |
Marketing Research |
Foundations of marketing research; marketing research process; literature review; research hypothesis formulation; research design; research tool design; sampling design; data analysis design; data collection; using package programs for statistical data processing; drawing conclusions from research findings; research report writing; qualitative marketing research |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Essential skills include technical and vocational skills for employment. |
|
23 |
Thai Cultural Heritage |
Background and importance of Thai cultural heritage, Thai history, art, literature, Buddhism, politics and society, Thai heritage; the way to conserve and pass on the cultural heritage up to the current society |
The course supports SDGs 11 by Strengthen efforts to protect and preserve the world’s cultural and natural heritage. |
|
24 |
Sustainable Tourism |
Concepts of ecotourism, background and development of sustainable tourism; styles of sustainable tourism, guidelines for sustainable tourism management focusing on operation principles of ecotourism and cultural tourism, paraticipation of local communities including awareness of sustainable tourism and field work |
The course supports SDGs 12 by Examine the impact of sustainable development on job-creating sustainable tourism. |
|
25 |
Logistics for Tourism |
Types, characteristics and importance of tourism transportation, relation between tourism logistics and transportation, elements of tourism transportation, Type of transportation that suits style of tour operation, reservation and ticketing, management and operation guidelines of tourism transportation business, transportation terminal management for tourism, safety and security standard in transportation businesses both in national and international levels |
The course supports SDGs 8 by Design and implement policies that promote sustainable tourism, which will create jobs. |
|
26 |
Research in Tourism |
Principles of research, selecting a problem in tourism for doing a research, writing a proposal, designing research methodology, objectives, hypothesis, population and sample, constructing instrument, collecting data, data analysis, compiling and presenting research results |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Essential skills include technical and vocational skills for employment. |
|
27 |
Organization of Tours |
Concepts of organization of tours, types and components of tour conducting, methods and techniques to survey routes, draw maps, make itineraries, calculate ticket prices and plan recreational activities |
The course supports SDGs 8 by Design and implement policies that promote sustainable tourism, which will create jobs. |
|
28 |
Dhonburi Studies for Tourism |
Background, historical value, art, cultures, and local wisdoms of Dhonburi, including field trip study to learn communities’ diversity having a variety of cultural differences and to take the study results to interpret for cultural tourism planning and operation |
The course supports SDGs 12 by Sustainable development for tourism creates jobs. |
|
29 |
Community – Based Tourism |
Definition of community – based tourism, analysis of the role and the importance of communities in tourism destinations, awareness development, potential development, network development, participation of communities in tourism management and development, role of government and private organizations, problems, limitations and management guidelines and case studies |
The course supports SDGs 12 by Promote local culture and products |
|
30 |
English for Hotel |
Listening, speaking, reading and writing practice and role play in the communicative situation–front office, reservation, and food and beverage departments, telephone conversation, dealing with guests’ complaints |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Ensure that all youth are able to read and write. |
|
31 |
Intership in Tourism |
Pre-requisite : 3121601 Preparation for Internship in Tourism Professional internship as temporary staff either government , public enterprise or private sector in tourism, providing orientation and supervision on concluding the details of the internship, report writing for professional development and post-evaluation by job supervisors and consulting lecturers |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Essential skills include technical and vocational skills for employment. |
|
32 |
Service Psychology and Personality Development |
Meaning and significance of service psychology; creating and developing service skills; service problem-solving techniques in services; ethics for service careers; human relations; individual’s personality development for social adjustment; individual differences and appropriate behavior training including social etiquette |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Essential skills include technical and vocational skills for employment. |
|
33 |
Tourism Geography |
Tourism geography concepts and theories; types and significance of tourism resources; tourism resource conservation; technology concerning tourism geography; relationship between geographic features and resources in tourist attractions; transport for tourism; geographical features, topography, and climate of world’s and Thailand’s tourist attractions |
The course supports SDGs 12 by Awareness of sustainable development and a way of life in harmony with nature. |
|
34 |
Human Resource Management for Tourism Industry |
Background, theories, and principles of Human Resource Management in the Fourth Industrial Revolution (Industry 4.0); responsibility framework and procedures of Human Resource Management; task analysis; manpower planning; recruitment, selection, training, development, evaluation, and factors concerning Human Resource Management in modern tourism and hospitality services; Using innovation and technology to manage human resources of modern entrepreneurs |
The course supports SDGs 12 by Developing to strengthen scientific and technological capabilities that will drive towards more sustainable production and consumption patterns. |
|
35 |
Tour Guiding and Tour Leading |
Principles of becoming tour guides and tour leaders; qualifications and characteristics; professional code of ethics; principles of speaking and tour guiding techniques; recreational activities for tourism; related laws and orders; arrival and departure formalities; work procedures for tourist guides and tour leaders; use of technology for tour leading; solving unexpected problems during tour leading; provision of first aid and security maintenance following safety and health standards for tourists; practicums on tour guiding and tour leading in actual tourist attractions |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Essential skills include technical and vocational skills for employment. |
|
36 |
Innovation-Driven Enterprises in Tourism Industry |
Innovation-Driven Enterprises in tourism industry; procedures in business setup; marketing opportunity assessment; accounting; business planning; business possibility evaluation and practicum |
The course supports SDGs 8 by Design and implement policies that promote sustainable tourism, which will create jobs. |
|
37 |
English for Business |
Listening, speaking, reading, and writing skills necessary for business correspondence; reading business articles from books and published media; English structures and vocabulary in formal business contexts; summarizing; oral presentation in business; practice of conversation with native speakers; forms of business correspondences; formats of sales letters, order letters, inquiry letters, adjustment letters, and complaint management; writing letters, emails, and response letters |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Essential skills include technical and vocational skills for employment. |
|
38 |
Japanese Reading and Writing |
Interpretative Japanese reading, read between the lines, Japanese writing sentences and short paragraphs |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Ensure that all youth are able to read and write. |
|
39 |
Laws, Ethics, and Social Responsibility for Tourism |
Concepts, definitions, and forms of professional morality, ethics, and code of conduct; Tourism Business and Guide Act; laws directly involved in tourism; rights and duties of service providers and service receivers |
The course supports SDGs 16 by Promote and enforce non-discriminatory laws and policies for sustainable development. |
|
40 |
Logistics Management for Tourism |
Principles of logistics; roles of logistics systems in tourism business; types of logistics for tourism; sea freight, air freight, and land freight; factors concerning tourist transport; tourist transport planning for tourism; laws concerning logistics for tourism; future tourism logistics development |
The course supports SDGs 11 by Providing access to sustainable, accessible, safe, and affordable transportation systems. |
|
41 |
Business Finance |
Prerequisite : 3141100 Introduction to Accounting Principles Or 3141101 Accounting Principles 1 The basic principles of financial management for business; the responsibilities of financial managers; maximization of enterprise value; financial analysis, cash flow analysis, financial planning and control, fundamental analysis on risk and return, time value of money, short-term and long-term financing, the costs of capital ,current asset management, non-current-assets investment techniques and capital budgeting |
The course supports SDGs 3 by Financial risk protection. |
|
42 |
Accounting Software Package |
Required Course: 3141102 Accounting Principles 2 3141204 Introduction to Information Systems The general structure of accounting software programs, use accounting software in the preparation of accounting documents, transaction records, and link-system account information processing |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Professional training and an information and communication technology program |
|
43 |
Internship in Accounting |
Required Course : Have earned at least 30 credits in Accouting Subject Professional experiences account in enterprises, government agencies or privatization, both the theoretical and practical knowledge gained from the study to enterprises, provide orientation and post training, discuss experiences and guidelines for troubleshooting, students are required to the project or term paper or graduate thesis under the supervision of a faculty adviser |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Essential skills include technical and vocational skills for employment. |
|
44 |
Introduction to Accounting Principles |
Introduction to double entry accounting; business transaction analysis, books of original entry, ledgers, work sheets, trial balances; adjusting and closing entries; financial statements for service businesses, trade businesses, and manufacturing businesses; disclosure of accounting information; ethic principles in accounting and code of ethics for professional accountants |
The course supports SDGs 3 by Financial risk protection |
|
45 |
Business English for Professionals |
Usages of English listening, speaking, reading, and writing concerning career and business administration for staff in an organization; business documentation, summation of main business ideas and concepts |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Ensure that all youth are able to read and write. |
|
46 |
Corporate Social Responsibility |
Definitions, significance, roles, functions, principles and ethics of organizations towards society; shared value building, good governance; stakeholders’ advantage acceptance; respecting to rule of law, internationalism and human rights; practice in handling CSR projects |
The course supports SDGs 16 by Ensure responsible decision-making processes at all decision-making levels. |
|
47 |
Business Statistics |
General knowledge of statistic; population and Samples; Characteristics of business data and their collection; Analysis business data with descriptive statistics; elementary probability theory; random variables; uniform, binomial, multinomial, hypergeometric, poisson and normal distributions; sampling distribution; analysis of variance; regression analysis and correlation analysis using application in business |
The course supports SDGs 17 by supporting statistical capacity building in developing countries. |
|
48 |
Innovation Management in Entrepreneurship |
Guidline for Business innovation management, creating an innovation in management, product innovation, innovation for differentiation and competitiveness, and management for innovation change, cover the practice for professional business growth management by formulating short run and long run business strategic plan |
The course supports SDGs 8 by Promote development-oriented policies that support productive activities, entrepreneurship, creativity, and innovation. |
|
49 |
Planning and Project Management for Entrepreneurship |
Project identification, project activities, project implementation plan, budget plan, project risk prevention plan, cost analysis, benefit, and profitability for managing project; applying management tools and mathematic in project management in order to improve efficiency, effectiveness; and project responsibility to society |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Technical and vocational skills for employment, decent work, and entrepreneurship. |
|
50 |
Business Research for Entrepreneurship |
Prerequisite : 3103200 Business Statistics The procedure of doing research, proposal writing for entrepreneur; research problem identification, research planning, research objective setting, sampling, data collection; data processing, data analysis, and research instrument selection; software for data analysis and preparing a research report |
The course supports SDGs 4 and 8 by Ensure that all young men and women are able to read and write. Entrepreneurship, creativity, and innovation. |
|
51 |
Internship in Entrepreneurship |
Prerequisite : 3103406 Preparation for Internship in Entrepreneurship Developing working experience in entrepreneurship under supervision of advisor. integrating skills knowledge, theory, and practice gaining from in class learning to real life situation, informing the concept of internship through pre-orientation and discuss the result through post-orientation and arrangement for graduate paper |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Essential skills include technical and vocational skills for employment. |
|
52 |
Entrepreneurship in Digital Age |
Concepts and theories of being entrepreneurs; Importance of digital age, which effect entrepreneur; Concept of lead life like an entrepreneur; Boost creativity and develop skills for digital age entreupreneur; Types of setting up organisation. Getting ready to start new business. Business environment, which effect entrepreneurship; Application of sufficient economy philosophy in entrepreneurship management to suit the society context; Case study from the real world successful entrepreneur to give inspiration of being ntrepreneur and take self initiative |
The course supports SDGs 1 and 4 by Ensure equal rights to economic resources, Essential skills include technical and vocational skills for employment. |
|
53 |
Startup Innovative Entrepreneurship |
Roles and the significance of startup, opportunity factors for startup, business model to solve daily life problems, concept of startup entrepreneurship orientation and capability; startup ecosystem, the startup entrepreneurship mindset, innovative thinking; design thinking, business model canvas development, startup funding, startup pitching |
The course supports SDGs 8 by Technology and innovation upgrades. |
|
54 |
Human Resource Management for Entrepreneurship |
Overview of human equity management, process of human equity management, human equity management functions, job design and job analysis, recruitment and selection, training and human resource development, performance management, compensation and fringe benefits, carreer management, employee retention strategy, labour relations, and human resource information system for entrepreneurship |
The course supports SDGs 4 and 8 by Professional training and an information and communication technology program Entrepreneurship, creativity, and innovation. |
|
55 |
Business Statistics |
Basic knowledge of business; statistics to measure the trend towards the central Probabilities and business utilization; Sampling and research methodology; hypothesis testing; analysis of variance regression; correlation analysis; and chi square test in context of business applications |
The course supports SDGs 17 by supporting statistical capacity building in developing countries. |
|
56 |
Small and Medium Enterprises Management |
Concepts and principles related to Small and Medium Enterprises; forms of business establishment; startup guidelines, creating competitive advantage, location identification, marketing management, operations, manufacturing, finance and accounting, human resources management and risk and insurance management; ethics and entrepreneur’s social responsibility |
The course supports SDGs 8 and 9 by Design and implement policies that promote sustainable tourism, which will create jobs, Increasing access to information and communication technologies. |
|
57 |
Entrepreneurship and Business Creation |
Theories about business and entrepreneurship; seeking new business discovery opportunities, analysis and evaluation of business opportunities, entrepreneurial business environment; technological advancement of the future against business competition; practice and present a business model design for building business growth and starting a new business |
The course supports SDGs 1, 8, and 4 by Implementation of plans and promotion of development-oriented policies that support productive activities, entrepreneurship, creativity and innovation, technical and vocational skills for employment, and decent work. |
|
58 |
Social Entrepreneurship |
Concepts and theories of social entrepreneurship; opportunity, strategy, social venture, social innovation, economics outcomes, social marketing, social returns, and social finance, integrating sustainability in the environment; community, ethics and social responsibility |
The course supports SDGs 1 and 8 by Ensure equal rights to economic resources, Make per capita economic growth sustainable in the context of the country. |
|
59 |
Sales Management for Entrepreneurship |
Fundamentals of sales management, convert sales management, and sales communication; Evaluating the sales team, adding a new member to the sales team; The process of hiring a sales team and their training; Sales team expectations, team development for effective sales management; Sales measurement, results evaluation, team management, time management and sales forecasting |
The course supports SDGs 8 by Make per capita economic growth sustainable in the context of the country. |
|
60 |
Radio Broadcast Production |
Required course: Script Writing for Radio Broadcasting and Television Principles and concept: production of radio broadcasting programs, documentary news, variety, music program, advertisement, radio play; practicing skill in radio broadcasting’s production process and applying such skill |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Professional training and an information and communication technology program |
|
61 |
English for Radio Broadcasting and Television |
English listening, speaking, reading and writing skills; interviewing technique; presentation of work in radio broadcasting and television profession |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Ensure that all youth are able to read and write. |
|
62 |
English for Broadcasting and Streaming Media |
English listening, speaking, reading and writing skills; interviewing technique; presentation of work in broadcasting and streaming media |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Ensure that all youth are able to read and write. |
|
63 |
Application Software in Business |
Application of operating system and business application software, word processing, spread sheet software, presentation software and publishing software ; internet usage for business |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Professional training and an information and communication technology program |
|
64 |
Data Structure and Algorithm |
Foundation of data structure, array, stack, queue, link list, tree, graph; searching algorithms; data sorting method |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Professional training and an information and communication technology program. |
|
65 |
Computer Programming |
Principles of windows-based application fundamental; components and properties, dialogue box, option buttons, check boxes, list box and menu tool bar; usage of windows help facilities; user interface form designing; decision making statement; repeating statement; subroutine and function declaration; processing statement; database connection command |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Professional training and an information and communication technology program. |
|
66 |
Multimedia Production |
Definition, components and types of multimedia; the process of multimedia design and development with multimedia hardware and software |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Technical and vocational skills for employment. |
|
67 |
Concept of Digital Business |
Development of business system; definitions and types of digital business; digital business infrastructure; the importance of digital system to business; digital business system; technology for digital business; digital business management |
The course supports SDGs 4, 8, and 9 by Professional training and an information and communication technology program Entrepreneurship, creativity, and innovation Increasing access to information and communication technologies. |
|
68 |
Graphic Design for Digital Business |
Basic elements of graphic system; Raster graphic; Vector graphic; principles and processes of graphic design; usage of package software in creating graphics for digital business |
The course supports SDGs 4 and 8 by Professional training and an information and communication technology program Promote development-oriented policies that support productive activities, entrepreneurship, creativity, and innovation. |
|
69 |
Computer Programming with Modern Language |
Computer system; computer language evolution; basic concept relating program coding; software development life cycle and methodologies; variables; operators; procedural programming; program debugging skill; usage of modern languages and tools for software development; applying programming concept in problem solving |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Professional training and an information and communication technology program |
|
70 |
Data Structures for Digital Business |
Linear data structure; non-linear data structure; sorting algorithm; searching algorithm; application of data structures and algorithms for digital business |
The course supports SDGs 4 and 8 by Professional training and an information and communication technology program Promote development-oriented policies that support productive activities, entrepreneurship, creativity, and innovation. |
|
71 |
Database Management System for Digital Business |
Basic concept of database system; database architectures; database model; relational database system; structure query language; E-R diagram and relational database design; normalization; database management language; no-SQL database; applying relational database for business database development |
The course supports SDGs 4 and 8 by Professional training and an information and communication technology program Promote development-oriented policies that support productive activities, entrepreneurship, creativity, and innovation. |
|
72 |
Business Statistics and Analysis for Digital Business |
General knowledge of statistic; data collection and presentation; basic data analysis; random variables and probability distribution of random variables; population and samples; hypothesis and Chi-Square testing; variance analysis; non-parametric statistic; regression and correlation analysis; time series; index; forecasting and decision making in digital business |
The course supports SDGs 4 and 8 by Professional training and an information and communication technology program Promote development-oriented policies that support productive activities, entrepreneurship, creativity, and innovation. |
|
73 |
Network Administration for Digital Business |
Definition of computer network; network topology; OSI model; mediums and devices for computer network; TCP/IP protocol; wireless network; computer network application in organization; information security and consistency foundation; harms and intrusions; information security tools and techniques; policy formulation in information system security; knowledge on Computer–Related Crime Act |
The course supports SDGs 4 and 8 by Professional training and an information and communication technology program Technology and innovation upgrades |
|
74 |
English for Digital Business |
Usage of computer terminology; English skill usage in IT career; composing generic English sentences for social network communication; posting and commenting in English; online English conversations; writing and replying to e-mails; usage of various data sources for communication skill development |
The course supports SDGs 4 and 8 by Promote development-oriented policies that support productive activities, entrepreneurship, creativity, and innovation. |
|
75 |
Application Development for Digital Business |
Principles of web design; computer language for web programming; functions of computer network and internet; web browser; web server; process of developing web application with packaging tools; web creating technology; web standard languages; web application development languages; graphic user interface design; web security; web application development for business; applying developing tools for business web application |
The course supports SDGs 4 and 8 by Professional training and an information and communication technology program Promote development-oriented policies that support productive activities, entrepreneurship, creativity, and innovation. |
|
76 |
Information System Analysis and Design for Digital Business |
Introduction to information; information system; system development life cycle; problem declaration; feasibility study; requirement analysis; process and database design; user interface design; system development and installation; system testing and maintenance |
The course supports SDGs 4 and 8 by Professional training and an information and communication technology program Technology and innovation upgrades |
|
77 |
Business Data Analysis and Visualization |
Basic concept of business intelligence; business intelligence project lifecycle; multidimensional analysis; business intelligence technologies; applying business intelligence in organizations; designing business intelligence architectures; managing business intelligence operations; concept of big data and computing; analytic technology; usage of visualization tool for design and presentation processes |
The course supports SDGs 9 by Increasing access to information and communication technologies. |
|
78 |
Publishing Design for Digital Business |
Concept of publishing design; printing and packaging innovation; publishing management in digital business; usage of package software in publishing design and production |
The course supports SDGs 4 and 8 by Professional training and an information and communication technology program Promote development-oriented policies that support productive activities, entrepreneurship, creativity, and innovation. |
|
79 |
Multimedia for Digital Business |
Elements of multimedia; principles of multimedia design and production; usage of appropriate hardware and software to create multimedia for digital business; presentation and dissemination of multimedia on the Internet |
The course supports SDGs 4 and 8 by Professional training and an information and communication technology program Promote development-oriented policies that support productive activities, entrepreneurship, creativity, and innovation. |
|
80 |
Seminar in Digital Business |
Principles; concepts of seminar; personnel; process; seminar documentation; seminar management for sharing experience in digital business; in-depth analysis on focusing topics or issues in digital business for applying in business administration; knowledge integration and techniques for decision making; commenting on data usage from documents, journals, research, and internet media |
The course supports SDGs 4 and 8 by Professional training and an information and communication technology program Entrepreneurship, creativity, and innovation |
|
81 |
Mobile Application Development |
Application software development on mobile device; installation and implementation; development tools; process of application development; elements and features of user interface; user interface design; data transmission and output including images, audios, and videos; various forms of notification; file and memory management |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Professional training and an information and communication technology program. |
|
82 |
User Experience Design for Digital Business |
Concepts, principles, and guidelines related to user experience design; importance of user experience design; user experience design cycle; factors affecting user experience design; current issues on user experience design; trends of user experience design in digital society; hands-on practice by using technologies for user experience design |
The course supports SDGs 4 and 8 by Professional training and an information and communication technology program Promote development-oriented policies that support productive activities, entrepreneurship, creativity, and innovation. |
|
83 |
Virtual Reality Technology for Digital Business |
Concepts; backgrounds; principles; processes; structure and elements of virtual reality technology; augmented reality; mixed reality; extended reality; creating tools for virtual reality; virtual reality analysis, design and development; virtual reality technology practicing and applying in business |
The course supports SDGs 4 and 8 by Professional training and an information and communication technology program Promote development-oriented policies that support productive activities, entrepreneurship, creativity, and innovation. |
|
84 |
Preparation for Internship in Digital Business |
Preparation for internship in cognition of characteristics and careeropportunities in workplace; self-development in knowledge skill, attitude, motivation; basic knowledge necessary for operating in workplace |
The course supports SDGs 4 and 8 by Professional training and an information and communication technology program Entrepreneurship, creativity, and innovation. |
|
85 |
Business English |
Usages of English listening, speaking, reading, and writing; vocabularies, idioms, and phrases in business communications from business documents and articles in ordinary publications and e-publications |
The course supports SDGs 4 and 8 by Ensure that all young men and women are able to read and write Technology and innovation upgrades. |
|
86 |
Business English for Professionals |
Usages of English listening, speaking, reading, and writing concerning career and business administration for staff in an organization; business documentation, summation of main business ideas and concepts |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Ensure that all youth are able to read and write. |
|
87 |
International Trade Laws |
International law; barriers and elimination of barriers in international trade law; international trade regulations; public economic law on international business law; law and contract on foreign investment; international investment protection law; international loan; international payments; letter of credit; international commercial terms; international technology transfer; dispute settlement in international business |
The course supports SDGs 9 by Promote inclusive and sustainable industrial development. |
|
88 |
International Financial Management |
Prerequisite: 3141201 Business Finance Foreign exchange market, fixed and variable exchange rate; foreign exchange control balance of payment adjustment under fixed and variable exchange rate systems; international fund, Euro-Dollar Market and Asian Dollar Market |
The course supports SDGs 8 and 10 by Insurance and financial services for everyone. Ensure equal opportunity and reduce inequalities in outcomes. |
|
89 |
Business English Communication |
Practices of English language skills including listening, speaking, reading and writing for business communication; welcoming clients; telephoning; writing business letters, memos and emails; telling business activities and company profiles; product and service presentation; modern business vocabularies and expressions |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Ensure that all youth are able to read and write. |
|
90 |
Global Trade, Policies, and Trade Regulations |
Global trade, policies, and regulations; regional economic integration and the utilization of preferential trade agreements; trade barriers and the impacts on international trade; the regulations on export procedures; customs formalities; harmonization system; INCOTERMS; obligations under sale, insurance, carriage, and letter of credit contracts |
The course supports SDGs 9 by Promote inclusive and sustainable industrial development. |
|
91 |
Global Supply Chain Management |
Principles and importance of international logistic and supply chain management; supply chain system; customer accommodation; Procurement and Production; implementation of Information Technology in supply chain; inventory management; transportation management; warehousing management; packaging and material handling management; global supply chain and logistic strategy |
The course supports SDGs 9 by Promote inclusive and sustainable industrial development. |
|
92 |
Financial Technology |
Fundamentals of financial technology to provide financial services; the history of the revolution in financial technology; innovations in financial technology in financial services; applying big data for innovations in financial technology services; the market transformation of the financial technology revolution; investment opportunity and entrepreneur of cryptocurrencies and other cryptocurrencies |
The course supports SDGs 4, 8, and 9 by Professional training and an information and communication technology program Insurance and financial services for everyone. Increasing access to information and communication technologies. |
|
93 |
English in Human Resource Management |
English academic paper reading about human resource management, resume writing, application form, job advertisements and job descriptions, minute of the meeting as well as new employee interview |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Ensure that all youth are able to read and write. |
|
94 |
Labor Laws and Social Welfare |
Basic knowledge in labor laws, the history of labor laws in Thailand and the essence of the provisions in the labor laws of Thailand relating to human resource management include Civil and Commercial Code, Labor Protection Act, Labor Relation Act, Labor Judicial and Labor Court, workers recruitment occupation of aliens, social welfare and social security, compensation, Training, safety and health, labor relations and other legislation related to the operational management of human resources. |
The course supports SDGs 10 and 8 by Strengthen regulatory implementation, Promote development-oriented policies that support productive activities and create decent works. |
|
95 |
Labor and Employee Relations |
Basic knowledge in managing labor and employee relations, difference between labor and employee relations, principle of laws related to labor and employee relations, the collective bargaining suspension conflict in organizations mediation to settle the labor dispute, closures and strikes, context and circumstances relating to employee relations, the history of the development and role of trade unions, structure of the union, strategic planning, labor and employee relations and the nature of the organizations involved in both parties; employers, employees, government and international organizations |
The course supports SDGs 10, 16, and 8 by Protect labor rights and promote a safe and secure working environment for all workers. Promote and enforce non-discriminatory laws and policies for sustainable development. Empower and promote social, economic, and political inclusivity for all. |
|
96 |
Safety and Health Management |
Concepts, principle of safety and health in workplace, safety management in workplace, workplace environment, enhancing physical and mental health, stress management, analysis and evaluation of the damage and the effects of the accidents, laws relating to occupational safety and health |
The course supports SDGs 3 by Support mental health and wellbeing. |
|
97 |
Career Preparation |
Preparation for entering the labor market, recruitment process, preparing for job application, job interview and employee selection, resume writing, job application channel, working with others in the organization, personality, human relations, positioning in the workplace, organizational culture, leadership and team, communications and conflict management in organizations |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Professional training and an information and communication technology program. |
|
98 |
Selected Topics in Human Resource Management |
Prerequisite : 3102202 Human Resource Management Selecting issues relating to human resource management topics; indepth study by reading, searching, collecting information from various sources, critical thinking and opinion sharing for human resource management; topic approved and advised by instructor, report making and presentation |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Technical and vocational skills for employment. |
|
99 |
Communication and Information Management in Organization |
Significance of communication; concepts and principles of communication in organization; theories and practices of language skills for organizational communication including thinking, listening, speaking, reading and writing to be able to apply in daily-life communication; organization communication; concepts and methods of developing, applying and publishing information in the organization including various impacts of organization information; efficient performance; case studies of success and failure of communication |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Ensure that all youth are able to read and write. |
|
100 |
Statistics and Business Research |
Concepts of quantitative analysis for business using statistical methodology to analyze data; sampling and determining sample size; scale of measurement; essential descriptive statistics; inferential statistics for hypothesis testing; advanced statistical analysis; use of package programs for statistical analysis; interpretation and report of statistical analysis for business research and Significance of business research; significance of research; code of ethics for researchers; steps of research; determining research problems; research objective setting; variables; hypothesis setting; research design; research population; random sampling; research instrument design; data collection; data processing and analysis; use of package programs for statistical analysis; writing a research report and disseminating research findings |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Encouraging the popularity of cultural diversity and the contribution of culture to sustainable development. |
|
101 |
New Media |
Technical presentations of communication art via new media; the importance of new media; technology and innovation; internet; online social networking; law related to new media and the impact of new media. |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Technical and vocational skills for employment. |
|
102 |
English for Film |
Fundamental principles of translating film equipment manuals from English to Thai; film terms; listening skills based on video clips; translation for making subtitle from English to Thai; translation for making subtitle from Thai to English; writing skills for film reviewing in English; writing skills for synopsis writing in English |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Ensure that all youth are able to read and write. |
|
103 |
Film and Community |
The principles concepts of local communities; using the film production process as a tool to convey the identity of the community; management of natural resources; environment and way of life; community-based economics; integrate learning between films and local community life through the mechanism of filmmaking; adaptation to the physical, biological, economic, social and cultural changes of the community; applying the science of filmmaking in accordance with the specific context of each community to develop into film media |
The course supports SDGs 12 by Awareness of sustainable development and a way of life in harmony with nature. |
|
104 |
English for Logistics of Supply Chain |
Communication methods and developing language 4 skills through forms, structures, vocabulary , idiom, report writing in relevant logistics and supply chain management situation and contexts; planning, purchasing & procurement, transportation, distribution, customer relationships, email correspondent |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Ensure that all youth are able to read and write. |
|
105 |
Marine Management |
Overall working scope and procedure of maritime business complied of ship types, business categorized water transportation, maritime transportation, and related agents, maritime insurance, including the personnel training; the product description, organization management, maritime business management, maritime transportation documents, and customs formality |
The course supports SDGs 11 by Reducing the negative environmental impact per capita in urban areas. |
|
106 |
Risk Management for Logistics and Supply Chain |
Principles and theories of risk management for logistics and supply chain starting from supplier, manufacturer, distributor, retailer, to end-customer; non-life insurance and responsibility; types of insurance; transportation insurance by land, marine and air; freight and cargo insurance |
The course supports SDGs 12 by Examine the impact of sustainable development on job-creating sustainable tourism. |
|
107 |
Production Planning and Control Systems |
Prerequisite : Production and Operations Management Principles of production and operation management in detail particularly in planning, controlling and producing e.g. forecast of demand and production quantity, determination of production factors, planning of order, arrangement of work order and production table; Inventory control, production capacity planning and production planning in cooperation with production system for highest effectiveness |
The course supports SDGs 12 by Awareness of sustainable development and a way of life in harmony with nature. |
|
108 |
Production and Operations Management |
Production process of goods and services; operations planning; introductory project management; technologies relating to operations; forecasting; site selection; location and process layout planning; operations system design and resources planning; inventory control; supply chain management and quality control of goods and services for higher efficiency of operations and the increase of sustainable competitive competency |
The course supports SDGs 12 by Sustainable development for tourism. |
|
109 |
International Import and Export Management |
Business operation for international trade; operating procedures for import and export; customs law; customs tariff; document of origin; customs valuation; value added tax; modes of tax refund; trade terms and conditions; tax benefits; customs formalities for import and export, preparation of paperless electronic virtual documents |
The course supports SDGs 8 by Achieve higher levels of economic productivity through diversification. |
|
110 |
Relationship Management in Supply Chain |
Meanings, concepts, process, management and tools; segmentation of customer and supplier relationship management; enhancement of customer satisfaction; customer product loyalty building; and negotiation with supplier techniques; level of relationship with supplier; supplier performance assessment strategies |
The course supports SDGs 12 by Developing to strengthen scientific and technological capabilities that will drive towards more sustainable production and consumption patterns. |
|
111 |
Material Handling and Packaging |
Importance of material handling system; tools and material handling equipment; design principles of material handling system; principles and techniques of packaging system; function and importance of packaging system in industry; characteristics of material for packing and packages; fundamental principles of packaging design for logistics |
The course supports SDGs 11 by Participatory human settlement planning and management. |
|
112 |
Economics investment in debt securities and derivatives |
Analysis of credit risk through consideration of certain key characteristics of the borrower- capacity to repay and collateral & covenant, use financial ratios to assess the capacity to repay bonds, yield volatility of government bonds, calculate the minimum value of convertible bonds, derivative instruments, (both domestic and international), as well as Forward & Futures Contract value assessment, pricing of foreign currency futures, the impact of various factors on options pricing, and evaluation of the swap with other types of financial instruments |
The course supports SDGs 9 by Promote inclusive and sustainable industrial development. |
|
113 |
Macroeconomics 1 |
Introduction to macroeconomics theory; the determination of the level of national income; consumption and saving function; investment function; government function; import and export function; monetary and fiscal policies; the public debt and international economic issues; financial institution; international trade theory; employment and unemployment; inflation and deflation; business cycle |
The course supports SDGs 8 and 10 by Insurance and financial services for everyone. Empower and promote social, economic, and political inclusivity for all. |
|
114 |
Business Economic |
Principles of microeconomics and macroeconomics for business decision making, demand, supply and market equilibrium, elasticity, analysis of consumer and producer behavior, market structure and pricing, fiscal policy, international trade and finance, employment and unemployment, interest rates, inflation, deflation, business cycle, the impact of economic changes and government intervention on business operations in the short and long term; practicing case studies for business economics |
The course supports SDGs 8 by Technology and innovation upgrades. |
|
115 |
Innovation and Economic Growth |
Concept in economic growth; economic growth theory; productivity growth; model of economic growth; economic innovation, technological innovation, digital economy, creative economy; case study of economic growth with innovation |
The course supports SDGs 8 by Develop and implement a global strategy for youth employment and implement the International Labor Organization’s Global Work Compact. |
|
116 |
English for Economics, Finance and Investment |
English communication skills, Practice language skills: listening, speaking, reading and writing in economic, finance and investment, especially in comprehension reading skill economics textbooks, articles and academic papers; include reading and news’s analysis |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Ensure that all youth are able to read and write. |
|
117 |
Innovation in Financial Economics and Financial Markets |
Financial and banking; financial risk and return analysis; activities in financial markets; apply tools and technology for analysis and decision making |
The course supports SDGs 8 and 10 by Insurance and financial services for everyone. Empower and promote social, economic, and political inclusivity for all. |
|
118 |
MICE and Events Industry |
Concepts describing MICE industry; roles of corporations in MICE industry; meetings; incentives; professional conventions; exhibitions; events; venue management; factors affecting decision making; and stakeholders in MICE industry |
The course supports SDGs 12 by Awareness of sustainable development and a way of life in harmony with nature. |
|
119 |
Thai History and Art and Culture for Tourism |
Background of Thailand from the past to present; religions, government, economy, society, culture, and international relations; history regarding historical sites and antiques; Thai art and culture; cultural diversity of ethnic groups in Thailand studied through festivals and folk recreation, paintings, sculptures, and architecture; and application of historical knowledge and art and culture to sustainable local development |
The course supports SDGs 12 by Awareness of sustainable development and a way of life in harmony with nature. |
|
120 |
Human Resource Management for Tourism Industry |
Background, theories, and principles of Human Resource Management in the Fourth Industrial Revolution (Industry 4.0); responsibility framework and procedures of Human Resource Management; task analysis; manpower planning; recruitment, selection, training, development, evaluation, and factors concerning Human Resource Management in modern tourism and hospitality services; Using innovation and technology to manage human resources of modern entrepreneurs |
The course supports SDGs 12 by Awareness of sustainable development and a way of life in harmony with nature. |
|
121 |
Tourist Behavior and Cross-Cultural Communication |
Concepts and theories describing tourist behavior; motivation; internal and external factors influencing decision-making process of tourists; behavioral segregation of different types of tourists; and cross-cultural communication |
The course supports SDGs 12 by Awareness of sustainable development and a way of life in harmony with nature. |
|
122 |
Information Technology for Tourism Industry |
Foundation of the structure of tourism information technology; tourism database system; E-commerce; Global Distribution System; reservation system; Distributor Management System in tourism industry; Customer Relationship Management System; application of tourism information technology |
The course supports SDGs 9 by Increasing access to information and communication technologies. |
|
123 |
English Reading and Writing Skills for Tourism and Hospitality Industry |
Skills of reading and filling out forms in English regarding businesses of tour leading, hotels, food and beverage, transportation, and aviation; reading and writing documents including electronic correspondences regarding tourism business and hospitality industry; reading train, bus, and flight schedule; writing an appointment; data recording; writing notices and announcements |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Ensure that all youth are able to read and write. |
|
124 |
Fundamental Japanese |
Vocabulary, grammar; fundamental Japanese reading, listening, speaking, and writing in daily life |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Ensure that all youth are able to read and write. |
|
125 |
Modern Retailing Business Management |
Definition of retail; Type of retail business; Modern retail business model; Modern retail strategy; Electronic business and electronic commerce; Consumer behavior in the retail; Market Analysis of the marketing environment; Market segmentation; Target market determination; Market positioning; Retail store design and layout; Warehouse management modern Retail Business; Planning business; Ethics business; Laws and organizations related to Retail Businesses |
The course supports SDGs 8 by Continuously improve the efficiency of the world’s resource use in consumption and production. |
|
126 |
English for Business Executives |
Developing English skills for executives on for speaking, listening, reading, and writing; summarizing and responding in meetings; business negotiations; exchange of ideas; critical writing; academic discussion; oral presentations searching for information for research; writing research report in English |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Ensure that all youth are able to read and write. |
|
127 |
Television Program Production 2 |
Planning of radio and television program production, strategies for program planning in the form of being a television program producer, training in television program production skills in complex production formats such as documentaries and television dramas, and solving problems in program production to be effective. |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Professional training and an information and communication technology program. |
Faculty of Science & Technology

The Faculty of Science & Technology at Bansomdejchaopraya Rajabhat University (BSRU) is dedicated to fostering sustainable development through its diverse range of academic programs. By integrating sustainable practices into various fields such as agriculture, aquaculture, and environmental sciences, the faculty aims to equip students with the knowledge and skills necessary to address global challenges. Many courses align directly with the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), focusing on climate resilience, sustainable resource management, economic productivity, and education. The faculty is committed to producing graduates who are prepared to drive change and promote sustainability in both local and global contexts.
Faculty of Science and Technology : 163 courses, which are embedded with sustainability, are offered by Bansomdejchaopraya Rajabhat University as follows.
|
N |
Course Name |
Course Description |
SDGs Embedded |
|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Science and Technology in Everyday Use |
Knowledge inquiry from natural world both in biological and physical fields; importance of scientific thinking process; technology in everyday use; toxic chemicals and chemical hazards; global warming and climate change; importance of balanced living |
The course supports SDGs 11 and 13 by Paying special attention to air quality and raising awareness on climate change mitigation |
|
2 |
Farm Management |
Farm situation in Thailand, types of farm, introducing principles of management and economic principles to be used in farming, consideration principles in farm management, renting, land tenure rights, farm credit, accounting, measuring the success of farming and various problems relating to farm management |
The course supports SDGs 2 by Strengthening resilience to climate change |
|
3 |
Internship in Agriculture |
Prerequisite: 4111274 Preparation for Internship in Agriculture Experience training on vocational course in agriculture, consisting of 3 field courses i.e. plant sciences, aquaculture or animal sciences including operational training relating agricultural occupation, in place of a governmental organizations or private sectors with an operation of agribusiness |
The course supports SDGs 2 by Strengthening resilience to climate change |
|
4 |
Economic Field Crops |
Field crops of economic importance in the world and Thailand, importance, planting areas, current situation in production of economic field crops, trend of production of economic field crops in the future, the production of economically important field crop species including cereals, tubers, leguminous plant, oilseed crops, fiber plants, industrial plants, energy plants and forage plants as well as advantages, problems in production and guides of problem solving Laborarory: planting and maintenance of economic field crops |
The course supports SDGs 8 by Achieve higher levels of economic productivity through diversification. |
|
5 |
The New Theory Agriculture and Royal Initiated Sufficiency Economy |
Importance, principles, operating methods in project the Royal and sufficiency economy, effects on natural resources to economic system at family levels, at community levels Laboratory: demonstration plots in agricultural new theory according to Royal Consideration by based on principles 30-30-30-10, assign students training and operating to understand in principles and relationship of plants and animals in this system |
The course supports SDGs 12 by Awareness of sustainable development and a way of life in harmony with nature. |
|
6 |
Water Quality Analysis and Water Management for Aquaculture |
Water analysis; components of water, contaminants in water, gases, minerals, nutrients and other compounds, chemical, biological and physical qualities of water for aquatic culture, improvement of water qualities suitable for aquaculture Laboratory: using equipment for analysis of water quality, collection of water samples, analyses of physical and chemical water quality, preservation and analysis of plankton samples, collection of samples and analysis of soil-surface animals |
The course supports SDGs 14 by Sustainable use of marine resources |
|
7 |
Agriculture Products Marketing |
Systems of agriculture products marketing, functions of marketing, marketing chains, marketing costs, overlapping marketing, problems and obstacles in market development relating agricultural products, governmental policies to regulate the market of agricultural products including plants, fisheries and livestock, analysis of marketing systems, management of risk in producers, processers and traders in agricultural products |
The course supports SDGs 2 by Strengthening resilience to climate change |
|
8 |
Soil and Water Management for Agriculture |
Importance of soil and water; physical; chemical; and biological properties of soil; water and plant nutrients; fertilizers and fertilizers application; maintenance practices; water and soil for growing crops; conservation of soil and water; the relationship of soil, water, and plant; principles and methods of crop irrigation; digital technology for water management; analysis of various properties of soil; moisture content of the soil; study of fertilizer samples; comparison of the properties of fertilizer by planting crop or trial; composting and the use of organic fertilizers in the field plot |
The course supports SDGs 12 by Awareness of sustainable development and a way of life in harmony with nature.. |
|
9 |
Science and Technology of Aquaculture Production |
Benefits of aquatic; species and economic importance in Thailand; principles of basic aquatic; reproduction and culture of aquatic fisheries; conservation of aquatic animals; acts on fisheries and tools for capturing aquatic fisheries; external and internal characteristics of fish and certain aquatic animal species; water quality analysis; nursing and fish cultures; production of fish feed; packing and transporting; aquatic animals taxonomy of fish; weighing and measuring for aquatic fisheries |
The course supports SDGs 14 by Sustainable use of marine resources |
|
10 |
Basic English for Agriculture |
Learning and understanding of basic vocabularyof agriculture as plant, animal, and fisheries; practice in reading and speaking skill for agricultural communication in daily life |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Technical and vocational skills for employment |
|
11 |
English for Professional Contexts in Agriculture |
Reading skill practices in agricultural technology articles, journals, documentaries, and textbooks; learning and understanding the meaning of words; skill training to interpret and summarize the content; presentation of agricultural related content |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Ensure that all youth are able to read and write. |
|
12 |
Technology for Integrated Plant Pests Management |
Importance of plant pests in the economy; types of plant pests; guidelines of plant pest control for each type; management technology of control and eradication of plant pests by agricultural methods with mechanical and physical control; use of chemicals; biological control; natural control including laws and various procedures in chemical usage; technology of drone to control plant pests; studies using a microscope to see example of plant diseases; studies on various technologies for plant pest control; studies on kinds of chemical pesticides |
The course supports SDGs 2 by Strengthening resilience to climate change |
|
13 |
Sustainable Agriculture and the New Theory Agriculture |
Sustainable agriculture situation; ecology principles of sustainable agriculture; the New Theory Agriculture according to the concept of the new theory agriculture of His Majesty King Bhumibol Adulyadej The Great; principles and operating procedures; examples and applications of King’s Science for urban agriculture; demonstration plots of the new agricultural theory according to the royal initiative based on the 30-30-30-10 principle |
The course supports SDGs 2 by Strengthening resilience to climate change |
|
14 |
Market and Modern Agricultural Business |
Systems of agriculture products marketing; functions of marketing; marketing chains; marketing costs; overlapping marketing; problems and obstacles in market development relating agricultural products; governmental policies to regulate the market of agricultural products including plants; fisheries and livestock; analysis of marketing systems; management of risk in producers, processors, and traders in agricultural products |
The course supports SDGs 2 by Strengthening resilience to climate change |
|
15 |
Mathematics Learning Management for Elementary Level |
Analyzing of mathematics curriculum for elementary level; methods, forms, techniques for learning management, designing, and practicing of learning management on numbers, algebra, measurement, geometry, statistics and probability; measurement and evaluation for learning management |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Ensure that all learners acquire the knowledge and skills necessary to promote sustainable development, including sustainable livelihoods and human rights. |
|
16 |
Mathematics Learning Management for Secondary Level |
Analyzing of mathematics curriculum for secondary level; methods, forms, techniques for learning management, designing, and practicing of learning management on numbers, algebra, measurement, geometry, statistics and probability, calculus; measurement and evaluation for learning management |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Technical and vocational skills for employment |
|
17 |
English for Mathematics Learning Management |
Reading and translating of mathematics contents or articles for learning management in basic education |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Ensure that all youth are able to read and write. |
|
18 |
Preparation for Professional Experience in Mathematics |
Basic knowledge in method and process of professional experience in mathematics; importance of professional experience in mathematics; principles of application letter writing; selection of working places; achieving of job interview; organizational culture; personality development; professional ethics; virtue and morality; labour law; social security; English for communication; report writing |
The course supports SDGs 8 by Promote development-oriented policies that support productive activities and create decent works. |
|
19 |
English for Food Entrepreneurs |
Principle and stratergies in reading and writing food ingredients, menu, recording, ordering food; practice |
The course supports SDGs 4 and 8 by Ensure that all young men and women are able to read and write. Entrepreneurship, creativity, and innovation |
|
20 |
Computer Graphic Design |
Designing art, drawing; color theory and graphic design; the principles of graphic design, composition; customizing graphics, and infographic; typographic design for communication, data Interpretation; graphics creation practice |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Technical and vocational skills for employment |
|
21 |
Reading Skills Development in English for Computer Teacher |
Enhancing students’ understanding of development reading skill for computer, academic article, sentence types, core parts, headwords and modifiers; develop their English reading skills necessary for academic texts and research papers; emphasis is placed on developing students’ skills in reading for main ideas; drawing conclusions and making inferences; using context clues to arrive at the meanings of unknown words; skimming and scanning, and developing their discourse competence; including critical reading skills |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Encouraging the popularity of cultural diversity and the contribution of culture to sustainable development |
|
22 |
Web Application Programming for Academy |
Basic concepts of web application; principles of web application functionality; web application programming structure; tools for web application programming; designing user interface; programming for server-side data processing; connecting and processing data from database; programming for academy management |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Professional training and an information and communication technology program |
|
23 |
Chemistry 1 |
Atom and periodic table; chemical bonding; stoichiometry; gases; liquids, solutions and solids; chemical thermodynamics; nuclear chemistry; environmental chemistry; petroleum and polymer |
The course supports SDGs 4 by All learners gain the knowledge and skills necessary to promote sustainable development. |
|
24 |
Statistical and Information Technology Application in Chemistry |
Statistical data collection; random sampling; statistical hypothesis testing and data analysis; applications of statistics for prediction and problem solving; experimental design; design of experiments (DOE) software and statistical analysis for chemistry; chemical structure drawing software; chemistry information resources and searching |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Increase the number of quality teachers. |
|
25 |
Chemical Enterprises |
Principles and process of enterprises in both government and private organization, paint industry, ceramics industry, food and drink industry, center laboratory, central institute of forensic science, center for scientific and technological instrument |
The course supports SDGs 11, 9, and 4 by Providing access to sustainable, accessible, safe, and affordable transportation systems, Increasing access to information and communication technologies, Technical and vocational skills for employment, decent work, and entrepreneurship |
|
26 |
Chemistry for Teachers 2 |
Pre-requisite: 4192101 Chemistry for Teachers 1 Chemical equilibrium; ionic equilibrium in aqueous solution; aqueous acid–base equilibriums; acid, base, salt, buffer; electrochemistry; introduction to organic chemistry; introduction to nuclear chemistry; environmental chemistry; related laboratory; applying chemistry knowledge for science learning management in basic education to suite with conditions and local contexts |
The course supports SDGs 4 by All learners gain the knowledge and skills necessary to promote sustainable development. |
|
27 |
Chemistry Safety |
Use of equipment in chemistry laboratory; classification of chemicals; chemical labeling and safety data sheet; chemical hazards; usage, preservation, management and storage of chemicals; management of hazardous chemical waste; methods for accident prevention and disease from chemicals; basic first aid |
The course supports SDGs 3 and 11 byStrengthen the prevention and treatment of substance misuse. Reducing the negative environmental impact per capita in urban areas |
|
28 |
Chemistry in Daily Life |
Chemicals in daily life; pollutions associated with chemicals; chemical reactions in atmosphere and water; chemistry of soil and fertilizer; chemical changes in food, medicine and medical instruments; chemistry in cosmetics |
The course supports SDGs 12, 3, and 6 by Management of all types of chemicals and waste, improving water quality by reducing pollution, and strengthening prevention and treatment of substance misuse. |
|
29 |
Learning Management in Chemistry |
Evolution of education; curriculum in the subject area of science learning according to the basic education core curriculum; chemistry learning management at the upper secondary level; curriculum analysis; writing lesson plan for chemistry; classroom control techniques; micro learning management |
The course supports SDGs 4 by All learners gain the knowledge and skills necessary to promote sustainable development. |
|
30 |
Chemistry and Community Products |
Local herbal exploration; study of important component product in daily life; production processes; herbal processing by drying; utilization of herbs in daily life product or agricultural products; production herbs by organic farming; appropriate applying local context |
The course supports SDGs 12 by Examine the impact of sustainable development on job-creating sustainable tourism. |
|
31 |
Microbiology |
General morphology of microorganism, microbial cultivation, microbial metabolism, microbial genetics, immunity against pathogen, microbial application for many cases such as aquatic microbiology, soil microbiology, food microbiology, industrial microbiology |
The course supports SDGs 9 by Promote inclusive and sustainable industrial development |
|
32 |
Environmental Microbiology |
Prerequisite: 4104201 Microbiology and 4104202 Microbiology Laboratory Relationship between microorganisms and environment; microorganisms in water, soil, and atmosphere; biogeochemical cycle occuring from microbial activity; waste water microbiology; waste water treatment by microorganisms; microbiological examination of water quality; define interesting issue for research study |
The course supports SDGs 6 by Increase water efficiency in all sectors and ensure sustainable water use and supply to address water scarcity and reduce the number of people suffering from it. |
|
33 |
English for Medical Science |
Vocabulary for medical science; basic grammar; reading and writing for academic articles; conversation for medical science; English for job applications |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Ensure that all boys and girls have access to development and care. |
|
34 |
Pharmacology and Toxicology |
Basic principle of pharmacology; pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics; pharmacological activity of drug classified to drug group; drug interaction; precaution and contraindication of drug; drug laws; basic toxicology |
The course supports SDGs 3 by Protecting public health and, in particular, universal access to medicines. |
|
35 |
Immunity and Technology in Vaccine Production |
Components of immune system in human body; immune responses against foreign antigen and pathogenic microorganisms; immunological disorder; immunological techniques; immunization by vaccine; types and technology of vaccine production |
The course supports SDGs 3 by Support drug research for communicable and non-communicable diseases. |
|
36 |
Genetic Engineering |
Prerequisite : 4105208 Genetics Basic principles and techniques of genetic engineering; construction of recombinant DNA technology; gene cloning and analysis; gene transfer techniques; PCR techniques; genetic engineering in bacteria; plants; animals; genetic engineering applications in agriculture; industry; environment and medicine |
The course supports SDGs 2 by Strengthening resilience to climate change |
|
37 |
Apiculture Technology |
Importance and advantages of honey bees; anatomy and physiology of honey bees; social and biology of honey bees; species and behaviors of honey bees; beekeeping equipments; managements of bee hives and farms; queen bee rearing; bee products; deseases and pests of honey bees |
The course supports SDGs 2 by Strengthening resilience to climate change |
|
38 |
Immunology 1 |
The mechanism and regulation of the immune system; cells and organs involved in the immune system; regulation of the immune response, immune response to infections, immunization, vaccines; the immune system associated with organ transplantation; cancer immunity; diseases caused by abnormal immune system or abnormal immune response such as hypersensitivity, autoimmunity and immune deficiency; antibody production; principles of immunology in disease prevention and treatment; and basic immunology laboratory tests |
The course supports SDGs 3 by Access to high-quality essential health services and access to medicines. |
|
39 |
Transfusion Science 2 |
Required Course : 4162343 Transfusion Science 1 Problem solving in ABO discrepancy; special tests; blood component preparation; apheresis; blood transfusion in newborn infants; hemolytic disease of the newborn; immunology of white blood cells and platelets; hematopoietic stem cells; human lymphocyte antigens (HLA) system and histocompatibility test for organ transplantation; laboratoty practice in blood bank; and advances in transfusion science |
The course supports SDGs 2 by Strengthening resilience to climate change |
|
40 |
Professional Law and Ethics |
Basic knowledge of General Law and Professional Law, the Penal Code of Thailand, Civil and Commercial Code, Labor Law, Social security Act, the National Health Act, Communicable Disease Act, Healing Arts Practices, Medical Profession Act, Practice of the Medical Technology Act, Health Facility Act, National Health Security Act, the Medical Equipment Act, Pathogens and Animal Toxins Act, and other Acts and Legal Notices related to medical technology profession |
The course supports SDGs 10 by Strengthen regulatory implementation |
|
41 |
Toxicology |
Overview of toxicology; classification of toxicants and drug abuses; routes of entry, absorption, distribution, toxicodinamics and toxicokinetics; sequestration mechanism of toxicants, elimination, and detoxification; sample collection for clinical laboratory testing; quality control and risk assessment clinical laboratory testing; quality control and risk assessment of toxicology of interest |
The course supports SDGs 3 by Support drug research for communicable and non-communicable diseases. |
|
42 |
General Microbiology |
General characteristics of microorganisms, safety in the microbiology laboratory; principles and techniques in microbiology laboratory; sterilization; staining methods; media preparation; culture methods; microbial metabolism; microbial genetics; immunity against pathogens, microbial application for many cases such as environmental microbiology, food microbiology, microbiome, industrial microbiology |
The course supports SDGs 15 by Empowering local communities |
|
43 |
Development and Design of Basic Robots |
Robot sensor system and actuator system design; robot structure design for various applications; hardware and control software design for robots; robots interactive system design; artificial intelligence for robots; robot building for specific problem solving |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Ensure that all boys and girls have access to development and care. |
|
44 |
Technology Management for Development |
Philosophy and concepts of technology management; importance and roles of technology in organizational management; technology and innovation cycle; innovation building process; technology and innovation management process: technology selection, procurement, deployment, assessment, development, and technology transfer; processes of creating innovation effectively; integration of technology and interdisciplinary innovations; principle and technique of strategic organization management in terms of technology and innovation for national competition: The exploitation and protection of intellectual property as a result of technology and innovation |
The course supports SDGs 8 by Design and implement policies that promote sustainable tourism, which will create jobs. |
|
45 |
Data Security |
Authentication meaning; authentication mechanisms; authorization; audit; radio frequency identification; application programming in authentication system with database; computer security |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Professional training and an information and communication technology program |
|
46 |
Smart System Robot Programming |
Basic introduction to robot operating system; opensource function accesion; robot operating system programming for robot movement control; robot operating system application for mapping; advanced functions application for robot movement control in boundary with user interaction |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Professional training and an information and communication technology program |
|
47 |
English for Medical Technology and Automatic Systems |
Technology of medical vocabulary, reading Technology of medical, listening to scientific and Technology of medical lecture searching, analyzing, summarizing and commenting on texts relating to Technology of medical, Presentation of medical technology formal in-formal form |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Ensure that all boys and girls have access to development and care. |
|
48 |
Multimedia Technology and Application |
Multimedia data type, digital conversion theory, data resizing, multimedia storage, tools usage, appropriate hardware and application for multimedia implementation, audio, video, images, animation, three-dimensional media, media production, relational creating, hyperlink, multimedia system design and development for services industry |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Promoting a culture of peace, non-violence, and global citizenship |
|
49 |
Web Application Programming |
World Wide Web technology; web application architecture; web development tools; software platform for website developers; web database management software; database connection software; web application development and design; web application security; graphics and multimedia for web application; interactive graphic interface for web programming; application programming interface platform |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Encouraging the popularity of cultural diversity and the contribution of culture to sustainable development |
|
50 |
Holistic Health Promotion |
Concepts and principles of health promotion; factors affecting holistic health promotion; theory and policy related to holistic health promotion; planning and operating of health promotion for individual, family and community; evaluation and problems of health promotion operations; practice in holistic health promotion in individual, family and community |
The course supports SDGs 3 by Support mental health and wellbeing. |
|
51 |
Fundamental of Electronics |
Electronic circuit and application for control devices or tools; electronic circuit to work with embedded systems, internet of things, and sensors; interfacing industrial equipment and home appliances of health equipment |
The course supports SDGs 3 by Recruitment, development, training, and retention of a health workforce |
|
52 |
Industrial Management |
Introduction to management ; science and art in industrial management; organization structure and policy; planning , control, and evaluation in industrial; quality management; psychology; resource planning; logistic management; economic in industrial; financial and budget controlling; cost; risk management |
The course supports SDGs 9 and 4 by Promote inclusive and sustainable industrial development |
|
53 |
Logistics and Supply Chain Management |
Introduction to logistics and supply chain management; role and main activity of Information System Management for logistics; inventory management concept; transportation; material handling; purchasing; delivery; the world logistics; the organization for efficiency in logistic; the operational control in logistics |
The course supports SDGs 12 by Awareness of sustainable development and a way of life in harmony with nature. |
|
54 |
Fundamental English for Industrial Technology |
Integrated of listening speaking reading and writing skill in basic level to apply in the day of life; sentence and non complex sentence writing; communicating apply in industrial work |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Ensure that all youth are able to read and write. |
|
55 |
Logistics and Distribution |
Transportation model in physical; transportation by land, air, pipeline, water transport; delivery and distribution; design of transportation system; form of distribution; agencies related to distribution; distribution channels; influencial factors of product distribution; location selection of distribution centers; the size and number of the distribution centers |
The course supports SDGs 7 by Expand infrastructure and develop technologies for delivering modern energy services. |
|
56 |
Energy and Environmental Management in Industrial |
The characteristics of environmental pollutant; hazardous waste and management; method to control and prevent the environmental pollutant; environmental technology; clean technology; law and regulation in environmental; energy using and energy saving in industrial plant; energy using in building; electricity using management in building; load of air condition calculation; methods to reduce energy used in building; energy economics in building; measuring the energy using in electric machine; heat transfer between inside and outside; efficiency ratio of air condition system |
The course supports SDGs 7 by Increase the share of renewable energy in the global energy mix. |
|
57 |
Industrial Management Strategy |
Principle of strategy management; strategy in industrial management; strategy to practical practice; decision on management; leader ship; culture and ethics of engineer works manager |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Encouraging the popularity of cultural diversity and the contribution of culture to sustainable development |
|
58 |
Technology for Sustainable Development |
Definitions and importance of technology; types of technology; development process of technology; appropriate technology; use of technology to solve problems caused by increased population; using technology wisely to develop a society; technological process for sustainable development |
The course supports SDGs 8 by Develop and implement a global strategy for youth employment and implement the International Labor Organization’s Global Work Compact. |
|
59 |
Laws and Professional Ethics of Thai Traditional Medicine |
Fundamental knowledge in law; moral and ethical standards; professional legislation; drug legislation; nursing home legislation; protection and promotion of Thai traditional medicine wisdom legislation; other law and regulation related to Thai traditional medicine |
The course supports SDGs 10 by Strengthen regulatory implementation |
|
60 |
English for Thai Traditional Medicine Clinical Approach II |
Listening; reading; speaking and writing skills in English in health sciences; ; writing a summary data analysis; Writing objectives of research; abstract; academic articles and reference |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Ensure that all youth are able to read and write. |
|
61 |
Practice in English for Thai Traditional Medicine Clinical Approach II |
Practice listening; reading; speaking and writing skills in English in health sciences; ; writing a summary data analysis; Writing objectives of research; abstract; academic articles and reference |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Ensure that all youth are able to read and write. |
|
62 |
Thai Midwifery I |
Concept and principle of Thai midwifery; function and role; ethics and law related to Thai midwifery; fertilization and pregnancy; anatomy and physiology of pregnancy; parturition mechanism; practice for assisting in parturition; health promotion for normal pregnant woman and fetus in antepartum and intrapartum as well as for maternal and infant in postpartum; abnormalities of childbirth; obstetric complications; patient referral guidelines |
The course supports SDGs 3 by Reduce the global maternal mortality rate to less than 70 per 100,000 live births. |
|
63 |
Practice in Thai Midwifery I |
Practice midwifery in maternal nursing for normal pregnancy throughout delivery and postpartum; health promotion for normal pregnant woman and fetus in antepartum and intrapartum as well as for maternal and infant; breastfeeding promotion; bonding and attachment of maternal; child and family; counseling of parent roles and childrearing within the realm of law |
The course supports SDGs 3 by Reduce the global maternal mortality rate to less than 70 per 100,000 live births. |
|
64 |
Palliative care |
Applied Thai Traditional Medicine with multidisciplinary; holistic patient care; community medicine; elderly medicine; chronic non-infectious disease caring; rehabilitation plan; health promotion; based on the situation of the community |
The course supports SDGs 3 by Protecting public health and, in particular, universal access to medicines. |
|
65 |
Medicine for Thai Traditional Medicine |
Common diseases and syndromes; Clinical Problems Solving by integrating medical knowledge; Holistic health care; Working with healthcare professionals; Communicating with patients and relatives |
The course supports SDGs 3 by Providing comprehensive reproductive health education |
|
66 |
Internship in Thai Midwifery |
Prerequisite course : Applying the knowledge and skill gained from Thai midwifery subject to real life situations for holistic health care of pregnant women and infant in antepartum, intrapartum, as well as postpartum period according to the principal of Thai traditional medicine which regarding to moral, ethical and professional law of Thai midwifery; development of communication skill and relationship with patients and health care teams |
The course supports SDGs 3 by Reduce the global maternal mortality rate to less than 70 per 100,000 live births. |
|
67 |
Integrated experiences in Traditional Thai Medicine |
Applying the knowledge and skills gained from the studies to clinical practice in Thai traditional medicine by integrating the knowledge of Thai medicine, Thai pharmaceuticals, Thai massage and Thai midwifery to real patients, which under supervision of authorized practitioners; giving diagnosis, treatment, and suggestion for health care; integrating of treatment with allied health sciences professions in health care units |
The course supports SDGs 3 by Reduce the global maternal mortality rate to less than 70 per 100,000 live births. |
|
68 |
Internship in Thai Pharmacy |
Prerequisite course : 4161218 Thai Pharmacy III Internship in Good Agriculture Practices (GAP) ; herbal drug manufactories, herbal drug prescription as well as giving instruction for herbal drug use |
The course supports SDGs 3 by Protecting public health and, in particular, universal access to medicines. |
|
69 |
Sociology and Anthropology for Thai Traditional Medicine |
Foundation of sociology and anthropology, the difference and relationship between sociology and anthropology, application of sociology and anthropology for Thai traditional medicine; beliefs, mind and soul concerning health, illness, health care and health services based on theories of Thai traditional medicine; wisdom inheritance of Thai folk medicine |
The course supports SDGs 3 by Support mental health and wellbeing. |
|
70 |
Earth Science and Space |
Basic main component of earth sciences; lithosphere, hydrosphere, biosphere, atmosphere, weather and astronomical influences that affect the well-being of life, world exploration technology and weather forecasting; various phenomena; natural disasters affect organism and environment at the local, regional and global levels; related laboratory |
The course supports SDGs 13 by Developing education, awareness, and human capacity to mitigate climate change. |
|
71 |
Physics Teaching Methodology |
Analysis physics curriculum and textbooks; various methods, models and techniques in teaching physics; design and learning management of student-centered learning; technological pedagogical content knowledge (TPACK); physics learning plans and physics learning practice in high school level; evaluation and assessment |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Ensure that vulnerable groups, including people with disabilities, have access to education. |
|
72 |
Digital Commerce |
Concepts, format and fundamentals of digital commerce; approach to digital commerce; online marketing; online payment; internet marketing planning; customer ensuring; code of conduct for doing business on the Internet; ethics in electronic business; data protection and privacy; practices in package software |
The course supports SDGs 4 and 8 by Professional training and an information and communication technology program Entrepreneurship, creativity, and innovation |
|
73 |
Computer Entrepreneur |
Introduction to business operation; definition, significance and orientation of entrepreneurial; concept and format of computer entrepreneur; theories and practices of small medium and large enterprises business management; characteristics of business Thailand; ethics and codes of computer entrepreneur |
The course supports SDGs 4 and 8 by Professional training and an information and communication technology program Entrepreneurship, creativity, and innovation |
|
74 |
English for Computer Science |
English for improving listening, speaking, reading, writing, and presentation skills to prepare for producing academic articles in computer science topics and practicing reading and listening skills in topics of computer technology |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Ensure that all youth are able to read and write. |
|
75 |
Web Engineering and Web Application Development |
The fundamentals of web engineering; principles of web application functionality; web application development architecture; management and maintenance web applications; tools for web engineering; web application development; designing user interface; programming for server-side data processing; connecting and processing data from database |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Professional training and an information and communication technology program |
|
76 |
Digital Technology for Beauty and Wellness Business |
The roles and importance of digital technology for beauty and wellness business; combination of new technology; applying software package for computer and mobile devices in the development; care, services, information and online communications of wellness and beauty |
The course supports SDGs 3 and 4 by Access to high-quality essential health services and access to medicines. Create and upgrade educational equipment and tools that are sensitive to children and people with disabilities. |
|
77 |
English for Beauty and Wellness Business |
Communication, greeting, farewell, thanks, and apology; Give beauty and wellness business information; English conversation in various situation of beauty and wellness business; technical terms and terminology; reading and writing skills in papers, messages, and beauty and wellness business manuals |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Ensure that all youth are able to read and write. |
|
78 |
Introduction to Law and Ethics for Beauty and Wellness Business |
The general principles of law, ethics, and penalties for beauty and wellness business; laws relating heath business, and consumer protection; morality for services in health business, problems, and solutions; moral behaviors in Thai social value |
The course supports SDGs 10 by Ensure equal opportunity and reduce inequalities in outcomes. |
|
79 |
Health and Beauty |
Health services in the primary care system that support health care; concepts and principles of health and beauty in various ways; necessities and needs in health care according to age; physically and mentally by using lots of ways; healthy behaviors, consumption, relaxation, working out, and exercise the body; keeping the precept, praying, yoga, diet, physical estimation, taking care of beauty; using health and beauty products |
The course supports SDGs 2 by Strengthening resilience to climate change |
|
80 |
Nutrition and Anti-Aging |
Definitions and importance of nutrition; the relation between nutrition and health; nutritional problem situation; nutrition for different stages of human; nutritional status assessment; dietary guidelines, and health promotion by therapeutic nutrition for health; supplement for health and anti-aging; current situation on health and anti-aging business |
The course supports SDGs 2 by Strengthening resilience to climate change |
|
81 |
Measurement and Evaluation for Health |
The importance, methods, measurement, and assessment of health conditions; growth measurement; health deterioration; nutritional measurement; medical examination; tool utilization and health status assessment |
The course supports SDGs 3 by Providing comprehensive reproductive health education |
|
82 |
Marketing and Strategic Management in Beauty and Wellness Business |
Marketing principles, marketing planning, market segmentation, target market, product strategy and positioning of products; services, prices, distribution channels and supply chains; integrated marketing communications, marketing operations and control; customer relationship development; marketing ethics and social responsibility |
The course supports SDGs 9 and 12 by Increasing access to information and communication technologies. Developing to strengthen scientific and technological capabilities that will drive towards more sustainable production and consumption patterns. |
|
83 |
Physical Therapy |
Human anatomy and physiology changes; common diseases cause by physical changes and social mental problems; physical examination and therapy for slowing down degeneration and prophylactic of common diseases; gesture adjustment and preventing accident probably; changing environment for better quality of life |
The course supports SDGs 3 by Providing comprehensive reproductive health education Reduce the number of deaths and injuries from accidents. |
|
84 |
Entrepreneurship in Beauty and Wellness Business |
Principles of organization and business risk management; entrepreneurship in beauty and wellness businesses; market demand analysis; business plan; break-even analysis; basic accounting; accounting system necessary for business; regulations related to beauty and wellness businesses |
The course supports SDGs 8 by Protect labor rights and promote a safe and secure working environment for all workers. |
|
85 |
Nutraceutical and Beauty |
Definition and meanings of nutraceutical and functional food; law and product control; classification of nutraceutical and functional food for weight loss and healthy skin in the markets; nutritional and chemical elements in products; research of nutraceutical and functional food; the safety use of products on health |
The course supports SDGs 2 and 3 by Strengthening resilience to climate change, Support drug research for communicable and non-communicable diseases. |
|
86 |
English for Food Science and Technology 1 |
Reading skill practices in Food Science and Technology articles, journals, documentaries, and textbooks, learning and understanding the meaning of words, skill training to interpret and summarize the content |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Ensure that all youth are able to read and write. |
|
87 |
Principles of Food Analysis |
Pre-requisite : 4102241 Analytical Chemistry Principles and analytical methods in both qualitative and quantitative of food compositions; technique selection for analysis, proximate analysis, determination of water quality for use in food production, laboratory associated with analysis of food composition |
The course supports SDGs 2 and 12 by Adopt measures that ensure the proper functioning of food commodities and derivative markets and facilitate timely access to market information and food reserves to limit extreme food price volatility, Access to high-quality essential health services and access to medicines. |
|
88 |
Food Processing 2 |
Pre-requisite : 4115232 Food Processing 1 Application of technologies for food processing, extrusion, ohmic heating, high pressure, microwave heating, Infrared heating, minimally processed foods; effects of applications on food quality, waste management from food processing and utilizations of by-products |
The course supports SDGs 2 by Strengthening resilience to climate change |
|
89 |
Food Standards and Regulations |
Food standards and regulations for food industry, food national and international standards, law of food ingredients, food and nutritional labels, and environments; specification for international food trading and organizations relating to food standards and regulations; registration of food industries |
The course supports SDGs 9 and 2 by Promote inclusive and sustainable industrial development |
|
90 |
Principle of Food Plant Sanitation and Food Safety |
Pre-requisite : 4115321 Food Microbiology 4115322 Food Microbiology Laboratory Plant layout, designs and equipment establishments by following sanitation standards; good manufacturing practice, storages and transportation of food raw materials and products; food package and packaging hygiene, food personal hygiene, pest control, water quality control, use of microorganism as indicators for plant sanitation, principles of cleaning, chemical reagent, disinfection, waste and waste water treatment for saving the environments and related food quality assurance systems; laboratory associated with analysis of microorganisms on food contact surfaces and food handlers, analysis of index microorganisms in water, analysis of microorganisms in air environment and antimicrobial test of disinfectants |
The course supports SDGs 2 and 3 by Adopt measures that ensure the proper functioning of food commodities and derivative markets and facilitate timely access to market information and food reserves to limit extreme food price volatility,Support mental health and wellbeing. |
|
91 |
English for Food Science and Technology 2 |
Pre-requisite : 4115251 English for Food Science and Technology 1 Practice in reading English articles in technical matter relating to Food Science and Technology, able to summarize the content by oral presentation and report patterns, able to express opinion, providing definition in comparing word meaning, basic knowledge and skill for technical article writing |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Ensure that all youth are able to read and write. |
|
92 |
Food Production Planning and Supply Chain Management |
Role and importance of food production planning and supply chain management in food industry, production system, forecasting demand, industrial production factors determination, production capacity planning, production planning, scheduling and job assignment, materials and inventory control, production costs control, productivity in food industry, transportation of materials and products, product design, shipping packaging, marketing; case study of management in food production and supply chain traceability |
The course supports SDGs 9 and 12 by Promote inclusive and sustainable industrial development Developing to strengthen scientific and technological capabilities that will drive towards more sustainable production and consumption patterns. |
|
93 |
Internship in Food Industry |
Internship in food productions and quality controls in food industry and related organizations, both public and private organizations, study on processing process, business, food quality and assurance systems, sampling for analyzing foods with official methods in laboratories, food plant sanitation and managements of standard systems, writing academic reports and oral presentation or observation practices that representing practical skills in the training |
The course supports SDGs 12 by Developing to strengthen scientific and technological capabilities that will drive towards more sustainable production and consumption patterns. |
|
94 |
Introduction to Food Technology |
World food events; sources of human food; characteristics of food industry; food compositions; nutrition of food compositions; factors affecting food quality; food degradations and controls; basic principles of various food processing; meat products, milk products, sea foods, fats and oils, cereal products, fruits and vegetables, food beverages, fermented foods; food packaging and food safety |
The course supports SDGs 2 by Strengthening resilience to climate change |
|
95 |
Food and Nutrition |
Food and nutrition; metabolisms; necessary and problems of malnutrition; nutritional status and guidelines to solve problem; food quality evaluations and nutritional status; impacts of processing and storage on nutrients and quality changes on consumer health; functional foods and nutraceuticals; genetically modified foods and new food products affecting health consumer |
The course supports SDGs 2 by Strengthening resilience to climate change |
|
96 |
Food Processing 1 |
Prerequisite course: SC 18131 Introduction to Food Technology Principles of food processing; general characteristics of raw food materials; food deterioration and related factors; preparation of raw materials; blending techniques; thermal processing; dehydrations; chilling; freezing; irradiation and fermentations; applications of instruments; packaging; shelf-life of food products; effect of processing methods on food qualities |
The course supports SDGs 2 by Strengthening resilience to climate change |
|
97 |
Food Chemistry |
Prerequisite course: SC12009 General Biochemistry Chemical structure and composition of foods, water, proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, enzymes, vitamins, mineral, pigments, flavor agents and other active compounds; use of food additive; changes in physical, chemical, and functional properties of food compositions during processing and storage |
The course supports SDGs 2 by Strengthening resilience to climate change |
|
98 |
Food Plant Sanitation and Food Safety |
Prerequisite course: SC18121 Fundamental Microbiology for Food Technology Plant layout and equipment establishments by following sanitation standards; good manufacturing practice, storages and transportation of food raw materials and products; food personal hygiene in food plant, pest control; water quality control, principles of cleaning, waste and wastewater treatment in food plant; indicator microorganisms and food quality assurance systems relating to food plant sanitation |
The course supports SDGs 3 and 15 by Protecting public health and, in particular, universal access to medicines. Conservation, restoration, and sustainable use of terrestrial and freshwater ecosystems and their services. |
|
99 |
Water Quality Analysis |
Quantitative analysis; water sampling and preservation; analysis of physical, biological and chemical quality of water, interpretation, comparison with water quality criteria and standards for environmental management |
The course supports SDGs 6 by Achieve the goal of providing access to safe and affordable drinking water for all. |
|
100 |
Air Pollution Management Technology |
Air pollution system; dispersion modeling of air pollutants; industrial air pollution control (in terms of particulate matter and dissolved gas); emission mitigation for vehicles and legal other sources |
The course supports SDGs 13 and 3 by Developing education, awareness, and human capacity to mitigate climate change., Support mental health and wellbeing. |
|
101 |
Hazardous Waste Management |
Categories, characterization and properties of toxic substance and hazardous waste; toxicity, sources, reduction, collection, storage, transportation, sampling, analysis, legislations and regulations related to solid waste and hazardous waste management |
The course supports SDGs 11 by Strengthen efforts to protect and preserve the world’s cultural and natural heritage. |
|
102 |
English for Environmental Science 2 |
Pre-requisite : 4116216 English for Environmental Science 1 Skills in reading, translation and communication of research articles related to environmental science and found in international scientific journal |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Ensure that all youth are able to read and write. |
|
103 |
Environmental Analysis and Impact Assessment |
Concept of environmental impact assessment, regulations relating to the preparation of the report, analyzed and evaluated the environmental impact of the physical, biological human use and quality of life including the social and human health, criteria of mitigation and monitoring measures to monitor environmental quality |
The course supports SDGs 8 by Develop and implement a global strategy for youth employment and implement the International Labor Organization’s Global Work Compact. |
|
104 |
Wastewater Management Technology |
Wastewater characteristics; physical wastewater treatment process; chemical wastewater treatment process and biological wastewater treatment process; types of wastewater treatment systems; basis design wastewater treatment plant; controlling and maintenance wastewater treatment plants |
The course supports SDGs 6, 14, and 17 by Improve water quality by reducing pollution., Sustainable use of marine resources, supporting statistical capacity building in developing countries. |
|
105 |
Environmental Management System |
Approach to environmental management, analysis of environmental management systems, requirements, procedures, certification and environmental law with environmental management standards and other standards related good governance of the organization and sustainable development |
The course supports SDGs 12 and 11 by Sustainable development for tourism creates jobs.,Reducing the negative environmental impact per capita in urban areas |
|
106 |
Air Pollution Control |
Air pollution basics; air pollutants and impacts; meteorology and dispersion model of air pollution; air pollution control systems; air quality measurement; air pollution control legislation |
The course supports SDGs 13 and 3 by Developing education, awareness, and human capacity to mitigate climate change., Support mental health and wellbeing. |
|
107 |
Marine and Coastal Resources Management |
Definition of marine and coastal resource; significant important and usage; impact of human activity on marine and coastal environment; policy and planning in Thailand; conservation of marine and coastal resources |
The course supports SDGs 14 by Sustainable use of marine resources |
|
108 |
Fundamentals of Environmental Science |
Definition and scope of environment; fundamental of environment; environmental dimension; ecology and nature balance; resources; environmental technology; principles and methods of natural conservation; environmental pollution and treatment principles; climate change; integrated resources management |
The course supports SDGs 12 by Examine the impact of sustainable development on job-creating sustainable tourism. |
|
109 |
Natural Resources and Environmental Management |
Definition, types, importance and situation of natural resources and environment; sustainable development; principle of natural resources and environmental management; management guidelines for soil, water, air, forest, wildlife, marine and coastal resources, mineral and energy; management of natural resources and environment according to royal initiatives; local wisdom for natural resources and environmental management |
The course supports SDGs 12, 6, and 14 by Awareness of sustainable development and a way of life in harmony with nature.,Improve water quality by reducing pollution.,Sustainable use of marine resources |
|
110 |
Environmental Microbiology |
Prerequisite course: SC 01010 Biology 1 Classification of microbiology; microorganisms in the environment; air, soil and water; role and relationship of microorganisms in nutrient cycles; usage and application of microorganism for environmental restoration; wastewater treatment by microorganisms; treatment of organic pollutants by microorganisms; usage of microorganisms to reduce contamination of metals in environment; application of microorganism for energy production |
The course supports SDGs 3 by Reduce the number of deaths and illnesses from hazardous chemicals and from pollution and contamination. |
|
111 |
Environmental Ecology |
Principles theory and concepts of ecology; energy flow in ecosystem; nutrients cycle; environment factors effect on life distribution; interactions of living organism; population; communities; effect of human activities on ecosystem; environmental management approac h to restore the ecological balance; application of ecology to solve environmental problems |
The course supports SDGs 13 by Developing education, awareness, and human capacity to mitigate climate change. |
|
112 |
Environmental Geography |
Basic concepts of the earth system and spatial interaction, meaning and scope of environmental geography; geomorphic process; surface landform and topographic agent, surface water, ground water, wind, glacier and coastal landform; climatic characteristics ; watershed hydrology; human force and natural disaster impacts on environmental problems; using geoinformatics , maps, satellite images and ecological spatial plan for natural resources and environmental management |
The course supports SDGs 6, 12, 13, and 14 by Improve water quality by reducing pollution., Awareness of sustainable development and a way of life in harmony with nature., Developing education, awareness, and human capacity to mitigate climate change., Sustainable use of marine resources |
|
113 |
Natural Resources and Environmental Law and Policy |
Legal concepts in enhancement and conservation of environmental quality; international environmental law; Thailand’s natural resource and environmental quality management planning and policy; acts and regulations for conservation and environmentally protected areas, environmental impact assessment, pollution control; enforcement of natural resources and environmental law |
The course supports SDGs 12 by Examine the impact of sustainable development on job-creating sustainable tourism. |
|
114 |
Environmental Quality Monitoring |
Methods; tools equipment use to survey and monitoring environmental quality; air quality, water quality, soil quality, sound quality; planning survey; sampling sample; preservation; analysis; assessment of environmental quality in field; presentation of data from the survey |
The course supports SDGs 6, 13, 15, and 11 by Improve water quality by reducing pollution., Developing education, awareness, and human capacity to mitigate climate change., Empowering local communities, Participatory human settlement planning and management |
|
115 |
English for Natural Resources and Environment |
Environment terminology; reading and translation of English articles which relate to natural resources and environmental management from research, conference, environmental policy, international environment and climate change conferences, agreement, and other electronic media in current situation |
The course supports SDGs 11 by Participatory management of human settlements |
|
116 |
Pollution Prevention and Control |
Concepts, principles of environmental pollution management; pollution prevention technology; clean technology; control technology and treatment of water, air, soil, solid waste, hazardous waste and noise; risk assessment of environment and health |
The course supports SDGs 6, 13, 15, and 3 by Improve water quality by reducing pollution., Developing education, awareness, and human capacity to mitigate climate change., Empowering local communities,Support mental health and wellbeing. |
|
117 |
Sustainable Consumption and Production |
Sustainable development; bio economy, circular economy, and green economy concepts; principles of clean technology; sustainable consumption and production policies; principles, importance of producing and consuming environmentally friendly products and services; sustainable procurement; environmental label; environmentally friendly products; carbon footprint of products, organization, and daily life; low carbon cities |
The course supports SDGs 8 and 12 by Make per capita economic growth sustainable in the context of the country. Developing to strengthen scientific and technological capabilities that will drive towards more sustainable production and consumption patterns. |
|
118 |
Energy Conservation and Management |
The importance of energy on life; socio-economic development; the use of energy; situation and the world’s energy crisis; impact of energy for the climate change and the environment; energy strategy; energy policy; method and technology of energy conservation; energy management system ISO 50001; sustainable for energy management in Thailand |
The course supports SDGs 7 by Increase the share of renewable energy in the global energy mix. |
|
119 |
English for Engineers |
English structure, grammar and vocabulary in the context of technical practice in engineering, dealing with integration in listening, speaking, reading, and writing skills. Discussion in case study in engineering problems |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Ensure that all youth are able to read and write. |
|
120 |
Herbs and Local Wisdom |
Meaning of local wisdom; herbs and local wisdom for food, medicines, beauty; agriculture; research for application of local herbs associated with traditional wisdom |
The course supports SDGs 12 by Examine the impact of sustainable development on job-creating sustainable tourism. |
|
121 |
Infectious Disease and Non-Communicable Disease |
Meaning; scope; objective; chain of infection and nature of disease; principles of prevention and control; water-borne and food-borne disease; sexually transmitted disease; air-borne disease; zoonosis; vector-borne disease and nosocomial infection; group of non-communicable disease; situation; causation; sign and symptom; mechanism of disease; transmission; control and prevention; treatment; legal and related agencies |
The course supports SDGs 3 by Reduce the number of deaths and illnesses from hazardous chemicals and from pollution and contamination. |
|
122 |
Maternal and Child Health Care |
Pregnancy health care; normal delivery process; post partum care; new born health care; health care and health promotion for various age group of children |
The course supports SDGs 3 by Reduce the global maternal mortality rate to less than 70 per 100,000 live births. |
|
123 |
Basic Medical Care |
Assessment of health problems; health screening; diagnosis; treatment; medication use; medical procedures; provision of appropriate advise and referral |
The course supports SDGs 3 by Protecting public health and, in particular, universal access to medicines. |
|
124 |
Occupational Health and Safety in Public Health |
Meaning; background and concepts of occupational health and safety; environmental hazards in the workplace; evaluate and control the environmental hazards in the workplace; toxicology, ergonomic; occupational disease and prevention; accidents in the workplace; fire prevention and extinguishing; risk assessment in occupation; surveillance of the occupation and environment in the community; occupational health and safety management systems; organization; occupational health and safety laws; principles of occupational health services in the health care |
The course supports SDGs 3 by Protecting public health and, in particular, universal access to medicines. |
|
125 |
Health Management and Community Health Development |
General knowledge about community health; concepts, theories and community health management strategy; principles of community; the study of society and community; community diagnosis; problem analysis; indicators; community planning; comprehensive practice of field training; holistic health management; practice of community health development |
The course supports SDGs 3 by Protecting public health and, in particular, universal access to medicines. |
|
126 |
Mental Health |
Meaning; the importance of mental health; personality theory; personality development; the proper children raising and adaptation; mental health problems; stress management; mental health promotion |
The course supports SDGs 3 by Support mental health and wellbeing. |
|
127 |
Consumer Protection in Public Health |
Consumer rights; the principles and the operation of consumer protection in public health; safety standard of products and health service; foods; medicine; cosmetics; hazardous; narcotics; medical instruments; hospital; label; advertisement; situation and consumer experience; consumer protection organization; the concerned law; the consumer potential development |
The course supports SDGs 3 and 12 by Strengthen the prevention and treatment of substance misuse. Developing to strengthen scientific and technological capabilities that will drive towards more sustainable production and consumption patterns. |
|
128 |
Demography in Public Health |
Definition; theory; population composition demographic analysis; demographic conditions; factors associated with population dynamics; birth; mortality; migration; population policy; building the population pyramid; interpretation; world population trend situation; Thai population; impact of population change on society and public health; application of demography in public health |
The course supports SDGs 11 by Participatory management of human settlements |
|
129 |
Primary Health System |
Concepts of health; health system reform; principles of operation of community health; holistic health community health service; primary health services of all ages Health system reform; application of knowledge and technology to develop community health. International health system; world health system |
The course supports SDGs 3 by Access to high-quality essential health services and access to medicines. |
|
130 |
English for Public Health |
Techniques of using english; terminology of public health; integrations of skills in listening, speaking, reading, and writing; communication in the context of health care services; presentation of media associated with public health; the info search from information resources |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Ensure that all youth are able to read and write. |
|
131 |
Public Health Pathology |
Definition; scope; importance; principles and methods study in pathology; causes and pathogenesis; structural and functional changes; disease progression from cell injury; inflammation; infection; repair and healing; genetic abnormalities and environment; immune disorders; abnormalities of body fluid and blood circulation; state of nutrient excesses or deficiency; abnormalities of tumor progression; types of disease; disease progression in human body system; pathology application for public health and health promotion |
The course supports SDGs 3 by Protecting public health and, in particular, universal access to medicines. |
|
132 |
Infectious Disease |
Definition; scope; objective; chain of infection and nature of disease; principles of prevention and control for infectious diseases; water-borne and food-borne disease; sexually transmitted disease; airborne disease; zoonosis; vector-borne disease; nosocomial infection and emerging disease |
The course supports SDGs 5 by Ensure that women are fully involved and have equal opportunities for leadership at all levels of decision-making. |
|
133 |
Environmental Health |
Basic knowledge of environmental health; water supply management; wastewater treatment; sewage disposal; solid waste and hazardous waste management; air pollution controls; noise and vibration control; housing sanitation; public building sanitation; food sanitation; insect and rodent controls; nuisance management; public health disaster; environmental health regulations; environmental health operation in community |
The course supports SDGs 6,13, and 11 by Improve water quality by reducing pollution., Developing education, awareness, and human capacity to mitigate climate change., Participatory management of human settlements |
|
134 |
Public Health Nutrition |
Definition, importance of public health nutrition; sources of nutrients; nutrients and energy requirements for aging and different stages of human life cycle; calculation of dietary requirements; proper food arrangements for aging and people of various ages under normal health conditions and illness; nutritional assessment |
The course supports SDGs 2 by Strengthening resilience to climate change |
|
135 |
Non-Communicable Disease and Injury |
Epidemiological of significant non-communicable diseases; diabetes mellitus; hypertension; coronary heart diseases; stroke; cancer; alzheimer’s and dementia; the most common diseases in the aging; injury; the natural history of these diseases; magnitude; trends and assessment of risk factors; severity of the problems; prevention and control of non-communicable diseases aging injuries |
The course supports SDGs 3 by Support drug research for communicable and non-communicable diseases. |
|
136 |
Occupational Health and Safety in Public Health |
Background and concepts of occupational health and safety; organization; occupational health and safety standard and related laws; environmental hazards in the workplace and health impact; prevention evaluate and control the environmental hazards in the workplace; accidents in the workplace; occupational disease; ergonomic; toxicology; risk assessment in occupation; fire prevention and extinguishing; principles of control occupational disease; principles of occupational health services in the health care |
The course supports SDGs 3 by Reduce the number of deaths and injuries from accidents. |
|
137 |
Pharmacology for Public Health |
Principles of pharmacology; general knowledge about medicines; drug classification by law; definition and drug characteristic; dose measurement; dosage forms; how to drug; principles of drug administration drug use in aging, pregnancy, lactation and pediatrics; kinetics of pharmacology; drug action mechanism; therapeutic properties; indicators; contraindications and drug interactions; caution and introduction of drug using; the prescription; the language used in prescription and drug calculations on primary pharmacy; practicing in accordance with the theoretical content |
The course supports SDGs 2 by Strengthening resilience to climate change |
|
138 |
Public Health Psychology |
Principles and concepts of psychology; development psychology; perception; memory and forgetting; personality and adjustment; mental disorders; concepts of psychology in public health; stress management; mental health; defense mechanism; screening disorders; common psychiatric disorders in Thailand; mental health promotion at all ages; counseling psychology; application of health psychology for public health |
The course supports SDGs 3 by Support mental health and wellbeing. |
|
139 |
Public Health Administration |
Public health; public health development of Thailand; government agencies of the ministry of public health; medical and public health services in Thailand; health systems development; district health system; public health in local government organizations; Thailand’s health insurance system; primary health care and the national health development plan; concepts of health economics; general management principles; management process planning process; preparation of public health project work plans; project evaluation |
The course supports SDGs 3 by Protecting public health and, in particular, universal access to medicines. |
|
140 |
Principles of Exercise for Aging |
Concepts; importance; and benefits of exercise for health promotion for aging; principles of exercise for various age groups; factors relating to exercise; types of exercises for health promotion; the effect of exercise on body systems; applied exercise appropriate to aging have health problems; training in exercise for aging |
The course supports SDGs 3 by Support mental health and wellbeing. |
|
141 |
Fire Prevention and control |
Background and the significance of occupational safety in Thailand and global, types of disasters, the loss of disasters caused in the workplace, meaning, type and causes of fire in the workplace and fire management, principles of fire and disasters prevention, techniques of fire prevention, management of fire protection and suppression scene, legislation for the prevention of fire, planning and preparation of contingency plans to cater for fire and fire training |
The course supports SDGs 3 by Reduce the number of deaths and injuries from accidents. |
|
142 |
Occupational Health and Safety Management |
Introduction of occupational health and safety management, safety policy, safety organization, the roles and responsibility for occupational health and safety setting plan, targets and performance indicators, operational control for accident prevention and illness, monitoring of occupational health and safety operation |
The course supports SDGs 3 by Reduce the number of deaths and injuries from accidents. |
|
143 |
Industrial Ventilation |
Definition and significance of ventilation, basic theory of air properties and type of ventilation, principles of dilution ventilation and calculation methods for designed ventilation system used to chemicals control and thermal stability, principles, calculation design and elements of local exhaust ventilation system. Indoor air quality, legislation and standardization of ventilation for industry, method and Equipment of inspection and ventilation system testing |
The course supports SDGs 13 by Developing education, awareness, and human capacity to mitigate climate change. |
|
144 |
Industrial Hygiene Sampling and Analysis |
Planing and practice an industrial hygiene sampling, sampling techniques and analysis of workplace environmental hazard caused by exposure to physical, chemical and biological agents, hazards assessment of the worker health with the results of the analysis |
The course supports SDGs 3 by Recruitment, development, training, and retention of a health workforce |
|
145 |
Internship in Industrial Hygiene and Safety |
Practical exercises with a principle of workplace environmental survey, search and assess to workplace environmental issues, Practice by using a theory of industrial hygiene and safety to apply in manufacturing industry, such as; using the industrial hygiene measurements to measures the sound, light, heat and chemicals concentration from workplace environment |
The course supports SDGs 3 and 8 by Reduce the number of deaths and injuries from accidents. Protect labor rights and promote a safe working environment. |
|
146 |
Risk Assessment and Management |
Definition of accidents and hazard, hazard inspection, background and necessary of risk management, legislation, principles and techniques for hazards identification and risk assessment, risk reduction and control, reporting and planning of risk assessment and risk management, practice a survey of risk assessment |
The course supports SDGs 3 by Reduce the number of deaths and injuries from accidents. |
|
147 |
National and International Standard for Quality, Environment and Safety Management |
Concepts and elements of quality management systems, occupational health and safety management systems and environmental management systems, objectives, steps, systems, requirements and guidelines for the conduct those systems, Surveillance and monitoring management system operations, practice a standards contribution and monitoring of standards compliance |
The course supports SDGs 3 by Protecting public health and, in particular, universal access to medicines. |
|
148 |
Storage of Hazardous Materials |
Classification of chemicals and hazardous materials, systematic of chemical group, chemical labeling, safety marks, the details on the material safety data sheet, chemical storage, handling and transportation of chemicals and hazardous materials, security management and storage of chemicals and hazardous materials in the building and outside the building, measures control for prevent spills and emergency response, prediction of the chemical distribution in the air and dangerous levels by using a computer software, including; elimination of chemical contamination |
The course supports SDGs 3 by Strengthen the prevention and treatment of substance misuse. |
|
149 |
Environmental Pollution Management and Control |
Definitions and importance of environmental problems such as water, air and noise pollution, including; hazardous waste and chemical, manage the prevention and control of environmental pollution with the current and future suitability, apply method for the prevention and solve the problems of environmental pollution |
The course supports SDGs 6, 13, and 15 by Conservation, restoration, and use of ecosystems; improving water quality by reducing pollution; developing education; raising awareness and human capacity to mitigate climate change. |
|
150 |
Basic Occupational Health and Safety |
History scope and principle of occupational health and safety; occupational health and safety teamwork and organization; environmental hazards in the workplaces; industrial safety; accidents and occupational diseases; occupational health and safety prevention and control; standard and related law |
The course supports SDGs 3 by Reduce the number of deaths and injuries from accidents. |
|
151 |
Communicable, Non-Communicable Disease and Disease Control and Prevention |
Definition, scope, objective, chain of infection and nature of disease; principle of prevention and control; food-water-borne disease; sexually transmitted disease, airborne disease, zoonosis disease, vector-borne disease and nosocomial infection, non-communicable disease; situation, causation, sign and symptom of diseases; mechanism of disease; transmission, control and prevention, treatment, legal and related agencies |
The course supports SDGs 5 and 3 by Providing comprehensive reproductive health education, Support drug research for communicable and non-communicable diseases. |
|
152 |
Fundamental of Occupational Health, Safety and Work Environment Laws |
Importance, scope, development and evolution of occupational safety regulations; health and work environment laws; occupational safety health and work environment act, ministerial regulation and announcements related to occupational health and safety, factory act, labour protection act, social security act, compensation act |
The course supports SDGs 10 by Ensure equal opportunity and reduce inequalities in outcomes. |
|
153 |
Occupational Health and Safety Toxicology |
General knowlage of toxicology; principles of toxicology; absorption, distribution, biotransformation and excretion; describe the properties and toxicity of chemical agents affect to human health and environment; knowlage and apply the information of safety data sheets for safety management; system of classification and labeling of chemicals ;regulations and exposure standards biological exposure indices |
The course supports SDGs 3 by Strengthen the prevention and treatment of substance misuse. |
|
154 |
Industrial Process and Hazard |
Basic knowledge of industrial process; raw material, product and pollution in each various types of industries; especially, the industry where risk of dangerous work for worker; process safety management (PSM); study problems and potential hazards from industrial processes; recommendation for prevention; the factory visit for observe process in various types of industries |
The course supports SDGs 9 by Promote inclusive and sustainable industrial development |
|
155 |
Industrial Safety Engineering |
Principles of industrial safety management, usage of hand tools and machine tools in safely; machine safety guards, dangers of boilers; pressure vessels, and gas storage tanks and protection; Materials handling and storage safety; work permit system of confined space, working at height, maintenance for safety at work; safety audits/inspections |
The course supports SDGs 9 by Promote inclusive and sustainable industrial development |
|
156 |
Construction Safety |
Definition, importance, types of danger, causes and prevention of accidents in the construction sector; inspection the safety of construction; planing and safety management in machinery construction; practices on safety inspection in construction and on occupational diseases in construction; laws related to construction |
The course supports SDGs 3 by Reduce the number of deaths and injuries from accidents. |
|
157 |
First Aid |
Definition, importance of first aid; wounded assessment; vital signs; first aid for the wounded; first aid to poisoned persons; first aid for persons with seizures, unconsciousness, electric shock, drowning, fall from height and stopping breathing; first aid treatment for foreign objects in the eyes, ears, nose, throat, fire, scalds, sprained joints and broken bones; wounded transportation; mass casualty and disaster; first aid practice; coordination and appropriate referral for treatment; physical rehabilitation; morality and ethics for life support |
The course supports SDGs 3 by Reduce the number of deaths and injuries from accidents. |
|
158 |
English for Digital Media 2 |
English writing for digital media; letter, e-mail, summarize, abstract and memo; vocabulary for digital media business |
The course supports SDGs 4 and 8 by Ensure that all young men and women are able to read and write. Technology and innovation upgrades |
|
159 |
Ethic and Law for Computer Career |
Computing and information within the scope of ethics and law; copyright; patent; intellectual property; trademarks; using the laws control Information; electronic transaction law; cheating patterns and prevention; ethics in the production or development of animation and digital media |
The course supports SDGs 10 by Ensure equal opportunity and reduce inequalities in outcomes. |
|
160 |
Design and Development of 2D Games |
2D computer game design and development process; game level design; game user interface; game engine; programming for computer games; game characters using artificial intelligence control; integrate to 2D computer game research |
The course supports SDGs 2 by Strengthening resilience to climate change |
|
161 |
English for Scientists |
English skills in reading, writing, listening and speaking for communication in science and technology; recording, summarizing, interpreting and expanding science and technology articles and manuals in print and electronic media; oral and written presentations |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Ensure that all youth are able to read and write. |
|
162 |
Clinical Chemistry 3 |
“Pre-requisite: 4107322 Clinical Chemistry 2 Medically important enzymes, liver, pancreas, and thyroid function tests, diagnostic tests for myocardial infarction, tumor markers, blood drug levels, changes in biochemical substances in differences between sexes, age, senescence, pregnancy, exercise, congenital metabolic disorders, automated analyzers, molecular diagnostics, advances in clinical chemistry.” |
The course supports SDGs 3 by Reduce the global maternal mortality rate to less than 70 per 100,000 live births. |
|
163 |
Science for Quality of Life |
The scientific process encompasses the application of science in communication and coexistence, healthcare, physical fitness activities, the utilization of technology and innovation to enhance life quality, and the influence of scientific advancements, technology, and innovation. |
The course supports SDGs 8 and 3 by Technology and innovation upgrades Access to high-quality essential health services and access to medicines. |
General Education Courses

The General Education courses at Bansomdejchaopraya Rajabhat University (BSRU) are mandatory courses designed for every BSRU student to foster holistic development, equipping students with essential skills for personal, professional, and social growth. These mandatory courses align with the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) by embedding sustainability principles into the curriculum. From promoting inclusive education and linguistic diversity (SDG 4) to enhancing mental well-being (SDG 3) and supporting responsible consumption (SDG 12), each course contributes to the university’s commitment to creating informed and responsible global citizens.
General Education : 18 courses, which are embedded with sustainability, are offered by Bansomdejchaopraya Rajabhat University as follows.
|
N |
Course Name |
Course Description |
SDGs Embedded |
|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Civil Way and Law in Daily Life |
Constitutional rights and duties of Thai citizen; public participation in state activities; promoting the principle of good faith; integrity and transparency; law in daily life; general principle on Civil and Criminal Codes; other relevant laws. |
The course supports SDGs 8 by Protect labor rights and promote a safe and secure working environment for all workers. |
|
2 |
Thai for Contemporary Communication |
Fundamental knowledge about language and communication, characteristics of the Thai language, critical usage of Thai language in contemporary social context, culture of language usage, critical and creative listening, speaking, reading and writing skills for specific purposes, language skill integration to create work and communication through proper technologies. |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Ensure that all youth are able to read and write. |
|
3 |
Korean Language in Daily Life |
Characteristics of Korean language; vocabulary; grammar; listening, speaking, reading and writing of Korean language skills for communication in daily life; way of life and culture of native speakers; integrating Korean language skills creatively. |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Ensure that all youth are able to read and write. |
|
4 |
Khmer Language in Daily Life |
Characteristics of Khmer language; vocabulary; grammar; listening, speaking, reading and writing of Khmer language skills for communication in daily life; way of life and culture of native speakers; integrating Khmer language skills creatively. |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Ensure that all youth are able to read and write. |
|
5 |
Chinese Language in Daily Life |
Characteristics of Chinese language; vocabulary; grammar; listening, speaking, reading and writing of Chinese language skills for communication in daily life; way of life and culture of native speakers; integrating Chinese language skills creatively. |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Ensure that all youth are able to read and write. |
|
6 |
Japanese Language in Daily Life |
Characteristics of Japanese language; vocabulary; grammar; listening, speaking, reading and writing of Japanese language skills for communication in daily life; way of life and culture of native speakers; integrating Japanese language skills creatively. |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Ensure that all youth are able to read and write. |
|
7 |
Malay Language in Daily Life |
Characteristics of Malay language; vocabulary; grammar; listening, speaking, reading and writing of Malay language skills for communication in daily life; way of life and culture of native speakers; integrating Malay language skills creatively. |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Ensure that all youth are able to read and write. |
|
8 |
Lao Language in Daily Life |
Characteristics of Lao language; vocabulary; grammar; listening, speaking, reading and writing of Lao language skills for communication in daily life; way of life and culture of native speakers; integrating Lao language skills creatively. |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Ensure that all youth are able to read and write. |
|
9 |
Vietnamese Language in Daily Life |
Characteristics of Vietnamese language; vocabulary; grammar; listening, speaking, reading and writing of Vietnamese language skills for communication in daily life; way of life and culture of native speakers; integrating Vietnamese language skills creatively. |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Ensure that all youth are able to read and write. |
|
10 |
Spanish Language in Daily Life |
Characteristics of Spanish language; vocabulary; grammar; listening, speaking, reading and writing of Spanish language skills for communication in daily life; way of life and culture of native speakers; integrating Spanish language skills creatively. |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Ensure that all youth are able to read and write. |
|
11 |
Healthy and Happy Life |
Sources of happiness; developing value of life; setting life goals; health enhancement and health problems in various age groups; daily nutrition; communicable and non-communicable diseases prevention; disaster prevention; strengthening social immunity; self-esteem and appreciation to others; accepting and respecting individual differences; creative problem solving; lifelong learning. |
The course supports SDGs 3 by Support mental health and wellbeing. |
|
12 |
Creative Business |
Looking for career opportunities and income; principles of economics for running business; types of business entrepreneurship; writing business plan; analysis and management of business data; technologies and innovations leading to build career in digital age; determination of business direction; management of modern business management tools; development approach of creative product and business integration in creative entrepreneurship. |
The course supports SDGs 12 by Developing to strengthen scientific and technological capabilities that will drive towards more sustainable production and consumption patterns. |
|
13 |
Financial Planning for Stability |
Managing personal and family finances; building financial discipline; path to financial security; time value of money; control over personal income and expenses; introduction to taxation; building good financial credit; debt management; risk management and insurance; savings and financial investment to maximize profit; digital financial transactions; integration of financial planning leading to stability. |
The course supports SDGs 9 by Promote inclusive and sustainable industrial development |
|
14 |
Working Happily |
Goals and principles for work; psychology for work; art of teamwork; corporate communications; work ethics; benefits under labor law; consumer behavior; giving quality service and applications of theories to work happily |
The course supports SDGs 3 by Support mental health and wellbeing. |
|
15 |
Thinking for Life Advancement |
Brain system and thinking; thinking skills; thinking process; analytical thinking; scientific thinking; problem-solving thinking; critical thinking; holistic thinking; mathematics and basic statistics for decision making; applicative thinking for credit cards, installment payment, Ponzi scheme, stock, Bitcoin; savings; insurance; tax planning; new theory agriculture; and self-development for disruptive technology. |
The course supports SDGs 8,9 and 10 byTechnology and innovation upgrades Empower and promote social, economic, and political inclusivity for all. |
|
16 |
Digital Literacy Skills |
Digital technology; living in digital society; digital intelligent, health in digital age; digital commerce; digital law; security in digital age; application of digital tools for developing learning and work |
The course supports SDGs 9 byIncreasing access to information and communication technologies. |
|
17 |
Digital Technology for Beginner Businessman |
Business model and careers path in digital era; platform for online business and marketing; tools and techniques to make product photography; tools and techniques to make video presentation; tools and techniques for live broadcasting; tools and techniques to make product logos; content and ads creating; products promotion through various platforms; basic principles and tools for customer relationship management; laws for digital business; practice creating online business |
The course supports SDGs 8 byDesign and implement policies that promote sustainable tourism, which will create jobs. |
|
18 |
Save Earth Save Us |
Man and environment; energy for life; environmental pollution; global change and natural disasters to human; science and living; preventing and solving environmental problems through scientific process; building awareness to save the earth; green technology and creating green innovations to save the earth |
The course supports SDGs 3 and 13 bySupport mental health and wellbeing. Developing education, awareness, and human capacity to mitigate climate change. |
Graduate School
The Graduate School at Bansomdejchaopraya Rajabhat University (BSRU) integrates sustainability into its curriculum through a wide range of courses designed to advance knowledge and skills in line with the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). These courses equip students with cutting-edge expertise in digital technology, education, health, and innovation, promoting sustainable development in various professional fields. From fostering research in advanced educational technologies (SDG 4) to supporting innovations in healthcare and pharmacy (SDG 3) and enhancing entrepreneurship and technological management (SDG 8), the Graduate School plays a pivotal role in preparing future leaders to drive sustainable progress.
The Graduate School : 17 courses, which are embedded with sustainability, are offered by Bansomdejchaopraya Rajabhat University as follows.
|
N |
Course Name |
Course Description |
SDGs Embedded |
|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Advanced Digital Technology Management for Education Research |
Concepts and principles of research in advanced digital technology management for education; research type, research design, research question, writing a research hypothesis, finding literature related to design, fundamental data analysis of descriptive statistics, data interpretation, discussion report, and application of research results in advanced digital technology management for education; detection and prevention of plagiarism; research ethics; guidelines for the use of subjects in humans; application of research results in digital technology management for Education; doing research to develop advanced digital technology management for Education; and tools for researching advanced digital technology management for Education |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Ensure that all learners gain the knowledge and skills necessary to promote sustainable development. |
|
2 |
Creating Digital Innovations for Education |
Learning theory for platform management and production of educational materials; design and construction of multimedia applications for education; working with messages, voices, images and videos in all aspects; to learn the steps involved in planning, multimedia design and educational material production |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Professional training and an information and communication technology program. |
|
3 |
Digital Teaching Platform |
Principles and concepts of digital teaching platform; creating and developing innovative learning to meet the needs of exchanging learning through the creation of various platforms; analysis and synthesis of extensive teaching and learning information to gain new knowledge; managing digital teaching and learning platforms for teachers in the digital era; design and development of knowledge management system platforms |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Ensure that all learners gain the knowledge and skills necessary to promote sustainable development. |
|
4 |
English for Ph.D. Students |
Development of English language skills for ph.D. equivalent to IELTS or TOEFL; enhancing English language skills and abilities, including speaking, listening, reading, summarizing from lectures and writing for presentation; the development of academic listening skills to summarize the essence; reading comprehension and critical writing; academic discussion; oral presentation; searching for research information; research paper writing |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Increase the number of quality teachers. |
|
5 |
Digital Technology for Ph.D. Students |
Computer programs and tools for data collection, gathering, and statistical analysis; Using of digital technology tools for doctoral research; and searching for information on the internet in various disciplines |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Professional training and an information and communication technology program. |
|
6 |
Principles of Technology and Innovation Management |
Importance of technology and innovation; principles of technology and innovation management; cycle of technology; technological and innovation processes; technology transfer; technology selection; technology procurement; using technology; technology assessment; technology development; technology activities responding to the strategic goals of the organization; ethical and moral in technology and innovation management |
The course supports SDGs 8 by Entrepreneurship, creativity, and innovation. |
|
7 |
Estimation and Technology and Innovation Forecast |
Directions and trends in science and technology Innovation policy; Technology forecasting and future operation approaches; the effects that may occur both in the short and long term; technology analysis to meet the strategic goals of the organization |
The course supports SDGs 8 by Technology and innovation upgrades. |
|
8 |
Advanced Organic Chemistry and Biochemistry |
Principles and techniques of separation and purification; identification; preparation of organic compound and bioactive compound derivatives; experiments in advanced organic chemistry; biomolecular structure; principles and metabolisms of carbohydrate; lipid; amino acid and protein; nucleic acid; the control and abnormality of metabolism; genes and gene regulation and basic genetic engineering techniques |
The course supports SDGs 3 by Providing comprehensive reproductive health education. |
|
9 |
Research Methodology in Thai Traditional Pharmacy |
Research methodology and research design in Thai Traditional Pharmacy; statistical analysis of the results; proposal writing and preparation of research report in Thai Traditional Pharmacy; application of research results and research ethics |
The course supports SDGs 17 by supporting statistical capacity building in developing countries. |
|
10 |
Pharmacology and Toxicology |
General principles of pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics; drug activities and their mechanisms of action; pharmacotherapy; pharmacological activities of natural products based on phytochemical groups and toxicology |
The course supports SDGs 3 by Support drug research for communicable and non-communicable diseases. |
|
11 |
Thai for Academic Communication |
Use of Thai for communication according to language principles and use in daily life; artistic communication; listening, watching, and reading literacy; using language for academic communication; referencing, information retrieval, and presentations of information or works through media and databases; speaking and writing for communication necessary for educational profession |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Essential skills include technical and vocational skills for employment. |
|
12 |
Digital Technology and Innovation of Educational Management |
Concepts of digital technology and innovation of educational management; design, development and use of mobile applications, artificial intelligence and digital technology for promotion and development of educational management quality; using innovation in communication; operation, evaluation, use of the results to develop creative educational management |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Create and upgrade educational equipment and tools. |
|
13 |
Curriculum and Innovation of Learning Management |
Curriculum development; curriculum trends in the changing era; development of innovation for curriculum management; modern learning theory; learning mangament for students with special needs; design of competency-based learning management; using and developing mobile applications; artificial intelligence and digital technology for learning management; designing and developing online lessons; media creation and learning resource management; measurement and evaluation of learning in digital era |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Ensure that all learners gain the knowledge and skills necessary to promote sustainable development. |
|
14 |
New Paradigm in Educational Measurement and Evaluation |
Aims, scope and techniques of educational measurement and evaluation; using and developing tools of educational measurement and evalution in digital era; authentic assessment; statistics used for educational measurement and evalution |
The course supports SDGs 17 by supporting statistical capacity building in developing countries. |
|
15 |
Educational Management Strategy and Learning Management |
Current state and context of educational management; model of educational management and learning management to sustainability through professional learning community; classroom management strategies; creative educational management strategies and productivity; developing educational management strategies and learning management in the 21st century; planning and designing using methods; resources and tools to upgrade the quality of education; study technical visit on educational management and learning management in advanced educational institutions |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Ensure that all learners gain the knowledge and skills necessary to promote sustainable development. |
|
16 |
English for Graduate Studies |
English sentence structures, listening speaking and situational conversations, reading articles and related researches in each field of studies, writing articles, abstract, and research result presentation |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Essential skills include technical and vocational skills for employment. |
|
17 |
Information Technology for Graduate Study |
Fundamental computer program; power point presentation and other forms; type of data collection and statistical analysis; and information retrieval in each field of studies through the Internet. |
The course supports SDGs 4 by Professional training and an information and communication technology program. |


















